UNITED
STATES
SECURITIES
AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington,
D.C. 20549
———————
FORM
10-K
———————
|
S
|
ANNUAL
REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
For
the fiscal year ended:
December
31, 2007
OR
|
£
|
TRANSITION
REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
For
the transition period from: _____________ to _____________
Commission
file number:
000-21394
|
|
GelStat
Corporation
|
|
|
|
(Exact
name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
|
|
Delaware
|
|
90-0075732
|
|
(State
or Other Jurisdiction
|
|
(I.R.S.
Employer
|
|
of
Incorporation or Organization)
|
|
Identification
No.)
|
|
3557
SW Corporate Parkway
Palm
City, Florida
|
|
34990
|
|
(Address
of Principal Executive Office)
|
|
(Zip
Code)
|
|
|
|
|
Registrant’s
telephone number, including area code:
(772) 283-0020
Securities
registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities
registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: Common Stock, $0.01 par value
Indicate
by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes
£
No
S
Indicate
by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act.
Yes
£
No
S
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities
Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such
reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes
£
No
S
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every
Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12
months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such
files). Yes
£
No
S
Indicate
by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not
be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in
Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K.
£
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller
reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and
“smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated
filer
|
£
|
Accelerated
filer
|
£
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
|
£
|
Smaller reporting company
|
S
|
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes
£
No
S
The
number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s common stock, as of date of filing this Report, was
127,447,078.
The
aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant on such date, based upon the closing price
of the common stock of $0.03 as reported by the OTC Bulletin Board on June 30, 2012 was $1,970,374.
INDEX
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part I.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1.
|
|
Business.
|
3
|
|
Item 1A.
|
|
Risk Factors.
|
8
|
|
Item 1B.
|
|
Unresolved Staff Comments.
|
12
|
|
Item 2.
|
|
Properties.
|
12
|
|
Item 3.
|
|
Legal Proceedings.
|
12
|
|
Item 4.
|
|
Mine Safety Disclosures.
|
12
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part II.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5.
|
|
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
|
13
|
|
Item 6.
|
|
Selected Financial Data.
|
14
|
|
Item 7.
|
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
|
14
|
|
Item 7A.
|
|
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
|
15
|
|
Item 8.
|
|
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
|
15
|
|
Item 9.
|
|
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
|
28
|
|
Item 9A.
|
|
Controls and Procedures.
|
28
|
|
Item 9B.
|
|
Other Information.
|
28
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part III.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10.
|
|
Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
|
29
|
|
Item 11.
|
|
Executive Compensation.
|
30
|
|
Item 12.
|
|
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
|
32
|
|
Item 13.
|
|
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
|
33
|
|
Item 14.
|
|
Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
|
33
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part IV.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15.
|
|
Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
|
34
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIGNATURES
|
|
|
35
|
PART
I
Explanatory
Note.
This Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007 has been compiled from information which is believed to
be true and correct in all material respects. This Report has been prepared in 2012 in order to correct filing delinquencies.
Certain
statements in this Report constitute "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation
Reform Act of 1995. All statements that address expectations or projections about the future, including without limitation statements
about product development, market position, expected expenditures and financial results, are forward-looking statements.
Some
of the forward-looking statements may be identified by words such as "expects," "anticipates," "plans,"
"intends," "projects," "indicates," "believes" and similar expressions. Any statements
contained herein that are not statements of historical fact should be deemed to be forward-looking statements. These statements
are not guarantees of future performance and involve a large number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Accordingly, actual
results or performance of Gelstat Corporation ("Gelstat" or the “Company”) will most likely differ significantly,
positively or negatively, from forward-looking statements made herein. Unanticipated events and circumstances are likely to occur.
Factors that might cause such differences include, but are not limited to, those discussed under Item 1A, Risk Factors.
These
factors include, but are not limited to, risks that Gelstat products may not perform as expected or may not receive the level
of market acceptance anticipated; anticipated funding may be unavailable; intense market competition may result in lower than
anticipated revenues or higher than anticipated costs; and general economic conditions, such as the rate of employment, inflation,
interest rates and the condition of the capital markets may change in a way that is not favorable to Gelstat. This list of factors
is not exclusive. Gelstat undertakes no obligation to update any forward-looking statements.
The
Company cautions the reader not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements.
ITEM
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
General
Gelstat
was incorporated on November 13, 1991 in the State of Minnesota under the name Developed Technology Resource, Inc. and reincorporated
in Delaware on October 27, 2010. The Company's principal executive office is located at 3557 SW Corporate Parkway Palm City, FL
(772) 283-0020 and its website is www.Gelstat.com. The information found at the Company's website is not incorporated in or made
a part of this report on Form 10-K.
Effective
April 30, 2003, the Company acquired Gelstat Corp. ("GC") as a wholly-owned subsidiary. GC was organized in June 2002
for the purpose of developing, manufacturing and marketing over-the-counter ("OTC") and other non-prescription consumer
health products related to migraine and sleep. The acquisition was accomplished by merger of GC (a Minnesota corporation) with
our wholly-owned subsidiary, NP Acquisition (a Minnesota corporation). In the merger, the former owners of GC received shares
of our common stock and GC became our wholly-owned subsidiary. No cash consideration was exchanged. The amount of the merger consideration
was negotiated at arm’s length based on the then recent trading price of our common stock and our assessment of the business
prospects of GC. In July 2003, the Company changed its name to Gelstat Corporation. On March 17, 2004, GS Corp. was merged into
its parent company, Gelstat Corporation. References in this Report to the "Company" or "Gelstat" mean Gelstat
Corporation.
In
2004, the Company established a subsidiary called GS Pharma, Inc. On January 5, 2005, GS Pharma assigned all rights in the license
previously granted to it by Gelstat to DTLL, Inc. (OTCBB: DTLI) in exchange for 12.5 million shares of DTLL. On November 14, 2005
the Company sold 12.4 million of its shares in DTLL for $500,000. As a result of the transaction, the Company will no longer be
consolidating DTLL results in the Company’s future financial statements. Because DTLL failed to pay its required payments
to have rights to the pharmaceutical applications, the rights reverted back to Gelstat.
In
late 2005, the Company became insolvent and only marketed its products on a limited basis.
In
2006 and through 2007 the Company struggled under the burden of significant debt and accounts payable, declining revenues, negative
cash flows from operations and lack of capital.
In
April 2008, WSR Consulting, Inc. (WSR)was engaged in an attempt to turn around the Company. In June 2008 a founder of WSR assumed
the position as interim CEO of the Company. The Company was quickly downsized and refocused to minimize the Company’s monthly
expenses while management attempted to clean up the balance sheet and secure capital.
In
July 2008, the Company’s patent #7,192,614 was forced to auction by a creditor and subsequently, purchased by and assigned
to that creditor. This was a key asset of the Company and seriously impaired its ability to continue as a going concern. Throughout
2008 the Company’s CEO and one of its board members used personal funds to rigorously negotiate with this creditor to retain
rights to the patent.
In
November 2009, the Company’s CEO, Mr. Gerald N. Kieft, one of its board members and a few investors were able repurchase
the patent from the creditor through an entity named High Alpha Partners, Inc. d/b/a Gelstat Direct. In December 2009, the entire
inventory held in Vero Beach, Florida was seized by the owner of the facility due to the Company’s back rent payments. In
July 2010, the Company’s CEO, Mr. Gerald N. Kieft, and a few investors were able to repurchase the inventory from the landlord
through Gelstat Direct.
In
September 2010, Gelstat Direct formally contributed assets it owned relating to Gelstat into a majority-owned subsidiary of High
Alpha Partners, Inc. named GSC Direct, Inc. In September 2011, 100% of the outstanding shares of GSC Direct, Inc. were acquired
by Gelstat in exchange for the issuance of 25,000,000 shares of Gelstat common stock. See Item 13, “Certain Relationships
and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
In
September 2011, GSC Direct, Inc. and its assets were merged into Gelstat in a share exchange.
Gelstat
is a consumer health care company dedicated to the cost-effective development and marketing of OTC and other non-prescription
consumer health care products. When development efforts ceased in 2005 due to lack of capital, its efforts had been focused on
proprietary, innovative products that addressed multi-billion dollar global markets.
The
Company's first product is Gelstat® Migraine is a patented homeopathic drug designed to provide acute relief from migraine
and migraine-like headaches. Gelstat Migraine was originally launched through distributors into retailers and wholesalers across
the United States. In 2008, the Company changed its business model to focus on Direct-to-Consumer sales and marketing efforts.
As such, the Company’s products are now sold primarily through its website www.gelstat.com and through a very limited number
of retailers.
Gelstat(TM)
Sleep is presently under final development and is intended to be marketed as a sleep aid. It was introduced to consumers in 2010
on a test basis to obtain data to determine product viability. Gelstat Sleep is expected to be classified as a dietary supplement.
The Company plans to formally launch the product in the fourth quarter of 2012 contingent on raising any required capital.
While
Gelstat expects to continue developing new products and will be opportunistic in regard to unanticipated opportunities within
the OTC health care product field, the two products listed above are expected to account for essentially all of the Company's
activity over the next 12 months.
Overview
of Regulations Regarding the Manufacture and Sale of Homeopathic Drugs and Nutritional Supplements.
This
overview is a brief summary and does not purport to be complete.
In
general, the Company's products are regulated both by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the "FDA") and by the U.S.
Federal Trade Commission (the "FTC") as well as States through their “little FTC” laws and rules as well
as other consumer protection laws. Internationally, the Company must comply with the federal and local laws of each country.
The
FDA treats homeopathic drugs, both prescription and OTC, differently than non-homeopathic drugs. Unlike non-homeopathic drugs,
homeopathic drugs are not required to submit to pre-market approval and are not required to be tested for safety and effectiveness.
Homeopathic drugs must meet the standards set forth by the Homeopathic Pharmacopoeia of the United States.
In
general, the FTC and the FDA prohibit fraud in the marketing of homeopathic drugs, monitor OTC versus prescription use of homeopathic
drugs, hold homeopathic drugs to several labeling requirements, and require production incompliance with current good manufacturing
practices (with some minor exceptions).
The
FDA prohibits "health fraud," defined as:
The
deceptive promotion, advertisement, distribution or sale of articles, intended for human or animal use, that are presented as
being effective to diagnose, prevent, cure, treat, or mitigate disease (or other conditions), or provide a beneficial effect on
health, but which have not been scientifically proven safe and effective for such purposes. Such practices may be deliberate,
or done without adequate knowledge or understanding of the article.
Only
those homeopathic drugs that treat "self-limiting" conditions that the average consumer can recognize and diagnose are
allowed to be marketed as OTC drugs. Homeopathic drugs that claim to treat serious diseases and those that require diagnosis by
a physician, such as AIDS or cancer, must be marketed as prescription homeopathic drugs - they cannot be sold as an OTC drug.
The
FDA requires that homeopathic drugs be properly labeled. “A drug or device shall be deemed to be misbranded if its labeling
is false or misleading in any particular fashion.” Furthermore, Section 352 of the Act requires that the name and place
of business of the manufacturer, packer, or distributor be placed on the package. Homeopathic drugs for retail sale must also
bear adequate directions for use that can be interpreted by the average lay person, and their ingredients as well as the dilution
of each active ingredient must be stated (with dilution stated as the number of 1:10 dilutions required to arrive at the final
concentration of active ingredient). The label must also state at least one major indication for the drug, the drug's established
name, and any applicable warnings.
The
FDA requires that homeopathic drugs be manufactured in general conformance with current good manufacturing practice ("cGMP").
However, there are two exceptions to this requirement. First, homeopathic drugs do not require expiration dating. Second, the
FDA does not presently require laboratory determination of the identity and strength of each active ingredient prior to the release
and distribution of the drug on the market. For further information on the FDA's regulation of homeopathic drugs, see the FDA's
Compliance Policy Guide, "Conditions Under Which Homeopathic Drugs May be Marketed," which is available on the FDA's
website, www.fda.gov, are also subject to the U.S. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994("DSHEA"). Under
DSHEA a manufacturer must only supply the FDA with information adequate to provide "reasonable assurance that the product
does not present a significant or unreasonable health risk of illness or injury." This information must be supplied at least
75 days before the product is available to consumers. DSHEA permits the labels of dietary supplements to contain truthful and
non-misleading structure/function claims and nutritional support claims that describe the role of the nutrient in supporting wellness.
Nutritional supplements are not allowed to make claims to diagnose, prevent, cure, treat, or mitigate disease.
Products
Gelstat(TM)
Migraine
Gelstat
Migraine is a patented homeopathic drug intended for use in providing acute relief from the pain and associated symptoms of migraine
and migraine-like headaches. It is believed to be more effective if used early in the course of an attack, but may be used at
any time. Gelstat Migraine is administered sublingually (under the tongue), where it is held in place briefly before being swallowed.
Gelstat Migraine is provided in single dose dispensers, which are intended to ensure ease of use as well as consistent, accurate
administration of medication.
In
a clinical trial of 30 patients who consistently develop moderate to severe migraine headache pain were treated with Gelstat Migraine
early in the course of an attack, while at the mild pain phase. The primary objective of the study was to assess the efficacy
of Gelstat Migraine in providing acute relief from migraine headache pain and associated symptoms. Results demonstrated that migraine
headache pain two hours after treatment was either mild or none in approximately 83% of patients. Pain-free response was obtained
by 48% of patients, with 34% reporting only mild pain. Moderate pain was reported by 17% and severe pain by 0% (none). Of those
pain-free at two hours, 71% remained pain-free during the 24 hour post-dose period and 85% remained pain-free or had only mild
pain. Moderately painful headache recurred in 14% of patients and severely painful headache in 0%. Migraine associated symptoms
such as photophobia, phonophobia and nausea were eliminated in 53% of those patients initially reporting such symptoms. Side effects
were infrequent and minor.
