
We could not find any results for:
Make sure your spelling is correct or try broadening your search.
Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency, a form of money that has no physical presence but exists only in digital form. It has a market capitalisation of approximately $2 trillion. Bitcoin has captured the world’s imagination, and businesses and individuals are increasingly accepting its potential for substantial returns and as a store of value.
There are several ways to invest and trade in Bitcoin.
Investing in Bitcoin involves buying a quantity of the cryptocurrency and holding it until the price goes up, then selling it to realise a profit.
To invest in Bitcoin you need to set up an account with a reputable cryptocurrency broker, transfer some money into the account, and buy some Bitcoin.
| Choose your broker | All brokers have their own features and their fees vary, so you need to do your research to find a reputable platform that fits your needs. |
| Set up an account | Provide your personal information as well as documents to verify your identity, create a username and password. |
| Deposit funds | Use a bank transfer, credit/debit card, or whatever payment methods the platform supports to put some money into your account. |
| Buy Bitcoin | Decide how much money you want to spend, and instruct the broker to carry out the transaction. The money will be deducted from your account, and the BTC will be added. |
This buy-and-hold strategy (or in cryptocurrency jargon, hodling) will allow you to add Bitcoin to your portfolio which should, over time, increase in value.
Bitcoin prices run on a classic ‘boom, bubble, bust’ cycle which traditionally lasts about four years. That means, the price will rise steadily, then it will start shooting up, reach the top, and crash. A few fallow years will follow when there is little interest in Bitcoin – this is called the Crypto Winter – then enthusiasm will spark again and the cycle starts over.
It goes without saying that the ideal scenario is to buy at the bottom and sell at the top, but timing the market exactly is all but impossible. However, as long as you think the Bitcoin price has further to rise then it is worth buying.
As with all assets, diversification is key, so don’t spend all your money on Bitcoin, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
This chart shows the Bitcoin price since it was invented in 2009, with the peaks of the previous cycles:
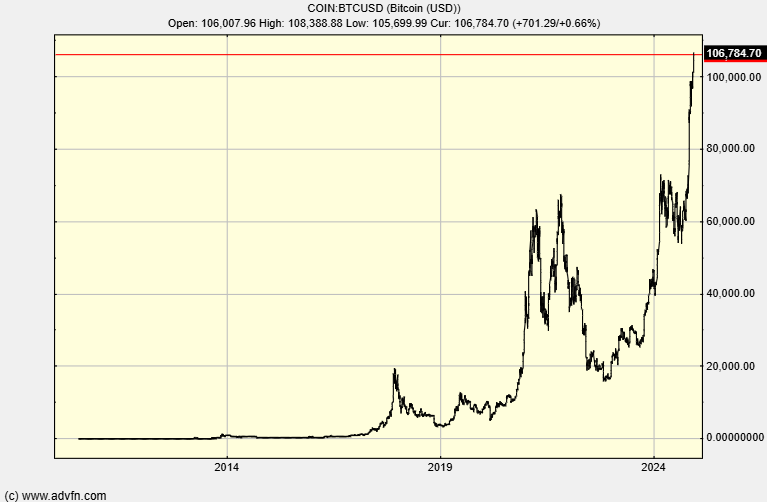
One way to build a position in Bitcoin is by using a strategy called dollar-cost averaging. This means that you invest a fixed amount on a regular basis, say every month, regardless of the Bitcoin price. This removes the stress from trying to choose the right time to invest.
As for when you should sell your Bitcoin – well, you can’t know exactly when the top has been reached, but you can probably spot when it’s close. If you look at the Bitcoin price and start to feel anxious, stop buying more. If you get really nervous, start to sell. You don’t have to sell everything at once, but you can sell a chunk each month to reduce your exposure. Of course, if it looks like the crash has started, then your choice is to sell your BTC holding as fast as you can – or just hang onto it and ignore the crash, in the knowledge that the next cycle should send the price even higher.
The Bitcoin price is very volatile and even in a bull market it does not move smoothly up, and in a bull market does not move smoothly down. This gives opportunities for short-term traders to capitalise on the volatile price movements to gain profits.
This can be as simple as keeping a close eye on the movement of the Bitcoin price and buying the dips, then selling once the price goes up again.
Remember, your exchange will charge a transaction fee for buying and selling Bitcoin, so the price movement needs to be large enough that the profits are not eaten up with fees.
Another option is to trade cryptocurrency indices, which track the performance of a basket of cryptocurrencies, not just Bitcoin. This allows for diversification, and it can mitigate some of the risks associated with cryptocurrency trading.
Options are financial derivatives contracts that give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a predetermined amount of an asset at a specific date in the future, at a specified price.
You can either buy a call option, which gives you the right to buy Bitcoin, or a put option, which gives you the right to sell Bitcoin.
