UNITED STATES
Securities
and Exchange Commission
Washington,
DC 20549
Form
20-F
|
[ ]
|
Registration Statement Pursuant to Section 12(b) or (g) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
|
|
Or
|
|
|
[X]
|
Annual Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
|
| |
For the Fiscal Year Ended |
APRIL 30, 2014 |
|
|
Or
|
|
|
[ ]
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
|
Or
|
|
| [ ] |
SHELL COMPANY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
| |
|
|
| Date of event requiring this shell company report |
|
| |
|
|
| |
for the transition period
from ______________ to _________________
|
|
|
Commission
File Number: |
0-28792 |
|
| |
|
|
| CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. |
|
| (Exact Name of Registrant As Specified In Its Charter) |
|
|
Not Applicable |
|
| (Translation of Registrant’s Name Into English) |
|
|
British Columbia, Canada |
|
| (Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) |
|
|
1020- 625 Howe Street, Vancouver, B.C. V6C
2T6 |
|
| (Address of Principal Executive Offices) |
|
|
Mr. Peter Dasler
Telephone 604.688.3211 - E-mail - pdasler@canalaska.com
1020 - 625 Howe Street,
Vancouver, BC, V6C 2T6 |
|
| (Name, telephone number, e-mail and address of company contact person) |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Title of Each Class |
|
Name on Each Exchange On Which Registered |
|
| |
Not Applicable |
|
Not Applicable |
|
| Securities Registered or to be Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act. |
|
| Common Shares without par value |
|
| (Title of Class) |
|
| |
|
| |
securities
For Which There is a Reporting Obligation Pursuant
to
Section 15(d) of the Act. |
| |
None |
| |
(Title of Class) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indicate the number of outstanding shares of each of the Issuer’s classes of capital or common shares as of the close of the period covered by the annual report. |
| 22,068,136 Common Shares without par value issued and outstanding at April 30, 2014 |
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a well known seasoned
issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. |
| |
yes |
|
no |
X |
|
|
|
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check
mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
|
| |
yes |
|
no |
X |
|
|
|
Note – Checking the box above will not relieve any registrant
required to filed reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 from their obligations under those
Sections.
|
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all
reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for
such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements
for the past 90 days.
|
| |
yes |
X |
no |
|
|
|
| Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the |
|
preceding
12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes No |
| |
| Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one) |
|
Large accelerated
filer Accelerated filer Non-accelerated filer X
|
| Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing: |
| |
| U.S. GAAP |
|
International Financial Reporting
Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board |
X |
OTHER |
|
| |
| |
|
Indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant
has elected to follow. |
| |
| |
Item 17 |
|
Item 18 |
|
|
|
| |
| If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of this Exchange Act). |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
yes |
|
no |
X |
|
|
| |
| (APPLICABLE ONLY TO ISSUERS INVOLVED IN BANKRUPTCY PROCEEDINGS DURING THE PAST FIVE YEARS) |
| Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed all documents and reports to be filed by Section 12, 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 subsequent to the distribution of securities under a plan confirmed by a court. |
| |
yes |
|
no |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TABLE OF CONTENTS |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
GLOSSARY OF MINING TERMS |
(vi) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS |
(viii) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PART I |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 1. |
IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISORS |
1 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 2. |
OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE |
1 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 3. |
KEY INFORMATION |
1 |
| |
A. |
Selected Financial Data |
|
1 |
| |
B. |
Capitalization and Indebtedness |
|
4 |
| |
C. |
Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds |
|
4 |
| |
D. |
Risk Factors |
|
5 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 4. |
INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY
|
9 |
| |
A. |
History and Development of the Company |
9 |
| |
B. |
Business Overview |
10 |
| |
C. |
Organizational Structure |
10 |
| |
D. |
Property Plant and Equipment |
10 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
(i) |
WEST MCARTHUR PROJECT, SASKATCHEWAN |
11 |
| |
|
(ii) |
CREE EAST PROJECT, SASKATCHEWAN |
13 |
| |
|
(iii) |
NW MANITOBA, MANITOBA |
14 |
| |
|
(iv) |
GREASE RIVER |
15 |
| |
|
(v) |
POPLAR |
15 |
| |
|
(vi) |
LAKE ATHABASCA |
15 |
| |
|
(vii) |
HODGSON |
15 |
| |
|
(viii) |
COLLINS BAY |
15 |
| |
|
(ix) |
CARSWELL |
15 |
| |
|
(x) |
PATTERSON |
15 |
| |
|
(xi) |
REEFTON |
15 |
| |
|
(xii) |
BC COPPER |
16 |
| |
|
(xiii) |
HANSON |
16 |
| |
|
(xiv) |
KASMERE |
16 |
| |
|
(xv) |
OTHER PROJECTS |
16 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 4A. |
UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
18 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 5. |
OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS |
18 |
| |
|
Significant Accounting Policies |
18 |
| |
|
Results of Operations - Consolidated Statement of Loss, Comprehensive Loss and Deficit |
|
| |
|
for the years ended April 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012 |
23 |
| |
A. |
Operating Results – Narrative Discussion |
24 |
| |
B. |
Liquidity and Capital Resources |
24 |
| |
C. |
Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, etc. |
27 |
| |
D. |
Trend Information |
27 |
| |
E. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements |
27 |
| |
F. |
Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations |
27 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 6. |
DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES |
27 |
| |
A. |
Directors and Senior Management |
28 |
| |
B. |
Compensation |
30 |
| |
C. |
Board Practices – Mandate of the Board of Directors |
35 |
| |
D. |
Employees |
35 |
| |
E. |
Share Ownership |
36 |
| ITEM 7. |
MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS |
36 |
| |
A. |
Major Shareholders |
36 |
| |
B. |
Related Party Transactions |
36 |
| |
C. |
Interests of Experts and Counsel |
37 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 8. |
FINANCIAL INFORMATION |
37 |
| |
A. |
Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information |
37 |
| |
B. |
Significant Changes |
37 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 9. |
THE OFFER AND LISTING |
37 |
| |
A. |
Offer and Listing Details |
37 |
| |
B. |
Plan of Distribution |
38 |
| |
C. |
Markets |
38 |
| |
D. |
Selling Shareholders |
39 |
| |
E. |
Dilution |
39 |
| |
F. |
Expenses of the Issue |
39 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 10. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION |
39 |
| |
A. |
Share Capital |
39 |
| |
B. |
Memorandum and Articles of Association |
39 |
| |
C. |
Material Contracts |
39 |
| |
D. |
Exchange Controls |
40 |
| |
E. |
Taxation |
40 |
| |
F. |
Dividends and Paying Agents |
47 |
| |
G. |
Statements by Experts |
47 |
| |
H. |
Documents on Display |
47 |
| |
I. |
Subsidiary Information |
47 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 11. |
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
47 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 12. |
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES |
48 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| PART II |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 13. |
DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARS AND DELINQUENCIES |
48 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 14. |
MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS |
|
| |
AND USE OF PROCEEDS |
48 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 15. |
CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
48 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16. |
NOT APPLICABLE |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16A. |
AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT |
49 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16B. |
CODE OF ETHICS |
49 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16C. |
PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16D. |
EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDES FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16E. |
PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER |
|
| |
AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16F. |
CHANGE IN REGISTRANTS CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16G. |
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 16H. |
MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
PART III
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 17. |
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 18. |
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
50 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 19. |
EXHIBITS |
51 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
SIGNATURES |
53 |
The following financial statements are
attached to and form a part of this report filed with the SEC:
Consolidated
Financial Statements of the Company:
| · | Report of Independent Registered Public
Accounting Firm on Consolidated Financial Statements for the years ended April 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Financial Position
as at April 30, 2014 and 2013. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Loss, Comprehensive
Loss and Deficit for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for
the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012. |
| · | Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
EXHIBIT INDEX
The following exhibits are attached to and form part of this Annual Report:
Exhibit |
| 1.1 |
Articles of Incorporation* |
| 11.1 |
Code of Ethics |
| 12.1 |
Section 302 Certification of the Company's Chief Executive Officer |
| 12.2 |
Section 302 Certification of the Company's Chief Financial Officer |
| 13.1 |
Section 906 Certification of the Company's Chief Executive Officer |
| 13.2 |
Section 906 Certification of the Company's Chief Financial Officer |
| 14.1 |
Management Discussion and Analysis dated July 29, 2014 |
| 14.2 |
Audit Committee Charter |
| 14.3 |
Corporate Governance Policy |