Initial
clinical trial data suggests that Gelstat Migraine may be more effective than competing OTC migraine relief products, and that
it may not be associated with the side effects common to other OTC products, such as stomach upset, or the development of rebound
headaches and chronic daily headaches. Prescription medications for migraine are generally associated with significant side effects,
none of which have been reported or noted with use of Gelstat Migraine. Further details regarding this initial clinical trial
are available on the Company’s website at
www.gelstat.com
. The information found at the Company's website is not
incorporated in or made a part of this report on Form 10-K.
Gelstat(TM)
Sleep
Gelstat(TM)
Sleep is presently under final development and is intended to be marketed as a sleep aid. It was introduced to consumers in 2010
on a test basis to obtain data to determine product viability. Gelstat Sleep is expected to be marketed as a nutritional supplement
for OTC (non-prescription) sales. The company plans to formally launch the product in the fourth quarter of 2012 contingent on
raising any required capital.
Gelstat
Sleep is provided as an orally dispersible tablet, a form of administration believed to be of particular benefit because of the
rapid onset of absorption and the high percent of active ingredient absorbed. It is believed that Gelstat Sleep may offer consumers
an effective OTC sleep aid without the risks and side effects associated with other OTC and prescription sleep aids.
The
tablets are specifically formulated for effective delivery of active ingredients. Unlike nearly all other non-prescription sleep
aids, Gelstat Sleep does not contain antihistamines. Antihistamines cause drowsiness, but they are often ineffective sleep aids,
and have side effects that create problems for many users.
Gelstat
Sleep is expected to employ a unique combination of active ingredients, each of which has independently been shown in some studies
to be effective in promoting healthy sleep. Those ingredients are combined with proprietary adjuncts as part of the delivery system
intended to provide rapid, effective and safe administration when used as directed. By utilizing an orally dispersible tablet
to deliver the planned combination of ingredients, the Company hopes to offer a product that is substantially advantageous relative
to competing products.
Sales
and Marketing
Domestic
Sales & Marketing
Gelstat
intends to market and distribute its products initially through direct-to-consumer marketing efforts and then through drugstores
and pharmacies, food stores, and mass merchandise retailers once the products have achieved significant brand recognition and
until the Company has the capital to support its marketing efforts. Presently, Gelstat offers Gelstat Migraine for sale through
its website and through a very limited number of retailers.
International
Sales & Marketing
The
global incidence of migraine and other conditions intended to be addressed by the Company's products approximates that found in
the United States. Gelstat is pursuing international opportunities for Gelstat Migraine simultaneous with its current domestic
sales and marketing activities.
Competition
There
are numerous other companies that manufacture and market products that compete with the present and intended products of the Company.
Most of the companies that compete with Gelstat have much greater market exposure, human resources and financial resources than
the Company. Most of the products that compete with the Company's products have greater brand recognition, and have already achieved
a certain amount of consumer acceptance.
The
Company believes that Gelstat Migraine competes primarily with other OTC migraine medications. The OTC migraine market is based
almost entirely on common analgesics, some having been slightly modified for use in the treatment of migraine (e.g. by the addition
of caffeine). Typical competitors include products like Excedrin Migraine(R), Motrin Migraine(R) and Advil Migraine(R).
Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs: ibuprofen, aspirin, etc.) have significant harmful side effects. Common side effects of these
OTC analgesics include rebound headaches (both caffeine and NSAIDs have been implicated as a cause of rebound headaches), chronic
daily headache, liver damage, kidney damage, ulcers and, less serious but more frequently encountered stomach upset. The Company
also competes with prescription migraine treatments. Triptans are now recognized as the prescription drug of choice for most migraine
patients, and have largely displaced other prescription medications. The proposed mechanism of action for all Triptans is vasoconstriction
(narrowing of blood vessels) via binding with serotonin receptors on blood vessels leading to relief of migraine pain and associated
symptoms.
Principal
Suppliers
Gelstat
is dependent on vendors, suppliers and strategic partners. The Company must reach and maintain agreements with third-parties to
supply it with the accounting, management, manufacturing, packaging, public relations, advertising, clinical trials, product brokering
and distribution, and other products and services necessary to affect its business plan. The Company believes that at least several
alternative sources exist for each service and component purchased for and used in the manufacture and marketing of its products.
However, Gelstat generally does not have long-term service agreements with those performing services for the Company or long-term
supply agreements with suppliers to provide product at any set price or at all. In addition, Gelstat currently does not have the
physical or human resources to independently manufacture its products or any other products that might be developed. While believing
that alternate vendors could be found, the need to change vendors, should it arise, could have a material adverse effect on the
Company. The Company intends to outsource all of its product manufacturing and packaging operations for the foreseeable future.
Intellectual
Property
The
Company plans to continuously define, expand and defend the intellectual property related to its products and delivery systems.
The Company was issued United States patent number 7,192,614 relating to Gelstat Migraine on March 20, 2007. Intellectual property
protection may be very important to the successful marketing and distribution of its products. Gelstat will therefore continue
to file patent and other intellectual property applications to protect inventions and improvements that are considered important
to the development of its products and business. Gelstat also relies on trade secrets, know how, continuing technological innovation
and licensing opportunities to develop and maintain its competitive position.
Research
and Development
Gelstat
is a marketing driven company presently dedicated to products addressing migraine, and problem sleep. Each of these is a multi-billion
dollar international market. Nonetheless, potential new product opportunities may be evaluated according to their likely competitive
advantage(economic as well as clinical), potential market size, patentability, and suitability for sale as non-prescription products,
likely consumer acceptance and perceived ability of the Company to successfully execute development and launch within the constraints
of present opportunities.
Gelstat
believes that clinical trials are essential to demonstrate efficacy in a manner recognized and accepted by the medical community
as well as the consumer and, accordingly, plans to conduct clinical trials on every product it develops.
Due
to capital constraints, Gelstat has currently suspended all R&D efforts and clinical trials but hopes to resume efforts in
the future once capital is obtained.
Employees
Gelstat
maintains an executive office in Palm City, Florida and a warehouse and distribution facility in Stuart, Florida. As of date of
filing this Report, the Company had no employees.
ITEM
1A. RISK FACTORS
Risks
Related to Our Business
Our
ability to continue as a going concern is in substantial doubt absent obtaining adequate new debt or equity financings.
Our
continued existence is dependent upon us obtaining adequate working capital to fund all of our operations. Working capital limitations
continue to impinge on our day-to-day operations, thus contributing to continued operating losses. Currently, the Company is entirely
dependent on outside investments to support its operations. Thus, if we are unable to raise funds to fund the development, manufacturing
and marketing of our products, we may not be able to continue as a going concern and you will lose your investment.
We
have a limited recent operating history on which to evaluate our potential for future success and to determine if we will be able
to execute our business plan. Therefore, it is difficult to evaluate our future prospects and the risk of success or failure of
our business.
Since
we encountered severe financial problems in 2005, we have had very limited operations. Revenue has been limited to some website
orders since we have lacked the capital for marketing. You must consider our business and prospects in light of the risks and
difficulties we will encounter as an early-stage company. These risks include:
|
|
·
|
our
ability
to
raise
sufficient
working
capital,
|
|
|
·
|
our
ability
to
effectively
and
efficiently
market
and
distribute
our
products,
|
|
|
·
|
our
ability
to
obtain
market
acceptance
of
our
current
products
and
future
products
that
may
be
developed
by
us,
and
|
|
|
·
|
our
ability
to
sell
our
products
at
competitive
prices
which
exceed
our
per
unit
costs.
|
We
may not be able to address these risks and difficulties, which could materially and adversely affect our revenue, operating results
and our ability to continue to operate our business.
The
success of our products is subject to ongoing and additional clinical trials which may not be successful.
The
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the “FDA”) does not require homeopathic drugs to be submitted to pre-market approval
and are not required to be tested for safety and effectiveness. Our GelStat Migraine product has undergone two clinical trials
and additional trials may be required. In order to test the efficacy of the GelStat Migraine product, we have put it through a
clinical trial and, if we have the necessary funding, anticipate putting the product through additional testing. Although this
product has already undergone two clinical trials with favorable results, we cannot assure you that the results will be favorable
in the future trials. Additionally, some consumers and retailers may defer purchasing the product until such time, if any, that
such additional trials are successfully completed. The results of future clinical trials are expected to strongly affect the economic
viability and perceived value of our products. There can be no assurance as to the outcome of future clinical trials on our current
or future products. If the clinical trial results for any of the Company’s initial products suggest that any of them are
not efficacious, or reveal unexpected problems such as serious side effects, the Company may be unable to successfully market
the products even if we desired to do so. In such event, the Company’s results of operations will be adversely affected
and you may lose your investment.
Because
successful development of our products is uncertain, our results of operations may be materially harmed.
Our
development of current and future products is subject to the risks of failure and delay inherent in the development of non-prescription
consumer health care products, including but not limited to the following:
|
|
•
|
delays
in
product
development,
clinical
testing,
or
manufacturing;
|
|
|
•
|
unplanned
expenditures
in
product
development,
clinical
testing,
or
manufacturing;
|
|
|
•
|
failure
to
receive
regulatory
approvals,
if
required;
|
|
|
•
|
emergence
of
superior
or
equivalent
products;
|
|
|
•
|
inability
to
manufacture
our
products
on
a
commercial
scale
on
our
own,
or
in
collaboration
with
third
parties;
and
|
|
|
•
|
failure
to
achieve
market
acceptance.
|
Because
of these risks, our development efforts may not result in any commercially viable products. If a significant portion of these
development efforts are not successfully completed, required regulatory approvals are not obtained, or any approved products are
not commercialized successfully, our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be materially harmed.
Any
unanticipated problems with product development and commercialization develop or our products are found to be ineffective or unsafe,
our business may fail.
Our
successful development of existing and new products is subject to the risks of failure and delay inherent in the development and
commercialization of products. We may experience unanticipated or otherwise negative research and development results. Existing
or proposed products may be found to be ineffective or unsafe, or may otherwise fail to receive required regulatory clearance
or approval. We may find that existing or proposed products, while effective, are uneconomical to commercialize or market. Existing
or proposed products may not achieve broad market acceptance.
Because
we will need to rely on third parties for the development, manufacture, sales and marketing of our current or future products,
our future success will be dependent on the timeliness and effectiveness of the efforts of these third parties.
We
do not have the capability and resources to manufacture, market or sell our current products or any future product. We intend
to outsource all of our product manufacturing and packaging operations for the foreseeable future. Accordingly, we will seek to
enter, at the appropriate time, into agreements with other companies that can assist us and provide certain capabilities that
we do not possess. Even if we do succeed in securing these alliances, we may not be able to maintain them if, for example, development
results are disappointing or approval of a product (if required) is delayed or sales of a product are below expectations. Furthermore,
any delay in entering into agreements could delay the development and commercialization of our products and reduce their competitiveness
even if they reach the market. Any such delay related to our agreements could adversely affect our business. Further, f
ailure
by such parties to provide the agreed services at an acceptable level could adversely affect our business.
If
our products gain widespread commercial acceptance, we could face potential difficulties in locating sufficient manufacturing
sources.
We
have used third parties to manufacture our products on a limited basis. If we are unable to produce our products in sufficient
quantities at an acceptable cost, we may lose customers and our business could be harmed. Our ability to expand production could
also be hindered by the availability of materials used to manufacture our products or the availability of qualified personnel.
These difficulties could result in reduced quality of our products or reduced sales, which could damage our industry reputation
and hurt our ability to generate revenues.
Because
the consumer healthcare product market is subject to substantial regulation by regulatory agencies, if we do not obtain the requisite
regulatory approvals we need to market our products, we will not be able to commercialize our products.
We
believe that all of our current and planned products will be marketed either as homeopathic products or as dietary supplements,
and that each will therefore be exempt from the new drug approval process required in the United States for prescription pharmaceuticals.
The Company’s products, product development activities and manufacturing processes are nonetheless subject to regulation
by the Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) and by comparable agencies in foreign countries. In the U.S., the FDA
regulates manufacturing, labeling and record keeping procedures even for non-prescription products. We use qualified third-party
manufacturers to perform these services; however, if these third-parties do not comply with the regulations, we may not be able
to sell our products. Nonetheless, the failure of such third parties to adhere to regulations could have a material adverse affect
on our business.
In
addition, product claims, labels, advertising and other communications with the public are closely monitored by the Federal Trade
Commission (“FTC”) and states under their “Little FTC Acts”. Failure to comply with any of the numerous
regulations which govern our industry could result in regulatory or enforcement actions which would have a material adverse affect
on our business. In addition, we are subject to those risks associated with any highly regulated industry wherein regulations
are subject to change that is both substantial and rapid. Regulatory change may force the Company to expend substantial time and
money becoming compliant, may make the Company’s business more expensive to operate and the products less profitable, or
not profitable at all, and might even prevent the Company from marketing one or more of its products. We are marketing our first
product, GelStat Migraine, as an effective solution in alleviating migraine headaches. Under FDA and FTC rules, we are required
to obtain scientific and/or clinical data to support any health claims we make concerning our products. Although we have neither
provided nor been requested to provide any such data to the regulators in support of this claim, we have in fact obtained supporting
scientific and clinical data. We cannot be certain, however, that the scientific and clinical data we have obtained or will obtain
in the future in support of our claims will be deemed acceptable or sufficient by any regulator. If the FDA or the FTC requests
any supporting information, and we are unable to provide support that is acceptable to the FDA or the FTC, either agency could
force us to stop making the claims in question, which would most likely have a negative impact on sales. Regulatory actions may
materially adversely affect the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
If
any of our products are alleged to have unacceptable adverse effects, we could be subject to liability which would adversely affect
our results of operations.