Call Option
If you think the Bitcoin price is going to rise, then you take out a call option which will let you purchase Bitcoin at a later date, at the price specified in the contract, which will be based on the current price. Then when the option is settled, if you were right and the price has gone up, you can buy the Bitcoin at the lower price, and sell them at the new higher price, making a profit. But if you were wrong and the price does not go up, you are not obliged to take up the option, so all you have lost is the fee charged by the broker.
Put Option
If you think Bitcoin’s price is going to fall, then you take out a put option which will let you sell Bitcoin at a later date, at the price specified in the contract. When the option is settled, if the price has gone down, you can sell Bitcoin at the higher price specified by the contract, then buy it back at the lower market price – making a profit on the difference in price. But if you were wrong and the price went up instead of down, you do not have to take up the option so you only lose your broker’s fees.
Spread betting is a popular form of derivative trading in an asset such as Bitcoin that involves taking a position on the price and whether you think it is going to go up or down.
You can trade both sides of the market – if you think the price is going up, you go long (buy) and if you think it’s going down you short (sell). You don’t actually buy or sell the BTC, instead you place a bet on the price movement. If the market moves in your favour, you will make a profit; but if it goes against you, you will make a loss.
You can use leverage when spread betting, which allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify your gains – but if things go wrong it will also increase your losses.
Spread betting is usually free from capital gains tax so it is a tax-efficient way of trading Bitcoin’s price movements.
Spread betting involves a high degree of risk and you should do your research and consider your risk tolerance before taking out a contract.
CFDs, or contracts for difference, are a type of derivative, a way to speculate on the price movements of Bitcoin without actually owning the underlying coins. They are similar to spread betting, but they are subject to capital gains tax.
CFDs let you take advantage of both falling and rising prices. If you think the Bitcoin price is going to rise, you place a Buy order, also known as going long. If you think the Bitcoin price is going to fall, you place a Sell order, also known as going short.
You can use leverage with Bitcoin CFDs, which allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify your gains – but if things go wrong it will also increase your losses.
Trading CFDs involves a high degree of risk and you should consider your risk tolerance before taking out a CFD. Do your research to make sure you understand the Bitcoin market, and how CFDs work.
Arbitrage is a trading method that takes advantages of price discrepancies in the cryptocurrency market. Bitcoin is traded on many different markets, and sometimes there will be a difference in the price shown on the exchanges.
You can therefore buy Bitcoin on an exchange where the price is lower, transfer it to an account on an exchange where the price is higher, and sell it to gain a profit. This strategy is not unique to the crypto world; it’s a common practice in traditional financial markets as well.
The key factor in Bitcoin arbitrate is speed. The prices fluctuate every second so you need to be alert and capture the price difference before it vanishes.
| High Liquidity | You can buy and sell Bitcoin quickly, making it easy to enter and exit positions. |
| Market Availability 24/7 | You can trade at any time, regardless of your time zone. |
| Decentralised Nature | Bitcoin is independent from traditional financial systems which makes it ideal for diversification. No one body controls the network or distribution. |
| High Market Volatility | The crypto market’s significant price fluctuations offer opportunities for high returns. |
| Security | Bitcoin is the most secure cryptocurrency and its network is built to prevent theft. |
| High volatility | Bitcoin’s price can fluctuate dramatically, leading to significant losses if a trade goes against you. |
| Complexity of Derivative Trading Instruments | Trading instruments such as CFDs are complex if you are new to trading, and using leverage without proper experience or understanding significantly increases your overall risk. |
| Risk of Rapid Market Changes | You need to be prepared for rapid market changes by having a solid risk management strategy in place. |
| Regulatory Uncertainty | Cryptocurrency regulations are different in various markets and this lack of consistency can expose you to market manipulation or fraud. |
1. Can beginners trade Bitcoin?
While it is possible for beginners to jump right in and start trading Bitcoin, you are advised to do your homework and learn everything you can about the Bitcoin market and the different ways to trade BTC before committing your money.
2. How do I choose an exchange or broker for Bitcoin trading?
You should choose a Bitcoin exchange or broker that has a good market reputation and that is known for transparency. Do research into exchanges and check their financial health. Check the fees charged, the turnaround time for transfer and settlement, and which exchanges offer the tools you need for your trading strategy.
3. Do I need a digital wallet to trade Bitcoin options or CFDs?
No. These derivative instruments mean you do not actually exchange the underlying token or end up owning any Bitcoin, therefore you do not need a wallet to store BTC.
4. How risky is Bitcoin trading?
No investment is completely risk-free, but Bitcoin is particularly risky because it is more volatile than traditional investments such as stocks or bonds.
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial, investment, or professional advice. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions or recommendations of any organizations or individuals mentioned. Always consult with a qualified financial advisor or other professionals before making any financial decisions. The author and publisher are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content provided.




.png)
Support: +44 (0) 203 8794 460 | support@advfn.com
By accessing the services available at ADVFN you are agreeing to be bound by ADVFN's Terms & Conditions