* Previously filed and incorporated by reference
from our Form 20-F filed with the SEC on September 14, 2010
GLOSSARY
OF MINING TERMS
The following are abbreviations and definitions of terms commonly
used in the mining industry and this Annual Statement:
| Aeromagnetic survey |
A geophysical survey using a magnetometer aboard or towed behind an aircraft. |
| Au |
The chemical symbol for gold. |
| Anomaly |
Any departure from the norm which may indicate the presence of mineralization in the underlying bedrock. |
| Anorthosite |
Light grey to almost black variety of gabbro, made up of plagioclase with a mafic content of less than 10%. |
| Aphebian |
Period of time in the Earth’s history between 2.5 and 1.8 billion years ago. |
| Archean |
Period of time in the Earth’s history between 3.8 and 2.5 billion years ago. |
| Assay |
A chemical test performed on a sample of ores or core to determine the amount of valuable metals contained. |
| Assessment Work |
The amount of work, specified by mining law, that must be performed each year in order to retain legal control of mining claims. |
| Athabasca Basin |
The region located in northern Saskatchewan province, Canada, hosting the world’s richest uranium deposits and all of Canada’s producing uranium mines. The basin is approximately 400 km across east/west and 150 km north/south. Its geology is characterized by metasedimentary bedrock overlain by younger sandstones. |
| Audio-Magnetotellurics (AMT) |
A geophysical method that measures the Earth’s varying electric and magnetic fields. |
| Basin |
In geology a round or oval depression in the Earth's surface, containing younger rock in its central part. |
| Batholith |
A large mass of igneous rock extending to great depth with its upper portion dome-like in shape. Similar smaller masses of igneous rocks are known as bosses or plugs. |
| Breccia |
A rock in which angular fragments are surrounded by a mass of fine-grained minerals. |
| CVV |
Stock symbol for CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. on the TSX Exchange |
| Chalcopyrite |
A sulphide mineral of copper and iron; the most important ore mineral of copper. |
| Channel Sample |
A sample composed of pieces of vein or mineral deposit that have been cut out of a small trench or channel, usually about 10 cm wide and 2 cm deep. |
| Chip Sample |
A method of sampling a rock exposure whereby a regular series of small chips of rock is broken off along a line across the face. |
| Claim |
An area marked on a map or the ground, where the Government has given current mineral title to the registered owner. Holder usually has the right to carry out mineral exploration and apply to mine on the located area. |
| Cretaceous |
The third and latest of the periods in the Mesozoic Era. |
| Diamond Drill |
A rotary type of rock drill that cuts a core of rock that is recovered in long cylindrical sections, 2 cm or more in diameter. |
| Dickite |
A polymorphic alumino-silicate clay that is formed from hydrothermal environments. |
| Diorite |
An intrusive igneous rock composed chiefly of plagioclase, hornblende, biotite or pyroxene. |
| Dravite |
A complex sodium/magnesium/aluminum/boron silicate formed from hydrothermal environments. |
| EM Survey |
A geophysical survey method which measures the electromagnetic properties of rocks. |
|
Exploration
|
Prospecting, sampling, mapping, diamond drilling and other work involved in searching for ore. |
| Exploration Permit |
See licence for New Zealand operations |
| |
|
|
| Fault |
Fracture in the Earth’s crust, along which there has been displacement of the sides relative to one another parallel to the fracture. |
| Gabbro |
A dark, coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock. |
| Geophysical Surveys |
The use of one or more geophysical techniques in geophysical exploration. |
| Grab Samples |
A sample of rock or sediment taken more or less indiscriminately at any place. |
| Gravity Gradient Survey |
A geophysical method used to map and mathematically model underground fault structures based on measurements of the gravity of rocks. |
| Gneiss |
Layered granite-like rock. |
| Gossan |
An iron-oxide rich weathered product overlying a sulphide deposit. |
| Granite |
A coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock consisting of quartz, feldspar and mica. |
| Gpt, or g/t |
Grams per tonne. |
| Hydrothermal Alteration |
The change in the mineralogy of the rock. The old minerals are replaced by new ones because there has been a change in the conditions. These changes could be changes in temperature, pressure, chemical conditions or any combination of these. Hydrothermal alteration is a change in the mineralogy as a result of interaction of the rock with hot water fluids, called “hydrothermal fluids”. |
| Hydrothermal Fluids |
It causes hydrothermal alteration of rocks by passing (hot) water fluids through the rocks and changing their composition by adding, removing or redistributing components. Temperatures can range from weakly elevated to boiling. Fluid composition is extremely variable. They may contain various types of gases, salts (briney fluids), water and metals. |
| Illite |
A layered alumino-silicate clay that is formed from hydrothermal environments. |
| Induced Polarization (IP) |
A geophysical survey method which measures the electrochemical properties
of rocks. Time domain IP methods measure the voltage decay or chargeability over a specified time interval after the induced voltage
is removed. Frequency domain IP methods use alternating currents (AC) to induce electric charges in the subsurface and the apparent
resistivity is measured at different AC frequencies.
|
| g/t Au |
Grams per tonne gold. |
| Kimberlite |
A blue/grey igneous rock which contains olivine, serpentine, calcite and silica. |
| Km |
A measure of distance known as a kilometre. |
| Leach |
To dissolve from a rock. For example, when acidic water passes through fractured rocks, soluble minerals leach or dissolve from the rocks. |
| Licence |
See claim, but not necessarily physically marked on the ground. |
| Lode |
Zone of metal veins. |
| Mb |
The chemical symbol for molybdenum. |
| Mg |
The chemical symbol for magnesium. |
| Mafic |
Igneous rocks with dark minerals. |
| Max-Min EM |
A specific type of electromagnetic geophysical survey. |
| MEL |
See licence, specifically for Manitoba, Canada |
| Mesozoic Era |
One of the grand divisions of geologic time, follows the Paleaozoic and succeeded by the Cenozoic. |
| Metallurgy |
The study of extracting metals from their ores. |
| Mineralization |
The concentration of metals and their chemical compounds within a body of rock. |
| Ni |
The chemical symbol for nickel. |
| NSR |
Net Smelter Returns. A royalty paid from the sale of mined minerals. |
| Opt |
Ounce per ton. |
| Ore |
A natural aggregate of one or more minerals, which at a specified time and place, may be mined and sold at a profit, or which from some part may be profitably separated. |
| Oz |
A measure of weight known as an ounce. |
| Permit |
Paperwork to allow certain types of activities in exploration |
| Placer |
A deposit of sand and gravel containing valuable metals such as gold, tin or diamonds. |
| Proterozoic |
Period of time in Earth’s history between 2.5 billion years ago and 544 million years ago. |
| Ppm |
Parts per million. |
| Pyrite |
A yellow iron sulphide mineral, normally of little value. It is sometimes referred to as "fool's gold". |
| Rare Earth Elements (REE) |
The rare earth elements (“Rare Earths” or “REE”) include the 15 elements in the Periodic Table of Elements, plus yttrium and scandium which have multiple uses in technology. |
| Radiometric dating |
The calculation of an age in years of geologic materials by any one of several age determination methods based on nuclear decay of natural radioactive elements contained in the material. |
| Sample |
A small portion of rock or a mineral deposit taken so that the metal content can be determined by assaying. |
| Sampling |
Selecting a fractional but representative part of a mineral deposit for analysis. |
| Shear or shearing |
The deformation of rocks by lateral movement along innumerable parallel planes, generally resulting from pressure and producing such metamorphic structures as cleavage and schistosity. |
| Strike |
The coarse or bearing of a bed or layer of rock. |
| Tailings |
Material rejected from a mill after most of the recoverable valuable minerals have been extracted. |
| Th |
The chemical symbol for thorium. |
| U |
The chemical symbol for uranium. |
| U3O8 |
Uranium oxide. The mixture of uranium oxides produced after milling uranium ore from a mine. Sometimes loosely called “yellowcake”. It is yellow in colour and is usually represented by the empirical formula U3O8. Uranium is sold in this form. |
| Unconformity |
A boundary separating two or more rocks of markedly different ages, marking a gap in the geologic record. |
| Unconformity Deposit Model |
The theoretical model for the characterization of major uranium
deposits located in the Athabasca Basin. Deposition/concentration of high-grade “unconformity” uranium deposits are
thought to result from the chemical interaction of dissolved uranium present in water-saturated sediments above the unconformity
with reducing gases and fluids generated from significant hydrothermal activity emanating from below the unconformity. High-grade
uranium deposits have been observed to occur at, above and/or below the unconformity.
Many unconformity-type deposits are marked by the surrounding presence
of sandstone and basement rocks that have also been chemically-altered due to hydrothermal activity. These larger rock “alteration”
zones represent the primary targets for uranium explorers as the altered physical properties of the rocks can be detected via various
airborne and land-based geophysical survey methods. In addition, the presence of geological fault structures is highly-correlated
with high-grade uranium deposition, with the fault structures likely acting as the conduits for the upwelling of hydrothermal fluids. |
| Uraninite |
A mineral consisting of uranium oxide and trace amounts of radium and thorium and polonium and lead and helium; uraninite in massive form is called pitchblende which is the chief uranium ore. |
| Vein |
A fissure, fault or crack in a rock filled by minerals that have traveled upwards from some deep source. |
| Volcanic rocks |
Igneous rocks formed from magma that has flowed out or has been violently ejected from a volcano. |
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING
STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 20-F and the exhibits
attached hereto contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements concern our anticipated results and developments in our operations in future periods,
planned exploration and development of its properties, plans related to its business and other matters that may occur in the future.