The
Company faces an inherent business risk of exposure to product liability claims in the event that the use of its products is alleged
to have resulted in adverse effects. Any such claims would likely have an adverse effect on the Company. The Company currently
has product liability insurance for claims against it up to one million dollars,on a per-occurrence basis. However, there can
be no assurance that such coverage would protect the Company in every instance, or that a claim might not substantially exceed
the limit of coverage beyond the Company’s ability to pay. Additionally, there can be no assurance that such insurance will
continue to be available to the Company in the future on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. If the Company is unable to
continue its product liability insurance coverage for any reason, it may have a material impact on the retailer’s willingness
to stock the Company’s products.
If
we lose our Chief Executive Officer, our business may materially suffer.
We
are highly dependent on Mr. Gerald Kieft, Chief Executive Officer, who is our sole officer and provides “as needed”
services. We do not carry “key-man” life insurance on Mr. Kieft. Furthermore, our future success will also depend
in part on our ability to identify, hire, and retain qualified personnel at senior and other management levels. We will experience
intense competition for qualified personnel and may be unable to attract and retain the personnel necessary for the development
of our business. Because of this competition, our compensation costs may increase significantly and our business may suffer.
If
we fail to establish a method to sell, market or distribute our products, our results of operations would be adversely affected.
Because
we have limited experience in the sale, marketing and distribution of consumer products, we intend on selling our products through
the Internet, direct-to-consumer advertising and certain traditional retail outlets. To achieve this, may work with a number of
brokers and distributors currently serving these markets. There can be no assurance that any broker or distributor will be able
to place our product with the aforementioned channels, or that once such initial placement is achieved any retailer or other outlet
will continue to carry our product, or that any broker or distributor will continue working with the Company and our products.
If
we do not obtain protection for our intellectual property rights, our competitors may be able to take advantage of our research
and development efforts to develop competing drugs.
Our
success will depend, in part, on our ability to maintain the confidentiality of our trade secrets and know how, operate without
infringing on the proprietary rights of others and prevent others from infringing our proprietary rights. We have received a United
States patent on our GelStat Migraine product however we cannot assure you that this patent will afford adequate protection to
us. The Company has hired I.P. counsel to assist us with obtaining I.P. protection on our products in international markets. However,
we cannot assure you that we will obtain any such I.P. protection on our products internationally.
Competitors
may successfully challenge our intellectual property rights, produce similar drugs or products that do not infringe our patents,
or produce drugs in countries where we have not applied for patent protection or that do not respect our patents.
If
any of these events occurs, or we otherwise lose protection for our trade secrets or proprietary know-how, the value of this information
may be greatly reduced. Patent protection and other intellectual property protection are important to the success of our business
and prospects, and there is a substantial risk that such protections will prove inadequate.
If
we are subject to intellectual property infringement claims, it could cause us to incur significant expenses, pay substantial
damages and prevent us from selling our products.
In
the drug development business, third parties accumulate large portfolios of patents. Third parties may claim that our patent and/or
products infringe or violate their intellectual property rights. Intellectual property litigation is characterized by unusually
large legal fees, consulting and expert fees and other costs. Any claims that we are violating the intellectual property rights
of another party could cause us to incur significant expenses which may likely exceed our capacity to pay the fees and costs.
If successfully asserted against us, an adverse intellectual property claim is likely to require that we pay substantial damages
in excess of our ability to pay and prevent us from using licensed technology that may be fundamental to our business. Even if
we were to prevail, any litigation regarding intellectual property could be costly and time-consuming and divert our attention
from our business operations. We may also be obligated to indemnify our business partners in any such litigation, which could
further exhaust our resources. Furthermore, as a result of an intellectual property challenge, we may be prevented from selling
our products unless we enter into royalty, license or other agreements. We may not be able to obtain such agreements at all or
on terms acceptable to us, and as a result, we may be precluded from offering some or all of our products.
If
we cannot manage our growth effectively, we may not become profitable.
Businesses,
which grow rapidly often, have difficulty managing their growth. If we grow as rapidly as we anticipate, we will need to expand
our management by recruiting and employing experienced executives and key employees capable of providing the necessary support.
We cannot assure you that our management will be able to manage our growth effectively or successfully. Our failure to meet these
challenges could cause us to lose money, and your investment could be lost.
Among
other things, implementation of our growth strategy would be adversely affected if we were not able to attract sufficient customers
to the products we offer in light of the price and other terms required in order for us to attain the necessary profitability.
Because
of our limited experience in commercializing our products, the market acceptance of the Company’s products is uncertain.
Our
success depends upon the acceptance by retail consumers of our products. Although we believe that our products are efficacious,
and that they will meet with consumer acceptance, we have no assurance of that. There is only limited data by which to gauge consumer
acceptance of the Company’s products. Most of the products that compete with the Company’s products have substantial
brand recognition, and have already achieved a certain amount of consumer acceptance. Those consumers who presently use a competitor’s
product to treat a condition designed to be treated by our products will have to be convinced to switch products, which is often
difficult. We believe that the successful completion of clinical trials demonstrating the efficacy of our products or, in the
case of GelStat Migraine, additional clinical trials, may be essential for the successful marketing of these products, especially
in light of entrenched competition. There can be no assurance that any clinical trials will be completed beyond the initial trials
of GelStat Migraine that have already been completed, or that such additional clinical trials will demonstrate the same degree
of efficacy as these initial trials, or any efficacy at all. Insufficient market acceptance of our products would have a material
adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Although
we plan to diversify our product offering, we may not be successful.
The
Company proposes as an important part of its business plan to complete development of additional products related to arthritis,
sinusitis and problem sleep. Offering new products is subject to a number of risks including:
|
|
·
|
Acquiring
ownership
or
distribution
rights
to
new
products;
|
|
|
·
|
Having
sufficient
capital
to
acquire
the
rights
to
new
products,
build
inventory
and
market
the
products, and;
|
|
|
·
|
Our
ability
to
generate
effective
marketing
programs.
|
No
assurance can be given that the Company will ever be able to successfully design, develop, and market any such additional new
products.
If
economic conditions in the United States and elsewhere do not materially improve, we may be hampered by our ability to sell our
products.
The
sharp economic downturn in the United States and elsewhere beginning in 2008 and the resulting unemployment has a tendency to
cause consumers to reduce spending except on necessities. While consumer healthcare products may be relatively resistant to this
trend, to the extent that consumers lack disposable money we believe that we will be adversely affected. Unless and until the
economy materially improves, we may be affected by these factors.
Risks
Related to Our Common Stock
Because
the market for our Common Stock is limited, persons who purchase our Common Stock may not be able to resell their shares
at or above the purchase price paid by them.
Our
Common Stock trades on the OTC Markets, which is not a liquid market. There is currently only a limited public market
for our Common Stock. We cannot assure you that an active public market for our Common Stock will develop or be sustained
in the future. If an active market for our Common Stock does not develop or is not sustained, the price may continue
to decline.
Because
we are subject to the “penny stock” rules, brokers cannot generally solicit the purchase of our Common Stock which
adversely affects its liquidity and market price.
The
Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") has adopted regulations which generally define “penny stock”
to be an equity security that has a market price of less than $5.00 per share, subject to specific exemptions. The
market price of our Common Stock on the OTC Markets has been substantially less than $5.00 per share and therefore we are currently
considered a “penny stock” according to SEC rules. This designation requires any broker-dealer selling
these securities to disclose certain information concerning the transaction, obtain a written agreement from the purchaser and
determine that the purchaser is reasonably suitable to purchase the securities. These rules limit the ability of broker-dealers
to solicit purchases of our Common Stock and therefore reduce the liquidity of the public market for our shares.
Due
to factors beyond our control, our stock price may be volatile.
Any
of the following factors could affect the market price of our Common Stock:
|
●
|
Our
failure to generate increasing material revenues from our products;
|
|
●
|
Our
failure to become profitable;
|
|
●
|
Our
failure to raise adequate working capital;
|
|
●
|
Our
public disclosure of the terms of any financing which we consummate in the future;
|
|
●
|
Actual
or anticipated variations in our quarterly results of operations;
|
|
●
|
Announcements
by us or our competitors of significant contracts, new products, acquisitions, commercial relationships, joint ventures or
capital commitments;
|
|
●
|
The
loss of significant business relationships;
|
|
●
|
Our
failure to meet financial analysts’ performance expectations;
|
|
●
|
Changes
in earnings estimates and recommendations by financial analysts;
|
|
●
|
Short
selling activities; or
|
|
●
|
Changes
in market valuations of similar companies.
|
In
the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation
has often been instituted. A securities class action suit against us could result in substantial costs and divert our
management’s time and attention, which would otherwise be used to benefit our business.
We
may issue preferred stock without the approval of our shareholders, which could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire
us and could depress our stock price.
Our
Board may issue, without a vote of our shareholders, one or more additional series of preferred stock that have more than one
vote per share. This could permit our Board to issue preferred stock to investors who support GelStat and our management
and give effective control of our business to GelStat and our management. Additionally, issuance of preferred stock
could block an acquisition resulting in both a drop in our stock price and a decline in interest of our Common Stock. This
could make it more difficult for shareholders to sell their Common Stock. This could also cause the market price of
our Common Stock shares to drop significantly, even if our business is performing well.
An
investment in GelStat may be diluted in the future as a result of the issuance of additional securities, the exercise of options
or warrants or the conversion of outstanding preferred stock.
In
order to raise additional capital to meet its working capital needs, GelStat expects to issue additional shares of Common Stock
or securities convertible, exchangeable or exercisable into Common Stock from time to time, which could result in substantial
dilution to investors. Investors should anticipate being substantially diluted based upon the current condition of
the capital and credit markets.
Because
we may not be able to attract the attention of major brokerage firms, it could have a material impact upon the price of our Common
Stock.
It
is not likely that securities analysts of major brokerage firms will provide research coverage for our Common Stock since the
firm itself cannot recommend the purchase of our Common Stock under the penny stock rules referenced in an earlier risk factor. The
absence of such coverage limits the likelihood that an active market will develop for our Common Stock. It may also make it more
difficult for us to attract new investors at times when we acquire additional capital.
Since
we intend to retain any earnings for development of our business for the foreseeable future, you will likely not receive any dividends
for the foreseeable future.
We
have never declared or paid any cash dividends or distributions on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain our future
earnings to support operations and to finance expansion and therefore we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common
stock in the foreseeable future.
ITEM
1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None
ITEM
2. DESCRIPTION OF PROPERTY
Gelstat
presently operates out of an executive office under shared-use arrangement with WSR, a company headed by its Chief Executive Officer,
in Palm City, Florida and leases a warehouse/distribution facility of approximately 2,100 square feet in Stuart, Florida. The
Company believes that its facilities are adequate for its operations for the foreseeable future and that each of such facilities
could be replaced without great difficulty.
ITEM
3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
From
time to time, we are involved in litigation in the ordinary course of business. We are not party to any material litigation.
On
January 19, 2006, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Milgaard RE Partnership vs. Gelstat Corporation.”
Milgaard RE Partnership, a promissory note holder, alleged Gelstat owed $76,734 under the note, including interest and fees. On
July 1, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Milgaard RE Partnership was issued 114,000, $0.03, five
year warrants and $3,600 cash.
In
September 2006, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Dr. Steven Klos vs. Gelstat Corporation.”
Dr. Klos, a promissory note holder, alleged Gelstat owed $100,000 regarding the note. In November 2009 a settlement agreement
was reached among parties whereby Gelstat paid Dr. Klos $25,000.
On
September 10, 2007, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Unicep Packaging, Inc. vs. Gelstat Corporation.”
Unicep Packaging, Inc., a vendor, alleged Gelstat owed $190,340 on an agreement entered into by the parties regarding packaging
of Gelstat’s products. On July 11, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Unicep was issued 400,000,
$0.03, 5 year warrants and $20,000 cash.
On
December 11, 2007, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Angela Diliddo and Bioinitiate Capital,
LLC. vs. Gelstat Corporation.” Angela Diliddo and Eleanor Kelly (sole principal of Bioninitiate), promissory note holders,
alleged Gelstat owed $120,000 and $60,000, respectively, regarding the notes. On July 1, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached
among parties wherein Angela Diliddo was issued 240,000 $0.03, 5 year warrants and $6,000 cash and Eleanor Kelly was issued 120,000
$0.03, 5 year warrants and $3,000 cash.
On
December 14, 2007, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Stepping Stones Partners, LP and Daniel
D. Hickey vs. Gelstat Corporation.” Stepping Stones Partners, LP/Daniel D. Hickey, a promissory note holder, alleged Gelstat
owed $120,000 regarding the note. On July 1, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Stepping Stones Partners,
LP/Daniel D. Hickey was issued 120,000 $0.03, 5 year warrants and $16,000 cash.
ITEM
4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not
applicable.
PART
II
ITEM
5. MARKET FOR COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The
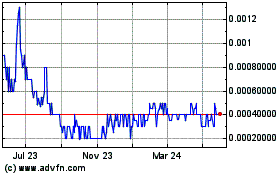
Company's $0.01 par value common stock is quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board under the symbol "GSAC." The following table
sets forth the low and the high closing sales prices for each quarter as reported on the OTC Bulletin Board during the years ended
December 31, 2007 and 2006. These quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark up, mark down or commissions, and
may not represent actual transactions. We had approximately 255 holders of record of our common stock as of the date of filing
this Report.
|
|
|
Closing Price*
|
|
CALENDAR
2007
|
|
Low
|
|
High
|
|
First Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.07
|
|
|
$
|
0.18
|
|
|
Second Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.07
|
|
|
$
|
0.27
|
|
|
Third Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.12
|
|
|
$
|
0.20
|
|
|
Fourth Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.03
|
|
|
$
|
0.13
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CALENDAR
2006
|
|
|
Low
|
|
|
|
High
|
|
|
First Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.17
|
|
|
$
|
0.79
|
|
|
Second Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.07
|
|
|
$
|
0.22
|
|
|
Third Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.05
|
|
|
$
|
0.20
|
|
|
Fourth Quarter
|
|
$
|
0.06
|
|
|
$
|
0.18
|
|
Dividends
The
Company has never declared or paid a cash dividend on its common stock and does not anticipate paying any dividends in the foreseeable
future.