These statements relate to analyses and other information that are based on forecasts of future results, estimates of amounts not
yet determinable and assumptions of management. Statements concerning reserves and mineral resource estimates may also be deemed
to constitute forward-looking statements to the extent that they involve estimates of the mineralization that will be encountered
if the property is developed, and in the case of mineral reserves, such statements reflect the conclusion based on certain assumptions
that the mineral deposit can be economically exploited. Any statements that express or involve discussions with respect to predictions,
expectations, beliefs, plans, projections, objectives, assumptions or future events or performance (often, but not always, using
words or phrases such as “expects” or “does not expect”, “is expected”, “anticipates”
or “does not anticipate”, “plans”, “estimates” or “intends”, or stating that certain
actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might” or “will”
(or the negative and grammatical variations of any of these terms and similar expressions) be taken, occur or be achieved,) are
not statements of historical fact and may be forward-looking statements. Such statements are included, among other places in this
Annual Report on Form 20-F, in the sections entitled "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results
of Operations”, "Description of Business" and "Description of Property." Forward-looking statements are
subject to a variety of known and unknown risks and should not be read as guarantees of future performance or results, and will
not necessarily be accurate indications of whether or not such results will be achieved. Uncertainties and other factors which
could cause actual events or results to differ from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements, including, without
limitation:
| · | risks and uncertainties relating to the interpretation of drill results,
the geology, grade and continuity of mineral deposits; |
| · | results of initial feasibility, pre-feasibility and feasibility studies,
and the possibility that future exploration, development or mining results will not be consistent with the Company's expectations; |
| · | mining exploration risks, including risks related to accidents, equipment
breakdowns or other unanticipated difficulties with or interruptions in production; |
| · | the potential for delays in exploration activities or the completion
of feasibility studies; |
| · | risks related to the inherent uncertainty of exploration and cost estimates
and the potential for unexpected costs and expenses; |
| · | risks related to commodity price fluctuations; |
| · | the uncertainty of profitability based upon the Company's history of
losses; |
| · | risks related to failure of the Company and/or its joint venture partner
to obtain adequate financing on a timely basis and on acceptable terms; |
| · | risks related to environmental regulation, permitting and liability; |
| · | political and regulatory risks associated with mining and exploration; |
| · | other risks and uncertainties related to the Company's prospects, properties
and business strategy. |
This list is not exhaustive of the factors
that may affect our forward-looking statements. Some of the important risks and uncertainties that could affect forward-looking
statements are described further in the sections entitled “Risk Factors”, “Information on the Company”
and “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects” and in the exhibits attached to this Annual Report on Form 20-F.
Should one or more of these risks and uncertainties materialize, or should underlying assumptions prove incorrect, actual results
may vary materially from those described in the forward-looking statements. Although the forward-looking information contained
in this Annual Report is based upon what the Company’s management believes to be reasonable assumptions, the Company cannot
assure investors that actual results will be consistent with such information. Forward-looking information reflects management’s
current beliefs and is based on information currently available to the Company. Such information reflects current assumptions regarding
future events and operating performance including, without limitation, a strong global demand for mineral commodities, continued
funding and continued strength in the industry in which the Company operates, and speaks only as of the date of this discussion.
The forward-looking information is made as of the date of this Annual Report. The Company does not assume any obligation to update
forward-looking statements if circumstances or management’s beliefs, expectations or opinions change, except as required
by law. For the reasons set forth above, investors should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements.
PART I
| ITEM 1. | | IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND
ADVISORS |
This Form
20-F is being filed as an annual report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information
under this item.
| ITEM 2. | | OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this item.
| A. | | Selected Financial Data |
| 1. | The selected financial data and the information
in the following tables of the Company for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012 were derived from
the consolidated financial statements of the Company. These consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance
with and in compliance with International Financial Reporting Standard as issued by the International Accounting Standards Boards
(“IFRS”), which differ in certain respects from the principles the Company would have followed had its consolidated
financial statements been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“U.S.
GAAP”). |
The Company’s consolidated
financial statements are presented in Canadian dollars. The consolidated financial statements are prepared on the historical cost
basis except for certain financial instruments which are measured at fair value.
The selected financial data should
be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements along with the notes thereto, the Management Discussion and Analysis
(“MDA”) dated August 7, 2014, filed herewith, and Item 5 – Operating and Financial Review Prospects.
| 2. | The table below summaries certain consolidated financial information in accordance with IFRS for
the years ending April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013, April 30, 2012 and April 30, 2011. The information has been derived from the consolidated
financial statements filed herewith. |
International Financial Reporting Standards
(in Canadian Dollars)
for the Fiscal Year Ended April 30
|
$000’s
|
2014 |
2013 |
2012
|
2011 |
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
1,044 |
1,265 |
4,394 |
9,642 |
| Other current assets |
466 |
144 |
466 |
981 |
| Mineral properties |
813 |
1,238 |
1,356 |
1,797 |
| Other non-current assets |
483 |
578 |
849 |
959 |
| Total assets |
2,806 |
3,225 |
7,065 |
13,379 |
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Current liabilities |
382 |
195 |
1,792 |
2,461 |
| Shareholders’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
| Common shares |
73,205 |
73,205 |
73,210 |
72,108 |
| Equity reserve |
10,807 |
10,682 |
10,506 |
10,170 |
| Investment revaluation reserve |
(24) |
(1) |
53 |
267 |
| Deficit |
(81,564) |
(80,856) |
(78,496) |
(71,627) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Revenues |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Exploration costs |
(127) |
876 |
5,119 |
7,717 |
| Other expenses |
835 |
1,484 |
1,750 |
2,079 |
| Net loss for the year |
(708) |
(2,360) |
(6,869) |
(9,796) |
| Unrealized loss (gain) on available-for-sale securities |
23 |
54 |
214 |
(257) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year |
(731) |
(2,414) |
(7,083) |
(9,539) |
| Weighted Avg.# of shares outstanding (000’s) |
22,066 |
22,058 |
20,425 |
18,114 |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted |
(0.03) |
(0.11) |
(0.34) |
(0.54) |
2. (a) The
table below summaries certain consolidated financial information for the year ending April 30, 2010 in accordance with U.S. GAAP
in Canadian dollars, which have been derived from previously published consolidated financial statements for the year ended dates.
U.S. GAAP (in Canadian Dollars) for the Fiscal
Year Ended April 30
|
$000’s
|
2010
|
|
Assets |
|
| Cash |
7,889 |
| Restricted cash |
833 |
| Other current assets |
1,409 |
| Mineral properties |
1,043 |
| Other non-current assets |
1,134 |
| Total assets |
12,308 |
| Liabilities |
|
| Current liabilities |
1,626 |
| Future income tax liability |
- |
| Shareholders’ Equity |
|
| Common shares |
67,655 |
| Contributed surplus |
10,108 |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
10 |
| Deficit |
(76,613) |
| Non-controlling interest |
9,554 |
| |
|
| Revenues |
- |
| Exploration costs |
6,652 |
| Other expenses |
2,973 |
| Loss before income taxes |
(9,625) |
| Future income tax (expense) recovery |
- |
| Net loss for the year |
(9,625) |
| Loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
1,418 |
| Loss attributable to common shareholders |
(8,207) |
| Unrealized (gain) loss on available-for-sale securities |
(1) |
| Comprehensive loss for the year |
(9,624) |
| Weighted Avg.# of Shares Outstanding |
15,376 |
| Net Loss Per Share – basic and diluted |
(0.53) |
2. (b) The
table below summaries certain consolidated financial information for the year ending April 30, 2010 in accordance with Canadian
GAAP in Canadian dollars, which have been derived from previously published consolidated financial statements for the year ended
dates.
Canadian GAAP (in Canadian Dollars) for the
Fiscal Year Ended April 30
|
$000’s
|
2010
|
|
Assets |
|
| Cash |
8,722 |
| Other current assets |
1,409 |
| Mineral properties |
46,245 |
| Other non-current assets |
1,134 |
| Total assets |
57,510 |
| Liabilities |
|
| Current liabilities |
1,626 |
| Future income tax liability |
3,399 |
| Shareholders’ Equity |
|
| Common shares |
60,878 |
| Contributed surplus |
9,665 |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
10 |
| Deficit |
(30,668) |
| Non-controlling interest |
12,600 |
| |
|
| Revenues |
- |
| Exploration costs |
477 |
| Other expenses |
2,960 |
| Loss before income taxes |
(3,437) |
| Future income tax (expense) recovery |
461 |
| Net loss for the year |
(2,976) |
| Unrealized (gain) loss on available-for-sale securities |
(1) |
| Comprehensive loss for the year |
(2,975) |
| Weighted Avg.# of Shares Outstanding |
15,376 |
| Net Loss Per Share – basic and diluted |
(0.19) |
3. (a) On
July 31, 2014 the exchange rate of the Canadian dollar into United States Dollars based on the nominal rate for U.S. Dollars reported
by the Bank of Canada was $1.00 equals C$1.09.
3.
(b) U.S. Dollar/Canadian Dollar Exchange Rates for Previous Six Months
| 2014 |
February |
March |
April |
May |
June |
| High |
0.9141 |
0.9128 |
0.9210 |
0.9247 |
0.9393 |
| Low |
0.8932 |
0.8866 |
0.9046 |
0.9085 |
0.9122 |
3.
(c) U.S. Dollar/Canadian Dollar Exchange Rates for
the Five Most Recent Financial Years
| Fiscal Year Ended |
Average |
High |
Low |
Close |
| April 30, 2014 |
0.9429 |
0.9983 |
0.8866 |
0.9124 |
| April 30, 2013 |
1.0035 |
1.0397 |
0.9683 |
1.0075 |
| April 30, 2012 |
0.9959 |
1.0630 |
0.9383 |
0.9879 |
| April 30, 2011 |
0.9873 |
1.0582 |
0.9218 |
0.9464 |
| April 30, 2010 |
1.0109 |
1.1079 |
1.0038 |
1.0158 |
| B. | | Capitalization and Indebtedness |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this item.
| C. | | Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this item.
The Company is engaged in the exploration of
mineral properties, an inherently risky business. An investment in our common shares is highly speculative and subject to a number
of known and unknown risks. Only those persons who can bear the risk of the entire loss of their investment should purchase
our securities. An investor should carefully consider the risks described below and the other information that we file
with the SEC and with Canadian securities regulators before investing in our common shares. There is no assurance that
funds spent on the exploration and development of a mineral deposit will result in the discovery of an economic ore body. Most
exploration projects do not result in the discovery of commercially mineable ore deposits. Additional risks that we
are not currently aware of or that we currently believe are immaterial may become important factors that affect our business. If
any of these risks occur, operating results and financial conditions could be seriously harmed, the market price of our common
shares could decline and the investor may lose all of their investment. The risk factors set forth below and elsewhere
in this Annual Report, may have a significant impact on our business, operating results and financial condition and could cause
actual results to differ materially from those projected in any forward-looking statements. See “Cautionary Note
Regarding Forward-Looking Statements”.
Cash Flows and Additional Funding Requirements
May Be Required
The Company has limited financial resources,
no sources of operating cash flows and no assurances that sufficient funding, including adequate financing, will be available.
If the Company’s exploration programs are successful, additional funds will be required in order to complete the development
of its projects. The sources of funds currently available to the Company are the sale of marketable securities, the raising of
equity capital or the offering of an ownership interest in its projects to a third party. There is no assurance that the Company
will be successful in raising sufficient funds to conduct further exploration and development of its projects or to fulfill its
obligations under the terms of any option or joint venture agreements, in which case the Company may have to delay or indefinitely
postpone further exploration and development, or forfeit its interest in its projects or prospects. Without further financing and
exploration work on its properties the Company expects its current 741,794 ha of property to reduce to 695,283 ha by December 31
2014, and 655,495 ha by December 31 2015. The Company’s Fond Du Lac property reached its last anniversary on February 25
2014, after February 2015 a new lease or a special lease extension will be required by the Fond Du Lac community from Aboriginal
and Northern Affairs Canada. The Cree East and West McArthur projects, with current work filings are in good standing for a minimum
15 years from the current date.
Commodity Prices
The profitability of the Company’s operations
will be dependent upon the market price of mineral commodities. Mineral prices fluctuate widely and are affected by numerous factors
beyond the control of the Company. The prices of mineral commodities have fluctuated widely in recent years. Current and future
price declines could cause commercial production to be impracticable. The Company’s future revenues and earnings also could
be affected by the prices of other commodities such as fuel and other consumable items, although to a lesser extent than by the
price of mineral commodities.
Competition
The mining industry is intensely competitive
in all of its phases, and the Company competes with many companies possessing greater financial resources and technical facilities
than itself with respect to the discovery and acquisition of interests in mineral properties, the recruitment and retention of
qualified employees and other persons to carry out its mineral exploration activities. The Company has a large land position in
the Athabasca Basin, and has carried out extensive exploration, but has not defined an economic deposit. CanAlaska relies on the
ongoing support of its JV partners to fund their portion of exploration, however additional funding from the current partners is
uncertain. Competition in the mining industry could adversely affect the Company’s prospects for mineral exploration in the
future.
Foreign Political Risk
The Company’s property interests are
currently located in Canada, Alaska, and New Zealand. Some of the Company’s interests are exposed to various degrees of political,
economic and other risks and uncertainties. The Company’s operations and investments may be affected by local political and
economic developments, including expropriation, nationalization, invalidation of government orders, permits or agreements pertaining
to property rights, political unrest, labour disputes, limitations on repatriation of earnings, limitations on mineral exports,
limitations on foreign ownership, inability to obtain or delays in obtaining necessary mining permits, opposition to mining from
local, environmental or other non-governmental organizations, government participation, royalties, duties, rates of exchange, high
rates of inflation, price controls, exchange controls, currency fluctuations, taxation and changes in laws, regulations or policies
as well as by laws and policies of Canada affecting foreign trade, investment and taxation.
Government Laws, Regulation and Permitting
Mining and exploration activities of the Company
are subject to both domestic and foreign laws and regulations governing prospecting, development, production, taxes, labour standards,
occupational health, mine safety, waste disposal, toxic substances, the environment and other matters. Although the Company believes
that all exploration activities are currently carried out in accordance with all applicable rules and regulations, no assurance
can be given that new rules and regulations will not be enacted or that existing rules and regulations will not be applied in a
manner which could limit or curtail production or development. Amendments to current laws and regulations governing the operations
and activities of the Company or more stringent implementation thereof could have a substantial adverse impact on the Company.
The operations of the Company will require
licenses and permits from various governmental authorities to carry out exploration and development at its projects. In Canada,
the issuance of governmental licenses and permits are increasingly being influenced by land use consultations between the government
and local First Nations communities. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to obtain the necessary licences and
permits on acceptable terms, in a timely manner or at all. Any failure to comply with permits and applicable laws and regulations,
even if inadvertent, could result in the interruption or closure of operations or material fines, penalties or other liabilities.
Title to Properties
Acquisition of rights to the mineral properties
is a very detailed and time-consuming process. Title to, and the area of, mineral properties may be disputed. Although the Company
has investigated the title to all of the properties for which it holds concessions or other mineral leases or licenses or in respect
of which it has a right to earn an interest, the Company cannot give an assurance that title to such properties will not be challenged
or impugned.
The Company has the right to earn an increased
economic interest in certain of its properties. To earn this increased interest, the Company is required to make certain exploration
expenditures and payments of cash and/or Company shares. If the Company fails to make these expenditures and payments, the Company
may lose its right to such properties and forfeit any funds expended up to such time.
Estimates of Mineral Resources
The mineral resource estimates used by the
Company are estimates only and no assurance can be given that any particular level of recovery of minerals will in fact be realized
or that an identified resource will ever qualify as a commercially mineable (or viable) deposit which can be legally or commercially
exploited. In addition, the grade of mineralization ultimately mined may differ from that indicated by drilling results and such
differences could be material.
Key Management
The success of the Company will be largely
dependent upon the performance of its key officers, consultants and employees. Locating mineral deposits depends on a number of
factors, not the least of which is the technical skill of the exploration personnel involved. The success of the Company is largely
dependent on the performance of its key individuals. Failure to retain key individuals or to attract or retain additional key individuals
with necessary skills could have a materially adverse impact upon the Company’s success.
Volatility of Share Price
Market prices for shares of early stage companies
are often volatile. Factors such as announcements of mineral discoveries, financial results, and other factors could have a significant
effect on the price of the Company’s shares and the amount of financing that can be raised by the Company.