Recent
Sales of Unregistered Securities
During
the three months ended December 31, 2007, the Company had no equity transactions.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2007 the Company issued 750,000 options at an exercise price of $.12 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $90,000.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2007 the Company sold 400,000 shares of common stock and 400,000 warrants with an exercise
price of $.25 for gross proceeds of $40,000.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2007 the Company issued 250,000 warrants at an exercise price of $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $27,500.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2007, the Company issued 200,000 shares of common stock at $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $20,000.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2007 the Company sold 700,000 shares of common stock and 700,000 warrants with an exercise price
of $.25 for gross proceeds of $70,000.
During
the three months ended March 31, 2007, the Company issued 400,000 shares of common stock at $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $40,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company sold 250,000 shares of common stock and 250,000 warrants with an exercise
price of $.25 for gross proceeds of $25,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006, the Company issued 1,150,000 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $.06 to $0.15
per share for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $136,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006, the Company issued 1,500,000 shares of common stock at $0.08 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $120,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006, 242,847 five-year options were exercised with a weighted average exercise price of $0.69
on a "cashless" or "net exercise" basis (based on the market price of the Company's common stock the day before
exercise) resulting in the issuance of 2,428 shares of common stock.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006, the Company issued 120,000 warrants at an exercise price of $.20 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $8,400.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 950,000 options at an exercise price of $.06 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $95,000.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company sold 2,433,888 shares of common stock and 2,433,888 warrants with an exercise
price of $.20 for gross proceeds of $219,050.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 197,010 shares of common stock at $.09 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $17,731.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 1,700,000 shares of common stock at $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $170,000.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 3,000,000 warrants at exercise prices ranging from $.25 - $.50 per
share for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $300,000.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 760,000 options at exercise prices ranging from $.07 - $.11 per share
for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $57,200.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2006, the Company issued 320,000 shares of common stock at $.12 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $38,400.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2006, the Company issued 500,000 warrants at an exercise price of $.09 per share for severance
valued at $60,000.
During
the three months ended March 31, 2006 the Company sold 60,000 shares of common stock and 30,000 warrants with an exercise price
of $.70 for gross proceeds of $30,000.
During
the three months ended March 31, 2006, the Company issued 535,000 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $.74 to $.22 per
share for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $241,700.
All
of the sales of the securities above were exempt from registration under Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933 and Rule 506
thereunder on the grounds that the securities were only sold to accredited investors who purchased for investment and legends
were placed on the securities.
ITEM
6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
Not
applicable for smaller reporting companies.
ITEM
7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
Please
refer to the consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto which is a part of this report for further information
regarding the results of operations of the Company.
Company
Overview
Gelstat
Corporation ("the Company" or "Gelstat") is a consumer health care company dedicated to the cost-effective
development and marketing of over-the-counter (OTC) and other non-prescription consumer health care products. The Company's first
product is "Gelstat® Migraine", a patented OTC homeopathic drug intended for use as a first-line, acute treatment
for migraine and migraine-like headaches. Gelstat Migraine is intended to provide acute (at the time of an attack) relief from
headache pain as well as other symptoms frequently associated with migraine. Gelstat(TM) Sleep is presently under final development
and is intended to be marketed as a sleep aid. It was introduced to consumers in 2010 on a test basis to obtain data to determine
product viability. Gelstat Sleep is expected to be classified as a dietary supplement.
Current
sales and marketing efforts are focused primarily on Gelstat Migraine.
Critical
Accounting Policies
In
response to financial reporting release FR-60, Cautionary Advice Regarding Disclosure About Critical Accounting Policies, from
the SEC, we have selected our more subjective accounting estimation processes for purposes of explaining the methodology
used in calculating the estimate, in addition to the inherent uncertainties pertaining to the estimate and the possible effects
on the our financial condition. The accounting estimates are discussed below and involve certain assumptions that, if incorrect,
could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Inventories
We
value our inventory at the lower of the actual cost or the current estimated market value of the inventory. Management reviews
sales, shipped goods and available inventory quantities on a weekly basis and record a provision for excess and obsolete inventory
if considered necessary. Changes in the marketplace or introduction of new products could result in an increase in the amount
of obsolete inventory quantities.
Revenue
Recognition
In
accordance with the Securities Exchange Commission's Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 104 (SAB 104) "Revenue Recognition",
the Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of a customer or distributor arrangement exists or acceptance occurs,
shipment has occurred, the price is fixed or determinable, and the sales revenues are considered collectible. Subject to these
criteria, except with respect to customers that buy products on Pay on Scan terms, we recognize revenue at the time of shipment
of the merchandise.
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company accounts for stock-based compensation using the fair value method following the guidance set forth in section 718-10 of
the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for disclosure about Stock-Based Compensation. This section requires a public entity
to measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of equity instruments based on the grant date fair
value of the award (with limited exceptions). That cost will be recognized over the period during which an employee is required
to provide service in exchange for the award – the requisite service period (usually the vesting period). No compensation
cost is recognized for equity instruments for which the employees do not render the requisite service.
The
Company recognizes expenses for the fair value of its outstanding stock warrants and options as they vest, whether held by employees
or others. The fair value of each stock warrant and option at the grant date is evaluated by using the Black-Scholes option pricing
model based upon certain assumptions, including the expected stock price volatility.
Results
of Operations
The
Company had revenues of $18,178 and $233,974 for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. The decrease in revenues
in 2007 is attributable to the Company marketing on a limited basis only.
Cost
of goods sold were $5,097 and $88,457 for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. The decrease in cost of goods
sold expense in 2007 is attributable to the corresponding decrease in revenues.
Selling,
general and administrative expenses were $105,689 and $332,235 for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. The
decrease in 2007 is due to the decrease in professional fees and advertising expense.
The
Company incurred $0 and $38,065 in research and development expense for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 respectively.
The decrease in 2007 is due to the Company discontinuing clinical trials.
The
Company recorded $43,243 and $56,702 of interest expense during the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. The
interest expense relates to a 7% accrual on the outstanding notes payable balance.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources
Cash
flows used in operating activities were $162,132 and $488,056 for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Negative
cash flows from operations for the years ended December 31, 2007 were due primarily to the net loss of $1,083,466, partially offset
by amortization of deferred compensation. Negative cash flows from operations for the year ended December 31, 2006 were due primarily
to the net loss of $1,817,827, partially offset by the amortization of deferred compensation.
Cash
flows used in investing activities were $4,000 during the year ended December 31, 2007 consisting of patent application costs
and lease deposits. Comparatively, cash flows of $2,254 used in investing activities during the same period in 2006 were due primarily
to patent application costs offset by lease deposits returned.
Cash
flows provided by financing activities were $158,005 and $274,050 during the year ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Positive cash flows from financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2007 were due to proceeds from issuance of common
stock and short-term notes payable. Positive cash flows from financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2006 were
due solely from proceeds from issuance of common stock.
As
of the date of filing this Report, the Company had approximately $5,000 cash. The Company needs to raise additional capital to
continue operations. There can be no assurance that additional capital will be available on terms acceptable to the Company or
on any terms what so ever. In addition, the Company may evaluate potential acquisitions and alliances, which may require equity
or cash resources. The Company's ability to continue the present operations and successfully implement its development plans is
contingent upon its ability to increase revenues and ultimately attain and sustain profitable operations and/or raise additional
capital.
Cautionary
Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
This
report includes forward-looking statements including statements regarding liquidity, revenues and cash flows.
The
words “believe,” “may,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,”
“should,” “plan,” “could,” “target,” “potential,” “is likely,”
“will,” “expect” and similar expressions, as they relate to us, are intended to identify forward-looking
statements. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about
future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy
and financial needs.
The
results anticipated by any or all of these forward-looking statements might not occur. Important factors, uncertainties and risks
that may cause actual results to differ materially from these forward-looking statements are contained in the Risk Factors contained
herein. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as the result of new information,
future events or otherwise. For more information regarding some of the ongoing risks and uncertainties of our business, see the
Risk Factors and our other filings with the SEC.
ITEM
7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Not
applicable for smaller reporting companies.
ITEM
8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
|
GELSTAT
CORPORATION
|
|
BALANCE SHEETS
|
|
AS
OF DECEMBER 31, 2007 AND 2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
12/31/2007
|
|
12/31/2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and
cash equivalents
|
|
$
|
1,161
|
|
|
$
|
9,287
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
49,200
|
|
|
|
116,467
|
|
|
Prepaid consulting
|
|
|
5,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Other
current assets
|
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
75,361
|
|
|
|
145,755
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patents
|
|
|
24,813
|
|
|
|
24,280
|
|
|
Lease
deposits
|
|
|
2,500
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total Other Assets
|
|
|
27,313
|
|
|
|
24,280
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL
ASSETS
|
|
$
|
102,674
|
|
|
$
|
170,035
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES
AND STOCKHOLDERS' (DEFICIT)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
$
|
1,019,758
|
|
|
$
|
790,248
|
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
491,440
|
|
|
|
448,197
|
|
|
Notes payable
|
|
|
472,000
|
|
|
|
472,000
|
|
|
Notes
payable - related parties
|
|
|
86,005
|
|
|
|
63,000
|
|
|
Total
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
2,069,203
|
|
|
|
1,773,445
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholder's (Deficit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock ($0.01
par value; 50,000,000 shares authorized; 25,653,020 and 23,953,020 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2007
and 2006, respectively.
|
|
|
256,529
|
|
|
|
239,529
|
|
|
Additional paid in
capital
|
|
|
14,060,108
|
|
|
|
13,853,775
|
|
|
Additional paid in
capital-warrants
|
|
|
219,916
|
|
|
|
155,749
|
|
|
Common stock to be
issued
|
|
|
95,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Deferred compensation
|
|
|
(55,487
|
)
|
|
|
(393,334
|
)
|
|
Retained
deficit
|
|
|
(16,542,595
|
)
|
|
|
(15,459,129
|
)
|
|
Total
Stockholders' (Deficit)
|
|
|
(1,966,528
|
)
|
|
|
(1,603,409
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' (DEFICIT)
|
|
$
|
102,674
|
|
|
$
|
170,035
|
|
|
GELSTAT CORPORATION
|
|
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
|
|
FOR THE YEARS
ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2007 AND 2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the Years ended December 31,
|
|
|
|
2007
|
|
2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
18,178
|
|
|
$
|
233,974
|
|
|
Cost of Goods Sold
|
|
|
5,097
|
|
|
|
88,457
|
|
|
Gross Profit (Loss)
|
|
|
13,081
|
|
|
|
145,517
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses
|
|
|
105,689
|
|
|
|
332,235
|
|
|
Common stock issued for services
|
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
|
433,831
|
|
|
Warrants issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
8,400
|
|
|
Options issued for services
|
|
|
90,000
|
|
|
|
152,200
|
|
|
Consulting expense
|
|
|
485,347
|
|
|
|
565,281
|
|
|
Management fees
|
|
|
285,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Bad debt expense
|
|
|
67,267
|
|
|
|
69,191
|
|
|
Payroll expense
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
307,439
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
38,065
|
|
|
Total expenses
|
|
|
1,053,304
|
|
|
|
1,906,642
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations
|
|
|
(1,040,223
|
)
|
|
|
(1,761,125
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Income and (Expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(43,243
|
)
|
|
|
(56,702
|
)
|
|
Net Other Income (Expense)
|
|
|
(43,243
|
)
|
|
|
(56,702
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes
|
|
|
(1,083,466
|
)
|
|
|
(1,817,827
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net
loss
|
|
$
|
(1,083,466
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,817,827
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss per common share:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and fully diluted
|
|
($
|
0.04
|
)
|
|
($
|
0.10
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding
|
|
|
24,971,376
|
|
|
|
18,346,192
|
|
|
GELSTAT CORPORATION
|
|
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
FOR THE YEARS
ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2007 AND 2006
|
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
|
12/31/2007
|
|
12/31/2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net (loss)
|
|
|
(1,083,466
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,817,827
|
)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) to net
cash flows (used in) operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of patent
|
|
|
966
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Bad debt expense
|
|
|
67,267
|
|
|
|
69,191
|
|
|
Amortization of deferred compensation
|
|
|
475,347
|
|
|
|
565,281
|
|
|
Common stock issued for services
|
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
|
433,831
|
|
|
Warrants issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
8,400
|
|
|
Options issued for services
|
|
|
90,000
|
|
|
|
152,200
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilitites:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(51,325
|
)
|
|
Prepaid consulting
|
|
|
(5,000
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
40,000
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
229,510
|
|
|
|
80,384
|
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
43,244
|
|
|
|
31,808
|
|
|
NET CASH (USED IN) OPERATING
ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
(162,132
|
)
|
|
|
(488,056
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patent acquisition costs
|
|
|
(1,500
|
)
|
|
|
(12,446
|
)
|
|
Lease deposits
|
|
|
(2,500
|
)
|
|
|
10,192
|
|
|
NET CASH (USED IN)
INVESTING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
(4,000
|
)
|
|
|
(2,254
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from short-term convertible notes
payable and warrants issued
|
|
|
23,005
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock,
net of expenses
|
|
|
135,000
|
|
|
|
274,050
|
|
|
NET CASH PROVIDED BY
FINANCING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
158,005
|
|
|
|
274,050
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
|
|
(8,127
|
)
|
|
|
(216,260
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF THE
YEAR
|
|
|
9,287
|
|
|
|
225,548
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF THE YEAR
|
|
$
|
1,161
|
|
|
$
|
9,287
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid during the years for:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Taxes
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL NON-CASH INVESTING AND FINANCING
INFORMATION:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock issued
for services rendered
|
|
$
|
20,000
|
|
|
$
|
433,831
|
|
|
Warrants issued for
services
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
8,400
|
|
|
Options issued for services
|
|
$
|
90,000
|
|
|
$
|
152,200
|
|
|
GELSTAT CORPORATION
|
|
STATEMENT OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT)
|
|
FOR THE YEARS
ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2007 AND 2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock Issued
|
|
Additional
|
|
APIC
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Deferred
|
|
Retained
|
|
Stockholders' equity
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
Amount
|
|
Paid In Capital
|
|
Warrants
|
|
to be issued
|
|
Compensation
|
|
(Deficit)
|
|
(Deficit)
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2005
|
|
|
15,564,275
|
|
|
$
|
155,642
|
|
|
$
|
12,634,930
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
(368,615
|
)
|
|
$
|
(13,641,302
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,219,345
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cashless exercise of options
|
|
|
242,847
|
|
|
|
2,428
|
|
|
|
(2,428
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock for cash, net of expense
|
|
|
2,743,888
|
|
|
|
27,439
|
|
|
|
246,611
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
274,050
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock for services
|
|
|
2,202,010
|
|
|
|
22,020
|
|
|
|
411,811
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
433,831
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock for prepaid consulting
|
|
|
3,200,000
|
|
|
|
32,000
|
|
|
|
258,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(290,000
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
8,400
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
8,400
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants issued for prepaid consulting
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
300,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(300,000
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of deferred compensation
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
565,281
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
565,281
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
152,200
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
152,200
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants issued with PPM
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(155,749
|
)
|
|
|
155,749
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the year
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(1,817,827
|
)
|
|
|
(1,817,827
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2006
|
|
|
23,953,020
|
|
|
$
|
239,529
|
|
|
$
|
13,853,775
|
|
|
$
|
155,749
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
(393,334
|
)
|
|
$
|
(15,459,129
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,603,408
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock for cash, net of expense
|
|
|
1,100,000
|
|
|
|
11,000
|
|
|
|
99,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
25,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
135,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock for services
|
|
|
200,000
|
|
|
|
2,000
|
|
|
|
18,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock for prepaid consulting
|
|
|
400,000
|
|
|
|
4,000
|
|
|
|
36,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
70,000
|
|
|
|
(110,000
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants issued for prepaid consulting
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
27,500
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(27,500
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of deferred compensation
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
475,347
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
475,347
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
90,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
90,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants issued with PPM
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(64,167
|
)
|
|
|
64,167
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the year
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(1,083,466
|
)
|
|
|
(1,083,466
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2007
|
|
|
25,653,020
|
|
|
$
|
256,529
|
|
|
$
|
14,060,108
|
|
|
$
|
219,916
|
|
|
$
|
95,000
|
|
|
$
|
(55,487
|
)
|
|
$
|
(16,542,595
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,966,527
|
)
|
GELSTAT
CORPORATION
NOTES
TO THE AUDITED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR
THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31,
2007 AND 2006
NOTE
1 - Organization and Business Background
GelStat
Corporation ("the Company" or "GelStat") is a consumer health care company dedicated to the cost-effective
development and marketing of over-the-counter (OTC) and other non-prescription consumer health care products. While development
efforts ceased in 2005 due to lack of capital, its efforts were focused on proprietary, innovative products that addressed multi-billion
dollar global markets.