Failure to Maintain Adequate Internal Control
Over Financial Reporting
The Company may fail to maintain adequate internal
control over financial reporting pursuant to the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. During the Company’s five most recent
fiscal years, management has documented and tested its internal control procedures in order to satisfy the requirements of Section
404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (“SOX”). SOX requires an annual assessment by management of the effectiveness of the
Company’s internal control over financial reporting and, for its fiscal years 2006 through 2011, SOX required an attestation
report by the Company’s independent auditors addressing the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting. However,
in April 2012 the requirement of auditor attestation was, with respect to “emerging growth companies,” repealed by
the “Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act” (“JOBS Act”). Because the Company is presently an “emerging
growth company” within the meaning of the JOBS Act, it is now exempt from the SOX requirement of auditor attestation regarding
its internal controls over financial reporting. The Company may fail to maintain the adequacy of its internal control over financial
reporting as such standards are modified, supplemented or amended from time to time, and the Company may not be able to conclude,
on an ongoing basis, that it has effective internal control over financial reporting in accordance with Section 404 of SOX. The
Company identified a material weakness over its internal control over financial reporting related to financial reporting as of April 30, 2013 which
has been remediated as of April 30, 2014. The Company’s failure to satisfy the requirements of Section 404 of SOX on an ongoing,
timely basis could result in the loss of investor confidence in the reliability of its financial statements, which in turn could
harm the Company’s business and negatively impact the trading price or the market value of its securities. In addition, any
failure to implement required new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in their implementation, particularly as a
result of reduced staff, could harm the Company’s operating results or cause it to fail to meet its reporting obligations.
If the Company expands, the challenges involved in implementing appropriate internal control over financial reporting will increase
and will require that the Company continues to monitor its internal control over financial reporting. Although the Company intends
to expend time and incur costs, as necessary, to ensure ongoing compliance, it cannot be certain that it will be successful in
complying with Section 404 of SOX.
Foreign Currency Exchange
A small portion of the Company’s expenses
are now, and are expected to continue to be incurred in foreign currencies. The Company’s business will be subject to risks
typical of an international business including, but not limited to, differing tax structures, regulations and restrictions and
general foreign exchange rate volatility. Fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Canadian dollar and such other currencies
may have a material effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations and could result in downward
price pressure for the Company’s products or losses from currency exchange rate fluctuations. The Company does not actively
hedge against foreign currency fluctuations.
Conflict of Interest
Some of the Company’s directors and officers
are directors and officers of other natural resource or mining-related companies. These associations may give rise from time to
time to conflicts of interest. As a result of such conflict, the Company may miss the opportunity to participate in certain transactions.
Mineral Exploration Risks
Mineral exploration activities and, if warranted,
development activities generally involve a high degree of risk, which even a combination of experience, knowledge and careful evaluation
may not be able to overcome. Environmental hazards, industrial accidents, unusual or unexpected geological formations, fires, power
outages, labour disruptions, flooding, explosions, cave-ins, land-slides and the inability to obtain suitable or adequate machinery,
equipment or labour are other risks involved in the operation of mines and the conduct of exploration programs. Operations and
activities in which we have a direct or indirect interest will be subject to all the hazards and risks normally incidental to exploration,
development and production of precious and base metals, any of which could result in work stoppages, damage to or destruction of
mines, if any, and other producing facilities, damage to life and property, environmental damage and possible legal liability for
any or all damage. We may become subject to liability for certain hazards which we cannot insure against or which we may elect
not to insure against because of premium costs or other reasons. The payment of such liabilities may have a material, adverse effect
on our financial position. At the present time, we do not conduct any mining operations and none of our properties are under development,
and, therefore, we do not carry insurance to protect us against certain inherent risks associated with mining. Reclamation requirements
vary depending on the location and the managing regulatory agency, but they are similar in that they aim to minimize long term
effects of exploration and mining disturbance by requiring the operating company to control possible deleterious effluents and
to re-establish to some degree pre-disturbance landforms and vegetation.
We Are An Exploration Stage Company
At present, none of our properties have a qualified
and measured body of ore and all our proposed exploration programs are an exploratory search for ore. We will only develop our
mineral properties if we obtain satisfactory results from our exploration programs. The development of uranium and other mineral
properties is affected by many factors, including the cost of operations, variations in the grade of ore mined, fluctuations in
metal markets, costs of processing equipment and other factors such as government regulations, including regulations relating to
royalties, allowable production, importing and exporting of minerals and environmental protection. We have relied and may continue
to rely upon consultants and others for exploration expertise. Substantial expenditures are required to establish reserves through
drilling, to develop metallurgical processes to extract the metal from the ore and, in the case of new properties, to develop the
mining and processing facilities and infrastructure at any site chosen for mining. We cannot assure you that any mineral deposits
will be discovered in sufficient quantities to justify commercial operations or that funds required for development can be obtained
on a timely basis. Depending on the price of uranium or other minerals produced, if any, we may determine that it is impractical
to commence or, if commenced, continue commercial production.
The marketability of any minerals acquired
or discovered may be affected by numerous factors which are beyond our control and which cannot be accurately predicted, such as
market fluctuations, the global marketing conditions for uranium and other metals, the proximity and capacity of milling facilities,
mineral markets and processing equipment, and such other factors as government regulations,
including regulations relating to royalties, allowable production, importing and exporting minerals and environmental protection.
Canadian and U.S. Reporting of Reserves
Are Different
Our reserve and resource estimates are not
directly comparable to those made in filings subject to SEC reporting and disclosure requirements, as we generally report reserves
and resources in accordance with Canadian practices. These practices are different from those used to report reserve and resource
estimates in reports and other materials filed with the SEC. It is Canadian practice to report measured, indicated and inferred
resources, which are not permitted in disclosure filed with the SEC by United States issuers. In the United States, mineralization
may not be classified as a "reserve" unless the determination has been made that the mineralization could be economically
and legally produced or extracted at the time the reserve determination is made. United States investors are cautioned not to assume
that all or any part of measured or indicated resources will ever be converted into reserves.
Further, "inferred resources" have
a great amount of uncertainty as to their existence and as to whether they can be mined legally or economically. Disclosure of
"contained ounces" is permitted disclosure under Canadian regulations; however, the SEC permits issuers to report "resources"
only as in-place tonnage and grade without reference to unit of metal measures.
Accordingly, information concerning descriptions
of mineralization, reserves and resources contained in this Annual Report, or in the documents incorporated herein by reference,
may not be comparable to information made public by United States companies subject to the reporting and disclosure requirements
of the SEC.
The Company believes
it is likely a "passive foreign investment company" which will likely have adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences
for U.S. shareholders
U.S. shareholders should
be aware that the Company believes it was classified as a passive foreign investment company (“PFIC”) during the tax
year ended April 30, 2014, and may be a PFIC in future tax years. If the Company is a PFIC for any year during a U.S. shareholder’s
holding period, then such U.S. shareholder generally will be required to treat any gain realized upon a disposition of common shares,
or any so-called “excess distribution” received on its common shares, as ordinary income, and to pay an interest charge
on a portion of such gain or distributions, unless the shareholder makes a timely and effective "qualified electing fund"
election (“QEF Election”) or a "mark-to-market" election with respect to the common shares. A U.S. shareholder
who makes a QEF Election generally must report on a current basis its share of the Company's net capital gain and ordinary earnings
for any year in which the Company is a PFIC, whether or not the Company distributes any amounts to its shareholders. However, U.S.
shareholders should be aware that there can be no assurance that the Company will satisfy record keeping requirements that apply
to a qualified electing fund, or that the Company will supply U.S. shareholders with information that such U.S. shareholders require
to report under the QEF Election rules, in the event that the Company is a PFIC and a U.S. shareholder wishes to make a QEF Election.
Thus, U.S. shareholders may not be able to make a QEF Election with respect to their common shares. A U.S. shareholder who makes
the mark-to-market election generally must include as ordinary income each year the excess of the fair market value of the common
shares over the taxpayer’s basis therein. This paragraph is qualified in its entirety by the discussion below under the heading
“Certain United States Federal Income Tax Considerations.” Each U.S. shareholder should consult its own tax advisor
regarding the PFIC rules and the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common
shares.
Estimates of Mineral Resources
The mineral resource estimates used by the
Company are estimates only and no assurance can be given that any particular level of recovery of minerals will in fact be realized
or that an identified resource will ever qualify as a commercially mineable (or viable) deposit which can be legally or commercially
exploited. In addition, the grade of mineralization ultimately mined may differ from that indicated by drilling results and such
differences could be material.