On
May 9, 2003, Developed Technology Resource, Inc. (DTR) filed a Current Report on Form 8-K with the Securities and Exchange Commission
reporting the merger of GelStat Corp. with NP Acquisition Corp. (NP Acquisition), then a wholly owned subsidiary of DTR. The stock
exchange transaction has been accounted for as a reverse acquisition and recapitalization of NP Acquisition, whereby Gelstat is
deemed to be the accounting acquirer (legal acquiree) and NP Acquisition to be the accounting acquiree (legal acquirer). The
accompanying consolidated financial statements are in substance those of Gelstat, with the assets and liabilities, and revenues
and expenses, of NP Acquisition being included effective from the date of stock exchange transaction. NP Acquisition
is deemed to be a continuation of the business of Gelstat. Accordingly, the accompanying consolidated financial statements
include the following:
(1) The
balance sheet consists of the net assets of the accounting acquirer at historical cost and the net assets of the accounting acquiree
at historical cost;
(2) The
financial position, results of operations, and cash flows of the accounting acquirer for all periods presented as if the recapitalization
had occurred at the beginning of the earliest period presented and the operations of the accounting acquiree from the date of
stock exchange transaction.
On
October 6, 2003, the Company's Board of Directors approved a stock dividend in the amount of one share for each share held of
record. All share data is presented to give effect to the retroactive application of the stock dividend as if it occurred on June
25, 2002 (date of inception of GelStat Corp.) All share data has been restated to give effect of the merger under which each GelStat
Corp. share was converted into .4360083 shares of DTR as adjusted for the stock dividend declared on July 19, 2004.
Effective
July 14, 2003, DTR changed its name to GelStat Corporation. Effective March 17, 2004, GS Corp. was merged into its parent, GelStat
Corporation.
In
2004, the Company formed a wholly-owned subsidiary, GS Pharma, Inc. (GS Pharma), to pursue various pharmaceutical (prescription
drug) opportunities that might exist relative to the Company's intellectual property. During the remainder of 2004, this subsidiary
evaluated potential business opportunities, but had no financial activity or licensing agreements in place.
Effective
January 1, 2005, GS Pharma entered into a license agreement with DTLL, Inc. ("DTLL"), a Minnesota corporation, in exchange
for 12,500,000 shares of DTLL common stock. Effective March 25, 2005, GS Pharma changed its name to GSC Subsidiary, Inc. On November
14, 2005, the Company sold 12.4 million of its shares in DTLL for gross cash proceeds of $500,000. As a result of the transaction,
the Company will no longer be consolidating DTLL results in the Company’s future financial statements.
NOTE
2 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis
of presentation
The
accompanying financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted
in the United States of America (U.S. GAAP) under the accrual basis of accounting.
Management's
Estimates
In
preparing financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management
makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets
and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the
reporting periods. These accounts and estimates include, but are not limited to, the valuation of accounts receivables, inventories,
income taxes and the estimation on useful lives of property, plant and equipment. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Basis
of Consolidation
The
consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of the Company and its subsidiary. All inter-company balances
and transactions within the Company and subsidiary have been eliminated upon consolidation.
Cash
and Cash Equivalents
The
Company considers all short-term investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash and equivalents
for purposes of the statement of cash flows.
Accounts
Receivable
Accounts
receivable are recorded at the invoiced amount and do not bear interest. The Company extends unsecured credit to its customers
in the ordinary course of business but mitigates the associated risks by performing credit checks and actively pursuing past due
accounts. As of December 31, 2007, the Company did not record an allowance for uncollectible accounts
Inventories
Inventories
are valued at the lower of cost (using the first-in, first out (FIFO) method) or market. Inventory items replaced by an alternative
and rendered unusable or diminished in value are considered to be obsolete. Obsolete inventory items are written down to zero.
Intangible
Assets
Patent cost, including legal fees and other costs associated with obtaining this patent, will be amortized over the
life of the patent using the straight-line method after the patent is approved by the authorities.
NOTE
2 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, Cont’d.
Revenue
Recognition
The
Company sells its products to a number of leading regional and national retailers, wholesalers, specialty distributors and catalog
merchandisers, both directly and through the services of external sales brokers. In accordance with the Securities Exchange Commission's
Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 104 (SAB 104) "Revenue Recognition in Financial Statements", the Company recognizes revenue
when persuasive evidence of a customer or distributor arrangement exists, shipment has occurred, the price is fixed or determinable,
and the sales revenues are considered collectible. Subject to these criteria, except with respect to customers that buy products
on Pay on Scan terms, the Company recognizes revenue at the time of shipment of the merchandise. The Company recognizes Pay-on-Scan
sales as revenues at the earliest of the following events: 1) the Company is notified of the customer's sales through periodic
sales reports; 2) the Company receives payments from the customer; or 3) the customer reorders a specified quantity of the relevant
product. Pay-on-Scan revenue recognition treatment typically ends when persuasive evidence exists that a customer or distributor
has agreed to terminate the Pay-on-Scan arrangement in favor of a traditional sales arrangement.
Cost
of Revenue
Cost
of revenues consists primarily of product costs and shipping and handling, which are directly attributable to the sale of products.
Advertising
Advertising
costs are charged to operations when incurred.
Research
and Development Costs
The
company expenses research and development costs as incurred.
Depreciation
Property
and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation is provided for using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives ranging
from three to seven years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the lease term or the estimated useful life.
Maintenance, repairs and minor renewals are expensed when incurred.
Impairment
Long-lived
assets and certain identifiable intangibles are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that
the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison
of the carrying amount of an asset to future net undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. Assets to be disposed
of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell.
Income
Taxes
The
Company accounts for income tax using FASB ASC 740
“Accounting for Income Taxes”
, which requires the asset
and liability approach for financial accounting and reporting for income taxes. Under this approach, deferred income taxes are
provided for the estimated future tax effects attributable to temporary differences between financial statement carrying amounts
of assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, and for the expected future tax benefits from loss carry-forwards and
provisions, if any. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the enacted tax rates expected in the years of recovery
or reversal and the effect from a change in tax rates is recognized in the statement of operations and comprehensive income in
the period of enactment. A valuation allowance is provided to reduce the amount of deferred tax assets if it is considered more
likely than not that some portion of, or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company accounts for stock-based compensation using the fair value method following the guidance set forth in section 718-10 of
the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for disclosure about Stock-Based Compensation. This section requires a public entity
to measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of equity instruments based on the grant date fair
value of the award (with limited exceptions). That cost will be recognized over the period during which an employee is required
to provide service in exchange for the award – the requisite service period (usually the vesting period). No compensation
cost is recognized for equity instruments for which the employees do not render the requisite service.
The
Company recognizes expenses for the fair value of its outstanding stock warrants and options as they vest, whether held by employees
or others. The fair value of each stock warrant and option at the grant date is evaluated by using the Black-Scholes option pricing
model based upon certain assumptions, including the expected stock price volatility.
Net
Loss per Common Share
The
Company calculates net loss per share in accordance with FASB ASC 260,
“Earnings per Share”
. Basic
loss per share is computed by dividing the net loss by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. No diluted loss
per share is required to be represented.
Recent
Accounting Standards
The
Company has implemented all new accounting pronouncements that are in effect. These pronouncements did not have any material impact
on the financial statements unless otherwise disclosed, and the Company does not believe that there are any other new accounting
pronouncements that have been issued that might have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations.
NOTE
3 – Patents
On
June 6, 2003, the Company filed a patent application with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) for “Compositions
and methods of treatment to alleviate or prevent migrainous headaches and their associated symptoms”. The patent #7,192,614
was issued on March 7, 2007. Legal fees and other costs associated with obtaining this patent were $25,780 and are being amortized
over the 20 year useful life of the patent, using the straight-line method. At balance sheet date, the carrying value of the patent
is $24,813.
NOTE
4 – Accrued Expenses
Accrued
expenses consisted of the following at December 31:
|
|
|
2007
|
|
2006
|
|
|
|
Accrued payroll
and payroll taxes
|
|
$
|
80,056
|
|
|
$80,056
|
|
Accrued and deferred rent
|
|
|
8,544
|
|
|
8,544
|
|
Accrued trade promotions expense
|
|
|
30,342
|
|
|
30,342
|
|
Accrued coupon programs
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
-
|
|
Accrued co-op advertising expense
|
|
|
34,411
|
|
|
34,411
|
|
Accrued merchandising programs
expense
|
|
|
101,263
|
|
|
101,263
|
|
Other accrued revenue reductions
|
|
|
9,642
|
|
|
9,642
|
|
Other accrued expense
|
|
|
3,379
|
|
|
3,379
|
|
Deferred Revenue-Pay on Scan
|
|
|
45,656
|
|
|
45,656
|
|
Deferred Revenue
|
|
|
69,600
|
|
|
69,600
|
|
Accrued
interest expense
|
|
|
108,593
|
|
|
65,350
|
|
Total
accrued expenses
|
|
$
|
491,440
|
|
|
$448,197
|
NOTE
5 - Short Term Convertible Notes Payable
The
Company had outstanding balances on its short-term notes payable of the following amounts at the respective dates:
|
|
|
12/31/2007
|
|
12/31/2006
|
|
Related Party, interest rate 6%, original due date, February 2, 2005; extended to June 2, 2005.
|
|
$
|
63,000
|
|
|
$
|
63,000
|
|
|
Non-affiliate third party, interest rate 6%, original due date, February 2, 2005; extended to June 2, 2005.
|
|
|
72,000
|
|
|
|
72,000
|
|
|
Non-affiliate third party, interest rate 6%, original due date, February 2, 2005; extended to June 2, 2005.
|
|
|
60,000
|
|
|
|
60,000
|
|
|
Non-affiliate third party, interest rate 6%, original due date, February 2, 2005; extended to June 2, 2005.
|
|
|
60,000
|
|
|
|
60,000
|
|
|
Non-affiliate third party, interest rate 6%, original due date, February 2, 2005; extended to June 2, 2005.
|
|
|
60,000
|
|
|
|
60,000
|
|
|
Non-affiliate third party, interest rate 6%, original due date, February 2, 2005; extended to June 2, 2005.
|
|
|
120,000
|
|
|
|
120,000
|
|
|
Non-affiliate third party, interest rate 6%, original due date, October 5, 2005.