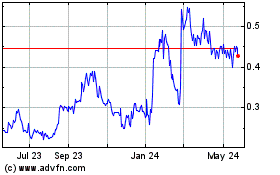
Our Stock Is Thinly Traded
The trading market for our shares is not always
liquid. The market price of our common shares has ranged from a high of $0.28 and a low of $0.09 during the twelve month period
ended April 30, 2014. Although our shares trade on the Toronto Stock Exchange, FINRA Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board and on the
Frankfurt Stock Exchange, the volume of shares traded at any one time can be limited, and, as a result, there may not be a liquid
trading market for our shares.
| ITEM 4. | | INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY |
| A. | | History and Development of the Company |
The Company was incorporated on May 22, 1985
under the laws of the Province of British Columbia, Canada under the name Canadian Gravity Recovery Group Ltd. On June 14, 1985,
the Company changed its name to CanAlaska Resources Ltd. On September 15, 1993, the Company consolidated its share capital on a
four for one basis and changed its name to International CanAlaska Resources Ltd. On October 19, 1999, the Company consolidated
its share capital on a five for one basis and changed its name to CanAlaska Ventures Ltd. The Company was transitioned under the
British Columbia Business Corporations Act on September 24, 2004. The Company changed its name to CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
on October 11, 2006. On November 8, 2010, the Company consolidated its share capital on a ten for one basis. On June 21, 2011,
the Company’s shares were listed for trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange and were de-listed from the TSX Venture Exchange.
On December 27, 2013 the Company’s shares were delisted from trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange and on December 30, 2013
its shares were listed for trading on the TSX Venture Exchange. The registered office is #1020 – 625 Howe Street, Vancouver,
BC, V6C 2T6, Canada. The telephone number is 604-688-3211 the fax number is 604-688-3217. The Company’s host agent in the
United States is Incorp Services Inc., 375 N. Stephanie Street, Suite 1411, Henderson, Nevada 89014-8909, USA.
The Company is an exploration stage company
engaged in the acquisition and exploration of mineral properties, principally in Canada. The Company aims to acquire and advance
its projects to a stage where they can be exploited at a profit or it can arrange joint ventures, whereby other companies provide
funding for development and exploitation. The Company’s principal focus has been exploring for high-grade uranium deposits
in the Athabasca Basin area of Saskatchewan.
The Company has responded to the drop in market
activity and values since the Fukushima nuclear incident by actively marketing its expertise and uranium exploration projects to
industry and end users for project financings or sales. There has been a slow resurgence in interest, and at the end of the fourth
quarter of our 2014 fiscal year, some renewed interest from North American and Chinese industry groups in response to the Canada-China
nuclear accord. Management has continued evaluating its priorities, taking steps to streamline non-discretionary expenditures,
continuing its efforts to raise funds and explore all opportunities to sell and/or joint venture its properties. The recoverability
of the amounts shown for mineral properties and related deferred costs is dependent upon the existence of economically recoverable
mineral reserves, the ability of the Company to obtain the necessary financing to complete the development, and upon future profitable
production or proceeds from disposition of the mineral properties. Due to the difficult market conditions facing junior uranium
exploration companies there is no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising additional financing. From time to time,
the Company will evaluate new properties and direct activities to these based on the Board of Director’s evaluation of financial
and market considerations at the time.
The Company intends to restrict its exploration
activity in the uranium sector until financial markets recover. Management intends to continue its efforts to joint venture or
sell its various uranium assets to reduce ongoing expenditures and strengthen its treasury. The Company has reduced the size of
its operations team to match reduced project funding and market financings.
The Company is in the early stages of exploration
on all of its mineral properties.
The Company generates the majority of its exploration
projects, and in the past has organized and managed technical staff and field crews to carry out project work on its own behalf
and for others. The Company has reduced its overall staff levels, and will continue this path if there is a continued decline in
the ability to support uranium exploration.
The Company can give no estimate of the time
to reach discovery on any of its projects. This is dependent upon the availability of funding, the prospectivity of the projects,
and the successful completion of exploration and drill programs.
As part of its efforts to conserve its cash
position and reduce obligations, between July 13 and July 31, 2012 the Company terminated the management contracts of all of its
senior management team and entered into new management contracts on August 1, 2012. For details of the new management contracts,
see “Executive Compensation” section of this 20-F.
| C. | | Organizational Structure |
CanAlaska Resources Ltd. USA (“CanAlaska
USA”) is a wholly-owned subsidiary incorporated by the Company in the State of Nevada on May 16, 1988 for the purpose of
mineral exploration in Alaska. The Company’s registered agent in the State of Nevada is Incorp. Services Inc., 2360 Corporate
Circle – Suite 400, Henderson, Nevada 89074-7722 USA.
In May 2014, Golden Fern Resources Limited,
the Company's wholly owned subsidiary in New Zealand, began liquidation proceedings. The New Zealand subsidiary is being liquidated
after the sale of the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. and there are no significant assets or liabilities remaining in
the entity.
CanAlaska West McArthur Uranium Ltd. (“CWMU”)
is a wholly-owned subsidiary that was incorporated under the Business Corporations Act of British Columbia on March 15,
2007. CWMU acts as the operator for the 50/50 West McArthur Joint Venture Project located in the Athabasca basin Saskatchewan,
Canada, with MC Resources Canada Ltd., (a division of Mitsubishi Development PTY Ltd.) and the Company.
Canada-Korea Uranium Limited Partnership (“CKULP”)
was registered under the Partnership Act (Section 51) on December 14, 2007, for the partners to carry out uranium exploration
and development of the Cree East Property located in the Athabasca basin, Saskatchewan, Canada. The partners include a consortium
of four Korean entities consisting of Hanwha Resources (Canada) Ltd., Kores Canada Corp., Kepco Canada Energy Ltd., SK Networks
Co., Ltd., (together referred to the “Consortium” (50%)) and the Company (50%).
CanAlaska Korea Uranium Limited (“CKUL”)
was incorporated on July 4, 2007 under the Business Corporations Act of British Columbia to act as General Partner of the
Canada-Korea Uranium Limited Partnership for the purpose of exploring the Cree East Joint Venture Property located in the Athabasca
basin, Saskatchewan, Canada. CKUL is held 50% by the Consortium members and 50% by the Company.
Poplar Uranium Limited is a wholly owned subsidiary
that was incorporated under the Business Corporations Act of British Columbia on August 22, 2007.
| D. | | Property, Plants and Equipment |
Overview
The Company currently has 18 projects within
the Athabasca basin area and has carried out exploration programs on four of these in the past year. In fiscal 2014, the Company
spent $0.3 million ($0.5 million net of $0.2 million from reimbursements from partners) on exploration costs in the Athabasca Basin
area. The two largest exploration projects were at West McArthur and at Cree East.
Exploration spending in the fourth quarter
of 2014 is significantly down from the same comparative quarter of 2013, as the Company has reduced its exploration spend to conserve
cash relative to the prior period. In the fourth quarter, the Company historically spent this time drilling in the winter season
in the Athabasca Basin at our various projects.
The following table summarizes the Company’s
expenditures for twelve months ended April 30, 2014.
|
($000's)
Total Exploration |
Cree East |
West McArthur |
Fond Du Lac |
NW Manitoba |
Other Athabasca Basin Projects |
New Zealand |
Other and Generative Projects |
Total |
| Camp Cost & Operations |
(12) |
- |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(8) |
| Drilling |
27 |
- |
6 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
34 |
| General & Admin |
26 |
36 |
1 |
11 |
14 |
25 |
55 |
168 |
| Geochemistry |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
1 |
| Geology |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
8 |
- |
- |
9 |
| Geophysics |
151 |
- |
- |
- |
32 |
- |
- |
183 |
| Other |
28 |
2 |
- |
76 |
3 |
- |
(12) |
97 |
| Gross Expenditures |
221 |
38 |
11 |
87 |
58 |
25 |
44 |
484 |
| Reimbursements |
(111) |
(19) |
- |
(83) |
- |
- |
- |
(213) |
| Net Expenditures |
110 |
19 |
11 |
4 |
58 |
25 |
44 |
271 |
The following section contains a comparative
breakdown of project expenditures for the Company’s significant projects. Reimbursements represents the amounts received
from our joint venture partners and option partners to be applied against the expenditures for the project.
| (i) | | West McArthur Project, Saskatchewan – Mitsubishi |
The West McArthur project in the Athabasca
Basin, Saskatchewan, was optioned in April 2007 to Mitsubishi Development Pty Ltd., a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Corporation of Japan.
Under the option agreement, Mitsubishi could exercise an option to earn a 50% interest in the property by investing $11.0 million.
In February 2010, Mitsubishi exercised its option with a payment to the Company and an unincorporated 50/50 joint venture was formed
between the parties to pursue further exploration and development of the property. As at April 30, 2014, the Company holds a 50%
interest in the West McArthur project. Mitsubishi holds the remaining 50% interest in the property. The Company acts as project
operator under the supervision and guidance of Dr. Karl Schimann, P. Geo. and Mr. Peter Dasler, P. Geo. and earns a fee between
5% and 10%, based on expenditures incurred. Included within Other expenses are management fees charged to and reimbursed by Mitsubishi
for CanAlaska acting as the project operator.
| ($000's) |
Quarterly |
Year Ended |
|
| West McArthur Project |
Q113 |
Q213 |
Q313 |
Q413 |
Q114 |
Q214 |
Q314 |
Q414 |
Apr-13 |
Apr-14 |
LTD |
| Camp Cost & Operations |
- |
- |
- |
(8) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(8) |
- |
2,976 |
| Drilling |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
6,745 |
| General & Admin |
31 |
26 |
12 |
8 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
11 |
77 |
35 |
2,132 |
| Geochemistry |
15 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
16 |
- |
339 |
| Geology |
48 |
16 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
65 |
- |
1,000 |
| Geophysics |
211 |
12 |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
227 |
- |
5,775 |
| Other |
20 |
3 |
6 |
- |
1 |
2 |
- |
- |
29 |
3 |
677 |
| Gross Expenditures |
325 |
58 |
23 |
- |
7 |
10 |
10 |
11 |
406 |
38 |
19,644 |
| Reimbursement |
(171) |
(30) |
(12) |
- |
(4) |
(5) |
(5) |
(6) |
(213) |
(19) |
(14,227) |
| Net Expenditures |
154 |
28 |
11 |
- |
3 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
193 |
19 |
5,417 |
The West McArthur project is located between
6 and 30 kilometres west of the producing McArthur River uranium mine operated by Cameco Corp, and covers approximately 36,000
hectares. On the property there is evidence of hydrothermal alteration extending well into the sandstone, matching the typical
alteration model of Athabasca unconformity style uranium deposits. There is evidence of uranium mineralization from drill testing
in multiple areas, either as enrichment at the unconformity or in basement stringers. The most compelling features for further
exploration are the uranium values in sandstone higher in the stratigraphy, the hematized and broken rock in the sandstone, and
the pattern of basement offsets and geophysical conductivity.
The project is accessible during the winter
drill season by seasonal winter ice roads and winter trails and during the summer exploration season by air and water. There is
no physical plant or permanent infrastructure on the property and no source of power. There are multiple extensive lakes which
can provide a source of water for the project.
The mineral rights for West McArthur were acquired
between October 2004 and February 2009 from the Ministry of Energy and Resources in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. The claim
numbers are as follows, S-107561, S-107562, S-107563, S-107565, S-107773, S-108010, S-108011, S-108012, S-111412 S-111413, S-111511
and S-111512. The mineral rights to West McArthur are valid and in good standing with the earliest claim requiring renewal in October
2029 with no further exploration expenditures required. An annual assessment report is required to be filed by the Company with
the Ministry of Energy and Resources to disclose the exploration activities on this claim. There is no fee for filing the annual
assessment report.
In April 2012, the Company announced a preliminary
summary of drilling at its West McArthur project. Seven diamond drill holes were completed in February and March 2012, to test
a series of individual zones where the resistivity lows were coincident with the EM conductors within the Grid 5 area. Total meterage
drilled in the season was 6,422 metres, including one abandoned drill hole. The winter 2012 drill programme has demonstrated on
Grid 5 the presence of requisite geological environment for unconformity uranium deposits. Significant faulting and fracturing
are present in a number of drill holes, with individual radioactive spikes or elevated radioactivity in zones of hydrothermal alteration.
In June 2012, the Company reported the results
of drill core geochemistry on the West McArthur property. Drill holes WMA028 and WMA034 produced very positive results for uranium.
Both intersected parts of a highly-altered graphitic pelite unit and are thought to be within 50 metres of the targeted conductor,
which was identified from the down-hole geophysical surveys. The targets generated
at the eastern end of Grid 5 matched and extended a historical conductor, which was drill-tested by Uranerz in 1989. Neither of
the two historical drill holes intersected their targeted basement conductor, but, significantly, contained dravite clay and pyrite
along with narrow, steep, clay rich fault gouges/breccia in the top 350-400 metres of the sandstone column. In one historical hole,
the upper 400 metres of sandstone showed anomalous uranium and trace elements. Drill holes WMA028 and WMA034 are located in this
area. Both show deep alteration into the basement rocks, indicating and confirming a substantial hydrothermal alteration system.
The potential of this project is for unconformity
style uranium mineralization of both the Simple (Low REE, basement hosted) and the Complex ( High REE, Sandstone hosted) types
of uranium. Previous exploration was hampered by the depths to the basement, however, recent advances with airborne geophysical
survey technology has enabled penetration to those depths. Multiple exploration programs since 2005 have identified targets with
strong geophysical feature, similar to those near existing uranium mines. Limited drill testing in several of these areas have
shown the basement offsets, hydrothermal clay alteration, and elevated uranium geochemistry consistent with the Athabasca unconformity
deposit model. The project, has four target areas which are being evaluated for further drill testing.
The property has undergone a series of exploration
programs, including extensive geophysics and drilling of over 35 drill holes since 2005. Approximately $19.6 million has been spent
by the joint venture.
The next drill programs are dependent on financing.
The project does not have a drill program planned for 2014. Active full season programs of 6-9 drill holes are generally budgeted
at $3 to $4 million, including drill geophysics, camp and logistics. The project currently has a maintenance budget of approximately
$100,000 for 2014 which will be funded 50% by CanAlaska and 50% by Mitsubishi.
As at April 30, 2014, the total exploration
costs incurred for the West McArthur project was $19.6 million. Further exploration expenditures for this project have been deferred
in 2013/2014 to await better capital market conditions in order to raise exploration funds. The West McArthur property is without
known reserves and any proposed program is exploratory in nature.

| (ii) | | Cree East Project, Saskatchewan – Korean Consortium |
The Cree East project is located in the south-eastern
portion of the Athabasca Basin, 35 kilometres west of the formerly producing Key Lake mine and 5 to 22 kilometres north of the
south rim of the Athabasca Basin. The project is comprised of 17 contiguous mineral claims totalling approximately 58,000 hectares.
In December 2007 a Korean Consortium (Hanwha Corp., Korea Electric Power Corp., Korea Resources Corp. and SK Networks Co. Ltd.),
agreed to spend $19.0 million on the properties to earn into a 50% interest in the Cree East project.
As
of April 30, 2014, the Korean Consortium has contributed its $19.0 million towards exploration of the project and holds a 50% ownership
interest in both CanAlaska Korea Uranium Ltd. and the Canada-Korea Uranium Limited Partnership. The remaining 50% interest is held
by CanAlaska. The following table summarizes the Korean Consortium
expenditures and advances by quarter and life to date (“LTD”) on the project. The table does not include a $1.0 million
payment made directly to CanAlaska in 2007 ($0.6 million) and 2010 ($0.4 million) for intellectual property associated with the
project. As at April 30, 2014, the Company is holding approximately $176,000 of joint venture funds.
| ($000's) |
Quarterly |
Year Ended |
|
| Cree East Project |
Q113 |
Q213 |
Q313 |
Q413 |
Q114 |
Q214 |
Q314 |
Q414 |
Apr-13 |
Apr-14 |
LTD |
| Camp Cost & Operations |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
(13) |
- |
4 |
(12) |
3,332 |
| Drilling |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
27 |
- |
- |
- |
27 |
6,740 |
| General & Admin |
5 |
- |
14 |
18 |
- |
13 |
5 |
9 |
37 |
26 |
502 |
| Geochemistry |
5 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
6 |
- |
537 |
| Geology |
49 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
73 |
1 |
1,583 |
| Geophysics |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
151 |
2 |
151 |
3,410 |
| Management Fees |
10 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
1 |
4 |
- |
17 |
20 |
22 |
1,574 |
| Other |
30 |
4 |
5 |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
7 |
42 |
7 |
1,471 |
| Net Expenditures |
104 |
8 |
25 |
47 |
1 |
46 |
(8) |
184 |
184 |
222 |
19,149 |
The project is accessible during the winter
drill season by seasonal winter ice roads and winter trails and during the summer exploration season by air and water. There is
no physical plant or permanent infrastructure on the property and no source of power. There are multiple extensive lakes which
can provide a source of water for the project.
The mineral rights for Cree East were acquired
between November 2004 and June 2010 from the Ministry of Energy and Resources in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. The claim
numbers are as follows, S-107757, S-107774, S-107775, S-107776, S-107777, S-107778, S-107779, S-107780, S-108357, S-108358, S-108382,
S-108383, S-108384, S-108385, S-108386, S-108387 and S-111809. The mineral rights to Cree East are valid and in good standing with
the earliest claim requiring renewal in November 2020 with no further exploration expenditures required. An annual assessment report
is required to be filed by the Company with the Ministry of Energy and Resources to disclose the exploration activities on this
claim. There is no fee for filing the annual assessment report.
The project area covers Athabasca group conglomerates
and sandstones. Sandstone unconformity overlies basement at depths in the order of 200 to 300 metres in the south. Structural breaks
which trend across the across the property further drop the basement to estimated depths of 800 to 900 metres across the northern
edge of the property The basement is composed of the Lower Proterozoic, (Trans Hudson) Mudjatik domain, granitoids and associated
minor supercrustals (psammites, pelites and metavolcanics) A significant portion of the property is considered to be underlain
by rocks of the highly prospective Wollaston Domain.