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
Related Parties, interest rate 8%, due date, September 24, 2007.
|
|
|
13,500
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Related Parties, interest rate 8%.
|
|
|
9,505
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
558,005
|
|
|
$
|
535,000
|
|
On
December 2, 2004, the Company issued unsecured convertible promissory notes related to a private placement of short term debt.
The notes were issued to six individuals in principal amounts ranging from $60,000 to $120,000 for a total of $474,000. The Company
agreed to repay the principal amount in its entirety within three business days after the Company closed on net proceeds of at
least $2,000,000 obtained through any offering of its securities, including any debt, common stock or preferred stock, or if earlier,
on February 2, 2005. If the Company closed on $2,000,000 or more in net proceeds through an offering of its securities, the promissory
note holders had the option to convert the principal amount into securities of the Company according to the same terms and provisions.
The conversion of the short-term notes payable was contingent upon the closing of a $2,000,000 stock offering and the incremental
intrinsic value would have been recognized when the triggering event occurred. In lieu of interest, the Company issued to the
note holders five-year warrants to purchase 79,000 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $3.00. The warrants were valued
using the Black-Scholes pricing model using the following factors: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 158%, risk-free
interest rate of 3.5% and expected lives of five years. The resulting original issue discount and the fair value of the warrants
were amortized over the life of the notes using the straight-line method, which approximates the interest method.
The
Company paid $24,000 of the principal balance of the notes during the three months ended March 31, 2005. During the first quarter
the note holders agreed to extend the payment of the remaining balance of $450,000 to June 2, 2005. In lieu of interest during
the period up to the extended due date, the Company issued to the note holders five-year warrants to purchase 75,000 shares of
common stock at an exercise price of $1.00. The warrants were valued using the Black-Scholes pricing model using the following
factors: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 163%, risk-free interest rate of 3.5% and expected lives of five years.
The resulting original issue discount and the fair value of the warrants of $276,000 were amortized over the extended life of
the notes using the straight-line method, which approximates the interest method.
The
Company paid an additional $15,000 of the principal during the three months ended June 30, 2005. During the six months ended December
31, 2005, the Company did not make any principal payments, and accrued 6% interest on the outstanding balance. The Company negotiated
a settlement of the remaining note balance of $435,000 in July 2011.
On
July 1, 2005, the Company issued a secured short term convertible promissory note payable in the amount of $100,000. The note
was secured by the outstanding receivables of the Company, which, as of July 1, 2005, totaled approximately $200,000. The Company
agreed to repay the principal amount in its entirety at the sooner of (i) three business days of that date on which the Company
closed on cumulative net proceeds of $2,000,000 or greater which were obtained through any offering of its securities, including
without limitation any debt, common stock or preferred stock or (ii) October 1, 2005. If the Company closed on $2,000,000 or more
in net proceeds through an offering of its securities, the promissory note holder had the option to convert the principal amount
into securities of the Company according to the same terms and provisions. The conversion of the short-term notes payable was
contingent upon the closing of a $2,000,000 stock offering and the incremental intrinsic value would be recognized when the triggering
event occurred. In lieu of interest, the Company issued to the note holder 50,000 shares of common stock valued at $39,000. The
Company negotiated a settlement of the note balance of $100,000 in November 2009.
During
the quarter ended September 30, 2007, the Company borrowed $13,500 from various related parties at an interest rate of 8%. The
Company agreed to repay the principal amount in its entirety, with all unpaid interest then accrued on September 24, 2007. No
principal or interest payments were made on the notes. Settlement agreements were reached with each of the related parties on
July 2011.
During
the quarter ended December 31, 2007, the Company borrowed $9,505 from various related parties at an interest rate of 8%. No principal
or interest payments were made. Settlement agreements were reached with each of the related parties on July 2011.
NOTE
6 – Deferred Compensation
The
Company’s deferred compensation includes common stock or warrants issued to consultants for services to be rendered related
to public relations, sales distribution consulting, investor relations and general operations conducted in the normal course of
business. The following table sets forth the details of deferred compensation:
|
|
|
12/31/2007
|
|
12/31/2006
|
|
728,000 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $0.54 - $0.98 per share were issued during the year ended December 31, 2005 for consulting services rendered from 05/01/2005 to 10/03/2006.
|
|
$
|
(468,140
|
)
|
|
$
|
(468,140
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Five-year warrants to purchase 285,000 shares of common stock were granted during the year ended December 31, 2005 with exercise prices ranging from $.50-$3.00 per share for services rendered from 5/1/2005 to 10/03/2006. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 201.89%, and risk-free interest rates ranging from 3.63% - 4.1%
|
|
|
(195,650
|
)
|
|
|
(195,650
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,700,000 shares of common stock at a share price of $0.10 were issued during the period ending 09/30/2006 for consulting services rendered from 08/28/2006 to 08/27/2007.
|
|
|
(170,000
|
)
|
|
|
(170,000
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Five-year warrants to purchase 3,000,000 shares of common stock were granted during the period ended 09/30/2006 with exercise prices ranging from $0.25 - $0.50 per share for services rendered from 08/28/2006 to 08/27/2007. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, and risk-free interest rate of 4.77%.
|
|
|
(300,000
|
)
|
|
|
(300,000
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,500,000 shares of common stock at a share price of $0.08 were issued during the period ending 12/31/2006 for consulting services rendered from 11/01/2006 to 10/31/2007.
|
|
|
(120,000
|
)
|
|
|
(120,000
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400,000 shares of common stock at a share price of $0.10 were issued during the period ending 03/31/2007 for consulting services rendered from 03/28/2007 to 03/28/2008.
|
|
|
(40,000
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Five-year warrants to purchase 250,000 shares of common stock were granted during the period ended 06/30/2007 with an exercise price of $0 .10 per share for services rendered from 05/01/2007 to 04/30/2010. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 468.93%, and risk-free interest rate of 4.54%.
|
|
|
(27,500
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
350,000 shares of common stock at a share price of $0.20 were issued during the period ending 09/30/2007 for consulting services rendered from 09/04/2007 to 03/03/2008.
|
|
|
(70,000
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of deferred compensation
|
|
|
1,335,803
|
|
|
|
860,456
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
(55,487
|
)
|
|
$
|
(393,334
|
)
|
NOTE 7 – Common Stock to be
Issued
As
of December 31, 2007, the balance of common stock to be issued was $95,000 due to the transactions as follows:
During
the three months ended September 30, 2007, the Board of Directors of the Company approved the issuance of 250,000 shares of common
stock at a price of $.01 per share, in exchange for cash payment of total $25,000. The cash payment was received in full during
the three months ended September 30, 2007, but the 250,000 shares had not been issued as of the date of this report.
Pursuant
to a consulting agreement, the Company agreed to issue 2,333,333 shares of common stock to a consultant at $.03 per share for
services rendered or to be rendered valued at $70,000. The shares have not been issued as of the date of this report.
NOTE
8 - Stockholders' Equity
During
the three months ended December 31, 2007, the Company had no equity transactions.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2007 the Company issued 750,000 options at an exercise price of $.12 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $90,000. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes
pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 749.04%, risk-free interest rate of
4.41% and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2007 the Company issued 400,000 shares of common stock and 400,000 warrants with an exercise
price of $.25 for gross proceeds of $40,000 which was allocated between common stock and warrants on a pro rata basis based on
the known fair values of both securities. The fair value of the common stock was $40,000 determined using the market price of
$.10 per share at issuance date; the fair value of the warrants was $56,000 determined based on the Black Scholes pricing model
using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 468.93%, risk-free interest rate of 4.60% and an
expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2007 the Company issued 250,000 warrants at an exercise price of $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $27,500. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes pricing
model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 468.93%, risk-free interest rate of 4.54%
and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2007, the Company issued 200,000 shares of common stock at $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $20,000.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2007 the Company issued 700,000 shares of common stock and 700,000 warrants with an exercise price
of $.25 for gross proceeds of $70,000 which was allocated between common stock and warrants on a pro rata basis based on the known
fair values of both securities. The fair value of the common stock was $70,000 determined using the market price of $.10 per share
at issuance date; the fair value of the warrants was $98,000 determined based on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following
assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 468.93%, risk-free interest rate of 4.60% and an expected life of five
years.
During
the three months ended March 31, 2007, the Company issued 400,000 shares of common stock at $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $40,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 250,000 shares of common stock and 250,000 warrants with an exercise
price of $.25 for gross proceeds of $25,000 which was allocated between common stock and warrants on a pro rata basis based on
the known fair values of both securities. The fair value of the common stock was $25,000 determined using the market price of
$.10 per share at issuance date; the fair value of the warrants was $30,000 determined based on the Black Scholes pricing model
using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate of 4.57% and an
expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 250,000 shares of common stock and 250,000 warrants with an exercise
price of $.25 for gross proceeds of $25,000 which was allocated between common stock and warrants on a pro rata basis based on
the known fair values of both securities. The fair value of the common stock was $25,000 determined using the market price of
$.10 per share at issuance date; the fair value of the warrants was $30,000 determined based on the Black Scholes pricing model
using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate of 4.57% and an
expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 1,150,000 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $.06 to $0.15
per share for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $136,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 1,500,000 shares of common stock at $0.08 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $120,000.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006, 242,847 five-year options were exercised with a weighted average exercise price of $0.69
on a "cashless" or "net exercise" basis (based on the market price of the Company's common stock the day before
exercise) resulting in the issuance of 2,428 shares of common stock.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 120,000 warrants at an exercise price of $.20 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $8,400. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes
pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate of
4.55% and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended December 31, 2006 the Company issued 950,000 options at an exercise price of $.06 per share for services
rendered or to be rendered valued at $95,000. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes
pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate of
4.6% and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 2,433,888 shares of common stock and 2,433,888 warrants with an exercise
price of $.20 for gross proceeds of $219,050 which was allocated between common stock and warrants on a pro rata basis based on
the known fair values of both securities. The fair value of the common stock was $219,500 determined using the market price of
$.09 per share at issuance date; the fair value of the warrants was $255,899 determined based on the Black Scholes pricing model
using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate ranging from 4.76%
- 5.08% and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 197,010 shares of common stock at $.09 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $17,731.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 1,700,000 shares of common stock at $.10 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $170,000.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 3,000,000 warrants at exercise prices ranging from $.25 - $.50 per
share for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $300,000. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based
on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free
interest rate of 4.77% and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended September 30, 2006 the Company issued 760,000 options at exercise prices ranging from $.07 - $.11 per share
for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $57,200. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the
Black Scholes pricing model using the following assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest
rates ranging from 4.86% - 5.10% and an expected life of five years.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2006, the Company issued 320,000 shares of common stock at $.12 per share for services rendered
or to be rendered valued at $38,400.
During
the three months ended June 30, 2006, the Company issued 500,000 warrants at an exercise price of $.09 per share for severance
valued at $60,000. The Company determined the fair value of the warrants based on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following
assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate of 5.08% and an expected life of five
years.
During
the three months ended March 31, 2006 the Company issued 60,000 shares of common stock and 30,000 warrants with an exercise price
of $.70 for gross proceeds of $30,000 which was allocated between common stock and warrants on a pro rata basis based on the known
fair values of both securities. The fair value of the common stock was $30,000 determined using the market price of $.50 per share
at issuance date; the fair value of the warrants was $22,200 determined based on the Black Scholes pricing model using the following
assumptions: dividend yield of 0%, expected volatility of 216.54%, risk-free interest rate of 4.32% and an expected life of five
years.
During
the three months ended March 31, 2006, the Company issued 535,000 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $.74 to $.22 per
share for services rendered or to be rendered valued at $241,700.
Stock
Option Plan
The
Company had a stock option plan (1997 Plan) in which the Company reserved 100,000 shares of common stock for issuance to outside
directors as compensation for their services as board members. During 2003, the Company terminated the 1997 Plan.
During
2003, the Company adopted the 2003 Incentive Plan (the Plan), pursuant to which stock options to acquire an aggregate of 3,600,000
shares of the Company's common stock may be granted to employees, directors and consultants. In general, options vest over a period
of up to three years and expire five years from the date of grant.
Information
regarding the Company's stock options is summarized below:
|
|
|
|
|
Number of
|
|
Weighted Avg
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
Options Outstanding -
|
|
|
December 31, 2005
|
|
|
|
2,658,750
|
|
|
$
|
0.87
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,710,000
|
|
|
|
0.07
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Canceled/Expired
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(895,000
|
)
|
|
|
0.44
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options Outstanding -
|
|
|
December 31, 2006
|
|
|
|
3,473,750
|
|
|
|
0.59
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
750,000
|
|
|
|
0.12
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Canceled/Expired
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options Outstanding -
|
|
|
December 31, 2007
|
|
|
|
4,223,750
|
|
|
$
|
0.51
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options exercisable -
|
|
|
December 31, 2006
|
|
|
|
2,485,750
|
|
|
$
|
0.76
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options exercisable -
|
|
|
December 31, 2007
|
|
|
|
3,959,750
|
|
|
$
|
0.53
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average fair value of options granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during the year-ended
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.09
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average fair value of options granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during the year-ended
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.12
|
|
|
Options outstanding at December 31, 2007 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding
|
|
Exercisable
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remaining
|
|
|
|
Weighted
|
|
|
|
Number of
|
|
|
|
Contractual
|
|
Number of
|
|
Average
|
|
Range of exercise prices
|
|
Options
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
Life Years
|
|
Options
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
|
$0.06 - $0.12
|
|
|
|
2,460,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.08
|
|
|
|
5.54
|
*
|
|
|
2,196,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.08
|
|
|
$
|
0.30
|
|
|
|
770,000
|
|
|
|
0.30
|
|
|
|
2.88
|
|
|
|
770,000
|
|
|
|
0.30
|
|
|
|
$0.92 - $1.20
|
|
|
|
656,250
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
|
0.65
|
|
|
|
656,250
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
|
$2.67 -$3.37
|
|
|
|
337,500
|
|
|
|
3.23
|
|
|
|
1.48
|
|
|
|
337,500
|
|
|
|
3.23
|
|
|
|
$0.30 - $3.37
|
|
|
|
4,223,750
|
|
|
$
|
0.51
|
|
|
|
3.97
|
|
|
|
3,959,750
|
|
|
$
|
0.53
|
|
|
|
* Note: 750,000 option, exercise price $.12, exercise period 10 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock Warrants
The
Company has also issued warrants in connection with equity offerings, for services rendered, and with short term notes payable,
as summarized below:
|
|
|
|
|
Number of
|
|
Weighted Avg
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
Warrants Outstanding -
|
|
|
December 31, 2005
|
|
|
|
1,683,529
|
|
|
$
|
0.85
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,333,888
|
|
|
|
0.27
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(500,000
|
)
|
|
|
0.09
|
|
|
Canceled/Expired
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants Outstanding -
|
|
|
December 31, 2006
|
|
|
|
7,517,417
|
|
|
|
0.42
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,350,000
|
|
|
|
0.20
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Canceled/Expired
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(18,000
|
)
|
|
|
1.20
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants Outstanding -
|
|
|
December 31, 2007
|
|
|
|
8,849,417
|
|
|
$
|
0.38
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average fair value of Warrants granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during the year-ended
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average fair value of Warrants granted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during the year-ended
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.13
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
During the year-end December 31, 2007 warrants were issued for the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,100,000 in connection with equity financing.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants outstanding at December 31, 2007 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding & Exercisable
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remaining
|
|
|
|
Number of
|
|
|
|
Contractual
|
|
Range of exercise prices
|
|
|
Warrants
|
|
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
|
|
Life Years
|
|
|
$.10-$.15
|
|
|
904,015
|
|
|
$
|
0.14
|
|
|
|
1.22
|
|
|
$.20-$.35
|
|
|
5,903,888
|
|
|
|
0.25
|
|
|
|
3.82
|
|
|
$.50-$1.00
|
|
|
1,728,701
|
|
|
|
0.64
|
|
|
|
0.31
|
|
|
$1.20-$1.67
|
|
|
90,525
|
|
|
|
1.50
|
|
|
|
1.26
|
|
|
$2.00-$3.00
|
|
|
222,288
|
|
|
|
2.68
|
|
|
|
1.93
|
|
|
$0.15-$3.00
|
|
|
8,849,417
|
|
|
$
|
0.38
|
|
|
|
3.95
|
|
NOTE
9 – Income Taxes
Due
to the operating loss and the inability to recognize an income tax benefit there is no provision for current or deferred federal
or state income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2007.
Deferred
income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial
reporting purposes and the amount used for federal and state income tax purposes.
Because
of the Company’s lack of earnings history, the deferred tax asset has been fully offset by a valuation allowance. The valuation
allowance increased by approximately $417,134 and $758,350 for the years ending December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Components
of the net deferred income taxes are as follows at December 31:
|
|
|
December
31,
|
|
|
|
2007
|
|
2006
|
|
Deferred income
tax assets
|
|
$
|
6,368,899
|
|
|
$
|
5,951,765
|
|
|
Less:
Valuation allowance
|
|
|
(6,368,899
|
)
|
|
|
(5,951,765
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Deferred income tax liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Net deferred
income tax assets
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The reconciliation of income
taxes computed at the federal statutory income tax rate to total income taxes for the period from inception through December
31, is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
Income tax computed at the federal
statutory rate
|
|
|
-34.00
|
%
|
|
|
-34.00
|
%
|
|
State income
tax, net of federal tax benefit
|
|
|
-4.50
|
%
|
|
|
-4.50
|
%
|
|
Total
|
|
|
-38.50
|
%
|
|
|
-38.50
|
%
|
|
Valuation
Allowance
|
|
|
38.50
|
%
|
|
|
38.50
|
%
|
|
Total
deferred tax asset
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
NOTE
10 - Related Party Transactions
On
December 2, 2004, the Company borrowed $102,000 from a director of the Company for a term ending on February 2, 2005, or, if earlier,
upon a $2,000,000 financing, as discussed in Note 5, above. In lieu of interest, the Company issued to the director a five-year
warrant to purchase 17,000 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $3.00. The repayment date for $78,000 of the note was
extended to June 2, 2005, and in lieu of interest for the extension period, the Company issued to the director a five-year warrant
to purchase 13,000 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $1.00. The Company paid an additional $15,000 of the principal
note balance during the three months ended June 30, 2005. During the six months ended December 31, 2005, the Company did not make
any principal payments, and accrued 6% interest on the outstanding balance. The Company negotiated a settlement of the remaining
note balance of $63,000 outstanding in July 2011.
During
the quarter ended September 30, 2007, the Company borrowed $13,500 from various related parties at an interest rate of 8%. The
Company agreed to repay the principal amount in its entirety, with all unpaid interest then accrued on September 24, 2007. No
principal or interest payments were made on the notes. Settlement agreements were reached with each of the related parties on
July 2011.
During
the quarter ended December 31, 2007, the Company borrowed $9,505 from various related parties at an interest rate of 8%. No principal
or interest payments were made. Settlement agreements were reached with each of the related parties on July 2011.
NOTE
11 - Legal Proceedings
On
January 19, 2006, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Milgaard RE Partnership vs. Gelstat Corporation.”
Milgarrd RE Partnership, a promissory note holder, alleged Gelstat owed $76,734 regarding the note, interest and fees. On July
1, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Milgarrd RE Partnership was issued 114,000, $0.03, 5 year warrants
and $3,600 cash.
On
September 7, 2006, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Dr. Steven Klos vs. Gelstat Corporation.”
Dr. Steven Klos, a promissory note holder, alleged Gelstat owed $100,000 regarding the note, interest and fees. On November 3,
2009, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Dr. Steven Klos was paid $25,000 cash.
On
September 10, 2007, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Unicep Packaging, Inc. vs. Gelstat Corporation.”
Unicep Packaging, Inc., a vendor, alleged Gelstat owed $190,340 on an agreement entered into by the parties regarding packaging
of Gelstat’s products. On July 11, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Unicep was issued 400,000,
$0.03, 5 year warrants and $20,000 cash.
On
December 11, 2007, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Angela Diliddo and Bioinitiate Capital,
LLC. vs. Gelstat Corporation.” Angela Diliddo and Eleanor Kelly (sole principal of Bioninitiate), promissory note holders,
alleged Gelstat owed $120,000 and $60,000, respectively, regarding the notes. On July 1, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached
among parties wherein Angela Diliddo was issued 240,000 $0.03, 5 year warrants and $6,000 cash and Eleanor Kelly was issued 120,000
$0.03, 5 year warrants and $3,000 cash.
On
December 14, 2007, the Company was served with a Summons and Complaint entitled “Stepping Stones Partners, LP and Daniel
D. Hickey vs. Gelstat Corporation.” Stepping Stones Partners, LP/Daniel D. Hickey, a promissory note holder, alleged Gelstat
owed $120,000 regarding the note. On July 1, 2011, a settlement agreement was reached among parties wherein Stepping Stones Partners,
LP/Daniel D. Hickey was issued 120,000 $0.03, 5 year warrants and $16,000 cash.
NOTE
12 – Going Concern
As
shown in the accompanying audited consolidated financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations
to date. It experienced a loss of $1,083,466 during 2007. The Company had a net deficiency of $16,542,595 as of December 31, 2007.
These factors raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
The
Company’s ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon its ability to generate future profitable operations
and/or to obtain the necessary financing to meet its obligations and repay its liabilities arising from normal business operations
when they come due. Management’s plan includes obtaining additional funds by equity financing and/or related party advances;
however there is no assurance of additional funding being available. These circumstances raise substantial doubt about the Company’s
ability to continue as a going concern. The accompanying financial statements do not include any adjustments that might arise
as a result of this uncertainty.
ITEM
9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
On
August 12, 2002, DTR engaged Gallogly, Fernandez and Riley, LLP ("GFR"), with offices in Orlando, Florida, to audit
the Company's consolidated financial statements for 2002. At no time prior to August 12, 2002, had DTR consulted with GFR regarding
the application of accounting principles to a specific or contemplated transaction, regarding the type of audit opinion that might
be rendered on the registrant's financial statements, or regarding any other matter.
On
January 6, 2004, Gelstat dismissed GFR as its independent auditor. The dismissal of GFR was recommended and adopted by the Company's
Audit Committee and approved by its Board of Directors. GFR audited the Company's financial statements for the fiscal year ended
December 31, 2002.
GFR's
report on the Company's financial statements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2002 did not contain any adverse opinion or
disclaimer of opinion and was not qualified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles. During the fiscal years ended
December 31, 2003 and 2002, and the subsequent interim period ending January 6, 2004 (i) there were no disagreements between the
Company and GFR on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure or auditing scope or procedure
which, if not resolved to the satisfaction of GFR, would have caused them to make reference to the subject matter of the disagreement
in connection with their reports and (ii) there were no "reportable events," as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation
S-K of the SEC. The decision to replace GFR was not the result of any disagreement between us and GFR on any matter of accounting
principle or practice, financial statement disclosure or audit procedure.
Concurrently,
on January 6, 2004, the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors and the Board of Directors approved the appointment of Virchow,
Krause & Company, LLP ("Virchow Krause") as the Company's independent accountant and auditor, said action to be
effective January 5, 2004. Virchow Krause has audited the Company's financial statements included in this Report on Form 10-KSB
for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2004 and 2003. The Company did not consult with Virchow Krause on any matters related
to accounting principles or practice, financial statement disclosures or audit procedures during the fiscal years ended December
31, 2003 and 2002 and the subsequent interim periods through January 6, 2004 prior to selecting and appointing Virchow Krause
as auditor. On May 1, 2007 Virchow Krause resigned as the Company’s auditors due to lack of payment.
On
August 23, 2011, the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors and the Board of Directors approved the appointment of Bongiovanni
& Associates, CPAs ("Bongiovanni") as the Company's independent accountant and auditor, said action to be effective
August 24, 2011. The decision to replace Virchow Krause was not the result of any disagreement between us and Virchow Krause on
any matter of accounting principle or practice, financial statement disclosure or audit procedure.
The
Company did not consult with
Bongiovanni
regarding either (i) the application
of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be
rendered on the Company’s financial statements; or (ii) any matter that was either the subject of a disagreement as described
in Item 304(a)(1)(iv) of Regulation S-K or a reportable event as such term is described in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K.
ITEM
9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation
of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
During
the course of their audit of our consolidated financial statements for 2007, our independent registered public accounting firm,
Bongiovanni advised management and the Audit Committee of our Board of Directors that they had identified deficiencies in internal
controls. The deficiencies are considered to be a "material weakness" as defined under standards established by the
American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. The material weakness relates to the lack of segregation of duties and financial
oversight controls, which in aggregate created an ineffective control environment. Because the company has no employees and only
one officer, it is not practical to remediate this material weakness.
We
have discussed our corrective actions and future plans with our Audit Committee and Bongiovanni. Further, our management, including
our Chief Executive Officer, have conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of disclosure controls and procedures (as such
term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"))
as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on such evaluation and due to the Company’s limited operations,
our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that the material weaknesses noted above will not, however,
impact the quality of the financial information provided on a quarterly or annual basis. In addition, because of this material
weakness, the Company’s disclosure controls are considered to be ineffective.
In
addition, there can be no assurances that our disclosure controls and procedures will detect or uncover all failure of persons
with the Company to report material information otherwise required to be set forth in the reports that we file with the Securities
and Exchange Commission.
Management’s
Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our
management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule
13a-15(f) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act). Our management, under the supervision and with the participation of our Principal
Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting
as of the end of the period covered by this report. In making this assessment, our management used the criteria set forth by the
Committee of Sponsor Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in
Internal Control-Integrated Framework.
Based
on that evaluation, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was ineffective based on
material weaknesses listed above.
Our
internal control over financial reporting is a process designed under the supervision of our Principal Executive Officer and Principal
Financial Officer to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of our
financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP. Internal control over financial reporting includes
those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly
reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded
as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures are being
made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding
prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect
on the financial statements.
Changes
in Internal Control
There
were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the period covered by this report that have materially
affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM
9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None
PART
III
ITEM
10. DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The
following table sets forth the directors, officers, and significant employees of the Company, their ages and positions with the
Company as of the date of filing this Report:
|
Name
|
|
Age
|
|
Position
|
|
Gerald N. Kieft
|
|
|
44
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer
|
|
William Colucci
|
|
|
73
|
|
|
Chairman of the Board of Directors
|
|
Paul W. Bucha
|
|
|
69
|
|
|
Director
|
|
Adrian Goldfarb
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
Director
|
Gerald
N. Kieft, Chief Executive Officer
Gerald
Kieft has been the CEO of Gelstat since June of 2008. Mr. Kieft was the founder and has been the CEO of Wall Street Resources,
Inc. from September of 2003 until present. Mr. Kieft was a co-founder and is the CEO of WSR from December of 2007 until present.
Mr. Kieft was the founder and has been the CEO of High Alpha Partners, Inc. from November of 2008 until present. Mr. Kieft was
the founder and CEO of GSC Direct, Inc. from September of 2010 to September of 2011.
William
R. Colucci, Chairman of the Board
William
R. (Bill) Colucci has been a consultant to and a director since 2007. From 2008-2010, he advised Ermis Pharmaceuticals in
developing a market strategy for their all natural acne and face products. From 2004 to 2007 he served as Corporate Secretary
for Universal Capital Management, Inc., a publicly traded Business Development Company. Since 1999, Mr. Colucci has served
as an independent consultant providing business consulting services to emerging growth companies. Mr. Colucci was elected
as a director for his experience with emerging growth companies.
Paul
W. Bucha, Director
Paul
Bucha has served as a director since 2011. Mr. Bucha, has been the CEO of Terra Mark II, LLC since December 2005. Under his leadership,
it was established to continue work on real estate projects in Bermuda and other environmentally sensitive locations after buy
out of majority owners of Terra Mark, LLC. joint venture with Greenfield Partners of Norwalk, Connecticut.
In
addition, Mr. Bucha has been a director of M Group, USA since 1994. M Group, USA is a family owned real estate and investment
company with projects in Switzerland, United Kingdom, Caribbean basin and USA. He has oversight of all aspects of company activities.
Mr. Bucha was appointed director because of his business experience.
Adrian
G. Goldfarb, Director- (Head of Audit Committee)
Mr.
Goldfarb has been a director of Gelstat since April 2008. Mr. Goldfarb has been Chief Financial Officer of Ecosphere Technologies,
Inc. (“Ecosphere”) from February 11, 2008 to July 1, 2012 and now provides consulting services to them on limited
basis. On July 1, 2012, Mr. Goldfarb was appointed President and CFO of Information Systems Associates Inc. From December 2007
until December 19, 2008, Mr. Goldfarb was the President of WSR a consulting services company WSR also provided Chief Financial
Officer services to Ecosphere and Mr. Goldfarb was a consultant. Since December 20, 2008, he has been a full-time employee and
resigned from his position as President of WSR. Mr. Goldfarb has more than 30 years’ experience in a number of different
technology companies, including IBM and a subsidiary of Fujitsu. From June 2002 to December 2007, Mr. Goldfarb was on the Board
of Directors of MOWIS GmbH, a Weather Technology Media company. He also was interim Chief Financial Officer where he led the management
team in securing seed capital, government grants and loans and bank guarantees. In May 2010, Mr. Goldfarb was elected a director
of Information Systems Associates, Inc. and is Chairman of the Audit Committee. Mr. Goldfarb was elected director because of his
public company experience and his accounting knowledge.
There
are no family relationships between any directors or executive officers of the Company, either by blood or by marriage.
The
Board of Directors has one standing committee consisting of an Audit Committee.
The
Audit Committee is responsible for reviewing the services rendered by the Company's independent auditors and the accounting standards
and principles followed by the Company. As of the date of filing this Report, the Company's audit and finance committee is comprised
of it one outside board member, Mr. Goldfarb, who is "independent" as defined in the rules of the Nasdaq Stock Market.
Mr. Goldfarb is also an "audit committee financial expert" as such term is defined in Item 407(d) of Regulation S-K
promulgated by the SEC and (ii) also meets NASDAQ’s financial sophistication requirements.
Section
16(A) Beneficial Ownership Compliance
Section
16(a) of the Exchange Act requires the Company's officers and directors, and persons who own more than 10 % of the registered
class of the Company’s equity securities to file reports of ownership on Forms 3, 4, and 5 with the SEC. Officers, directors
and greater than 10 % shareholders are required by SEC regulation to furnish the Company with copies of all Forms 3, 4, and 5
they file.
Based
upon the Company's review of the copies of such forms, and reports it has received from certain persons that they were not required
to file Forms 5 for the year ended December 31, 2007, the Company believes that all of its executive officers, directors and greater
than 10% beneficial owners have complied with all filing requirements applicable to them with respect to transactions during 2007.
Code
of Ethics
The
Company has adopted a code of ethics applicable to its principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting
officer, and persons performing similar functions. The code is filed as Exhibit 14.1 to this report.. A copy of the Code will
be provided without charge to any person upon request in writing to Gerald N. Kieft, CEO, at the address of the Company in Palm
City, Florida.
ITEM
11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The
following information related to the compensation paid by us for 2007 and 2006 to our Chief Executive Officer and the two other
most highly compensated executive officers serving at the end of the last fiscal year whose compensation exceeded $100,000.
|
S
ummary Compensation Table
|
|
Name and Principal Position
|
|
|
|
Year
|
|
Salary
|
|
Options Award
|
|
All Other Comp
|
|
Total
|
|
Stephen Roberts, Former CEO
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
$
|
46,154
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
46,154
|
|
|
Richard Ringold, Former CEO
|
|
|
(2
|
)
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3
|
)
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
$
|
77,885
|
|
|
$
|
54,400
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
132,285
|
|
|
William Colucci, CEO
|
|
|
(4
|
)
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
(1)
Resigned
6/30/2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2)
Resigned
01/01/2007
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3)
Appointed
06/30/2006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4)
Appointed
04/27/2007
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
|
|
Name and Principal Position
|
|
Number of Securities Underlying Options
|
Option Exercise Price
|
Option Expiration Date
|
|
|
|
Exercisable
|
|
Unexercisable
|
|
|
|
#
|
|
$
|
|
#
|
$
|
|
|
|
Richard Ringold, Former CEO
|
|
360,000
|
(1)
|
$330,000
|
|
-
|
$0
|
$0.92
|
07/08/08
|
|
|
|
11,250
|
(2)
|
$13,500
|
|
-
|
$0
|
$1.20
|
12/28/08
|
|
|
|
270,000
|
(3)
|
$909,900
|
|
-
|
$0
|
$3.37
|
07/01/09
|
|
|
|
520,000
|
(4)
|
$156,000
|
|
-
|
$0
|
$0.30
|
11/16/10
|
|
|
|
252,000
|
(5)
|
$17,640
|
|
168,000
|
$11,760
|
$0.07
|
08/09/11
|
|
|
|
250,000
|
(6)
|
$15,000
|
|
-
|
$0
|
$0.06
|
11/13/11
|
|
(1)
Fully vested 12.31.05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2)
Fully vested 12.31.05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3)
Fully vested 12.31.05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4)
Fully vested 12.31.07
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5)
Vest over 2
yrs - 42,000 every 3 mths
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(6)
Fully vested 11.15.06
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation Agreements
The
Company does not have any employment agreements at this time. Its sole officer performs part-time services without compensation.
Compensation
of Directors
The
Company at present has three outside directors, and does not separately compensate management directors for services related to
their participation on the board. The Company grants 500,000 shares of common stock to each outside director at the time of their
first election or appointment and 500,000 shares of common stock for each completed year of service. The Company at present provides
no cash compensation for any director.
The
table below provides information for 2007 in contrast to the above paragraph which is current.
|
Director Compensation
|
|
Name
|
|
Option Awards $
|
|
Total
|
|
Michael Chavanu
|
|
$
|
30,000
|
(1)
|
|
$
|
30,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
James LaFlamme
|
|
$
|
60,000
|
(1)
|
|
$
|
60,000
|
|
|
(1)
Computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 71
8
|
|
|
|
|
Equity
Compensation Plan
The
following table describes the Company's compensation plans under which the Company's common stock are authorized for issuance
as of December 31, 2007:
|
Equity Compensation Plan
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plan
|
|
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights
|
|
Number of securities remaining available for future issuances
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders
|
|
|
3,273,750
|
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
$
|
0.51
|
|
|
|
326,250
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders
|
|
|
9,799,417
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.42
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
Employee incentive stock options issued under the Company's 2003 Incentive Plan. Options outstanding at December 31, 2007 have exercise prices ranging from $0.06 to $3.37, vest over a period up to three years, and expire five years from the date of grant, with a weighted average remaining contractual life of 3.97 years.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM
12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
The
following table contains information as of the date of filing this Report, concerning the beneficial ownership of the Company's
common stock by persons known to the Company to beneficially own more than 5% of the common stock, by each director, by each executive
officer named in the Summary Compensation Table, and by all directors and executive officers as a group. Shares reported as beneficially
owned include those for which the named persons may exercise voting power or investment power, and all shares owned by persons
having sole voting and investment power over such shares unless otherwise noted.
|
|
|
Directors and Named Executive Officer
|
|
Amount and Nature of
|
|
|
|
Title of Class
|
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner
|
|
Beneficial Owner
|
|
Percent of Class
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Gerald N. Kieft
1
|
|
|
29,201,940
|
|
|
|
23
|
%
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
William R. Colucci
2
|
|
|
1,575,000
|
|
|
|
1
|
%
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Adrian G. Goldfarb
3
|
|
|
4,491,000
|
|
|
|
4
|
%
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Paul W. Bucha
4
|
|
|
500,000
|
|
|
|
0.04
|
%
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
All directors and executive officers as a group
|
|
|
35,767,940
|
|
|
|
28
|
%
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
William Brisben
5
|
|
|
38,500,000
|
|
|
|
28
|
%
|
1.
Gerald Kieft - 3557 SW Corporate Parkway, Palm City, Fl. 34990, calculation includes, 2.5 million warrants owned by WSR Consulting,
Inc. of which Mr. Kieft is the control person and 22.5 million shares owned by High Alpha Partners, Inc. of which Mr. Kieft is
the control person.
2.
William Colucci - 3557 SW Corporate Parkway, Palm City, Fl. 34990
3.
Adrian Goldfarb - 3557 SW Corporate Parkway, Palm City, Fl. 34990, calculation includes 1.175 million shares owned by Ronnie Sue
Goldfarb, Mr. Goldfarb’s wife.
4.
Paul W. Bucha - P.O. Box 849 Ridgefield, CT 06877
5.
William O. Brisben - 3557 SW Corporate Parkway, Palm City, FL 34990, calculation includes 10 million warrants.
ITEM
13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
In
September 2010, GelStat Direct formally contributed assets it owned relating to GelStat into a majority-owned subsidiary of High
Alpha Partners, Inc. named GSC Direct, Inc. In September of 2011, 100% of the outstand shares of GSC Direct, Inc. were acquired
by GelStat in exchange for the issuance of 25,000,000 shares of Gelstat common stock.
Gerald
N. Kieft (Gelstat’s CEO) is the founder, CEO and majority owner of High Alpha Partners, Inc. Adrian G. Goldfarb (member
of Gelstat’s Board of Directors) is the Treasurer of High Alpha Partners, Inc. High Alpha Partners, Inc. owned 75% of GSC
Direct, Inc. prior to its share exchange agreement with Gelstat. Mr. Kieft is the founder and CEO of GSC Direct, Inc.
ITEM
14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Gelstat’s
Audit Committee reviews and approves audit and permissible non-audit services performed by its independent registered public accounting
firm, as well as the fees charged for such services. In its review of non-audit service and its appointment of its
independent registered public accounting firm, the Audit Committee considered whether the provision of such services is compatible
with maintaining independence. All of the services provided and fees charged by its independent registered public accounting
firm in 2007 were approved by the Audit Committee. The following table shows the fees paid to our principal accountant
for the year ended December 31, 2007 and for the year ended December 31, 2006.
|
Audit Fees
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007
|
|
2006
|
|
Audit Fees
(1)
|
|
$
|
14,416
|
|
|
$
|
14,416
|
|
|
Audit Related Fees
(2)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Tax Fees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
All Other Fees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
14,416
|
|
|
$
|
14,416
|
|
|
(1) Audit fees - these fees relate to the audit
of our annual financial statements and internal control over financial reporting and the review of our interim quarterly financial
statements.
|
|
(2) Audit related fees -
these fees relate primarily to the auditors' review of our registration statements and audit related consulting of our
annual financial statements and internal control over financial reporting and the review of our interim quarterly
financial statements.
|
ITEM
15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SCHEDULES
(a)
Documents filed as part of the report.
|
(1)
|
Financial Statements. See
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements, which appears on page 15 hereof. The financial statements listed in
the accompanying Index to Consolidated Financial Statements are filed herewith in response to this Item.
|
|
(2)
|
Financial Statements Schedules. All
schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or because the required information is contained in the consolidated
financial statements or notes included in this report.
|
Copies
of this report (including the financial statements) and any of the exhibits referred to above will be furnished at no cost to
our shareholders who make a written request to GelStat Corporation, 3557 SW Corporate Parkway Palm City, Florida, 34990 Attention:
Mr. Gerald Kieft.
SIGNATURES
In
accordance with Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, the Registrant has caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the
undersigned, there unto duly authorized.
Date:
October 17, 2012
GELSTAT
CORPORATION
By:
/s/ Gerald N. Kieft
Gerald
N. Kieft
Chief
Executive Officer
(Principal
Executive Officer)
In
accordance with the Exchange Act, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the
capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signatures
|
Title
|
Date
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ GERALD N. KIEFT
|
Director and Principal Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer
|
October 17, 2012
|
|
Gerald N. Kieft
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ WILLIAM R. COLUCCI
|
Chairman of the Board and Director
|
October 17, 2012
|
|
William R. Colucci
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ ADRIAN G. GOLDFARB
|
Director
|
October 17, 2012
|
|
Adrian G. Goldfarb
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ PAUL W. BUCHA
|
Director
|
October 17, 2012
|
|
Paul W. Bucha
|
|
|
(35)
GelStat (PK) (USOTC:GSAC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Nov 2024 to Dec 2024
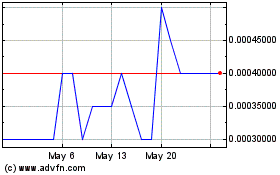
GelStat (PK) (USOTC:GSAC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Dec 2023 to Dec 2024