In May 2012, the Company reported receipt of
uranium assay results and trace element geochemistry for the winter drill program on the Cree East project. The results confirm
the anomalous multi-element enrichments in the large alteration zone identified at Zone B and additional gold and uranium mineralization
in drill hole CRE080, which intersected mineralized iron formation at Zone J.
The property has undergone extensive exploration
since 2005 with $19.1 million expended on surveys, extensive geophysical testing and over 70 drill holes testing targets.
The potential of this project is for unconformity
style uranium mineralization of both the Simple (Low REE, basement hosted) and the Complex (High REE, Sandstone hosted) types of
uranium. The area has numerous conductors and faults which act as both the conduit and the trap for potential uranium mineralization.
A number of structures and conductive targets have been identified from the Company's exploration efforts. The next substantial
work programs on the property will consist mainly of drill testing the current targets. Active full season programs of 15-18 drill
holes are generally budgeted at $3 to $4 million, including drill geophysics, camp and logistics. There is a program of geophysics
to be performed by an external third party for winter field season 2014, budgeted at $350,000 which will be funded by the joint
venture funds held. A $3 million summer drill program has been approved, subject to financing.
Under the Cree East agreement, CanAlaska is
entitled to charge an operator fee of 10% to recoup its indirect costs associated with the project, which the Company recognizes
as management fees. CanAlaska acts as project operator under the supervision and guidance of Dr. Karl Schimann, P. Geo. and Mr.
Peter Dasler, P. Geo.
As at April 30, 2014, the total exploration
costs incurred for the Cree East project was $19.1 million. In March 2014 the Joint Venture carried out geophysical surveys over
the Zone B target area. This surveying was in preparation for a proposed summer drill program. The summer drill program is dependent
upon financing by CanAlaska or others. The Korean Consortium and CanAlaska are actively marketing the Cree East project for option
or joint venture to allow for the continuation of the drill exploration. Work permits are in place for summer 2014 drilling. The
Cree East property is without known reserves and any proposed program is exploratory in nature.

| (iii) | | NW Manitoba, Manitoba |
This property consists of approximately 144,000
hectares and lies between 90 and 170 kilometres northeast along the Wollaston trend of basement formations hosting uranium deposits,
which include Rabbit Lake, Collins Bay and Eagle Point Uranium mines. In May 2012, the Company reported strong geophysical responses
matching geology and uranium mineralized boulders from the recent surveys within the target areas at its NW Manitoba uranium project.
The project was re-started in March 2012 following a four and a half year permitting delay due to consultations between the government
of Manitoba and the local community. The Company has now concluded an operating MOU with the local community and recommenced ground
survey work. The ground resistivity gravity geophysical surveys carried out in March 2012 localized anomalous features typical
of sulphide-bearing mineralization, and zones of clay alteration within areas of shallow overburden. There is a striking correspondence
between the location of gravity anomalies and the low resistivity zones from the survey. These targets
are similar in style to the Andrew Lake uranium project in Nunavut, which has similar resistivity and gravity geophysical responses
related to uranium mineralization hosted in regional fault structures.
In September 2013, the Company entered
into an option agreement with NEX-listed MPVC Inc. ("MPVC") for an interest in the NW Manitoba project. MPVC may earn
an 80% interest in the project by carrying out a three stage $11.6 million exploration program, making a cash payment of $35,000,
issuing 12 million common shares and issuing 6 million common share purchase warrants.
On February 28, 2014, the option
agreement with MPVC for the NW Manitoba project was amended to extend the date of certain provisions of the agreement from February
28, 2014 to March 14, 2014. In consideration for amending the option agreement, MPVC paid a further non-refundable cash deposit
in the amount of $50,000 on March 14, 2014.
In April 2014, the Company announced
that MPVC Inc. had received highly anomalous radon results of a recently completed, land-based survey over the Maguire Lake area.
MPVC reports that its geologic team is most encouraged by the distribution of radon, resistivity, magnetic and gravity anomalies
which are prime drill targets for uranium mineralization.
In Q114 and Q214, the Company recognized
an impairment on certain of its Grease River claims of approximately $57,000 as it did not renew its permits on these claims.
During fiscal 2014, the Company recognized
an impairment on certain of its Poplar claims of approximately $35,000 as it did not renew its permits on these claims.
In Q114 and Q414, the Company recognized an
impairment on certain of its Lake Athabasca claims of approximately $20,000 as it did not renew its permits on these claims.
In Q114, the Company recognized an impairment
on its Hodgson claim of approximately $109,000 as it did not renew its permits on this property. In Q314, the Company re-staked
certain claim blocks for $6,895.
In June 2013, the Collins Bay Extension option
agreement dated July 4, 2009 and amended on March 29, 2011 with Bayswater Uranium Corporation ("Bayswater") was amended
whereby the option period was extended from six years to eight years. In consideration for the extension, the Company accelerated
its staged common share issuances and issued 10,000 common share on July 12, 2013. As a result, in July 2013, the Company issued
an aggregate of 20,000 common shares under the amended option agreement for the Collins Bay Extension project.
In January 2014, the Company recognized an
impairment on its Carswell claim of approximately $136,000 as it did not renew its permits on this property.
In January 2013, the Company acquired three
block of claims, totalling 6,687 hectares located in the Patterson Lake area of the western Athabasca basin. In August 2013, the
Company optioned the claims to Makena Resources Inc ("Makena"). Makena may earn a 50% interest in the property by making
cash payments totalling $100,000 by June 1, 2015, issuing 2,500,000 common share by June 1, 2015 and incurring exploration expenditures
totalling $1.4 million by September 30, 2016.
In September 2012, Atlantic Industrial Minerals
Inc. (“Atlantic”) entered into an option agreement to acquire a 100% interest in the Reefton project, in South Island,
New Zealand by paying $300,000 in staged payments, issuing 300,000 shares of Atlantic to the Company and reimbursing the Company
for the annual permit fees for the property from 2012 to 2015 which are approximately $50,000 per year, and drilling 1,500 metres
by December 31, 2014. In September 2012 and October 2012, the Company received $50,000 from Atlantic for the 2012/2013 annual permit
fee as part of an operating agreement. On August 21, 2013, the option agreement with Atlantic was terminated.
In March 2014, the Company entered
into a purchase agreement to sell the exploration permit for the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. ("Stevenson")
for aggregate purchase consideration of $20,000. In Q414, the Company recognized a loss on disposal of the Reefton project of approximately
$4,000.
The Company has two claim blocks (Big Creek
and Quesnel). Big Creek was under option, but in July 2013, the option agreement with Discovery Ventures Ltd. and Tyrone Docherty
was terminated. The property is currently being marketed for sale or option.
In July, August and November 2013, the Company
staked the Hanson project which consists of fourteen blocks of claims in the area of the Pikoo kimberlite discovery, totalling
17,272 hectares located in Saskatchewan for $10,374.
In January 2014, the Company entered into a
purchase agreement for two claim blocks in the Hanson project to Copper Reef Mining Corp. ("Copper Reef") for aggregate
purchase consideration of $50,000 in cash and the issuance of 1,000,000 common shares in the capital of Copper Reef and completion
of $50,000 of exploration expenditures. The Company retains a 2% net smelter royalty in the agreement.
In April 2014, the Company announced that it
had entered into a binding agreement to sell its interest in its Kasmere South project in northwestern Manitoba to private company,
East Resources Ltd. for an aggregate cash payment totalling $1.8 million. On March 28, 2014, the Company received a non-refundable
cash payment of $200,000 from East Resources Ltd. Subsequent to year end, the Company also received the remaining cash instalments
of $100,000 and $1.5 million on May 30, 2014 and June 26, 2014 respectively.
The Company uses its technical staff between
field seasons to evaluate other mineral projects for acquisition, either by staking or by option, with the purpose of sale to third
parties. For a full description of the geology and setting of the current projects and of the Company’s other projects, reference
should be made to the “Projects” section, and accompanying news releases of work on the Company’s website at
www.canalaska.com.
| Other projects update |
Status |
Recent work undertaken |
| BC Copper |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Collins Bay Extension |
Option with Bayswater Uranium |
No significant work undertaken |
| Grease River |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Hanson |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Helmer |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Hodgson |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Kasmere |
Under application |
Exploration permits pending |
| Key |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Lake Athabasca |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| McTavish |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Moon |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Patterson |
Option with Makena Resources Inc. |
Airborne surveys have been contracted |
| Poplar |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Waterbury |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Rainbow Hill AK |
Seeking Venture partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Zeballos |
Seeking Venture Partner |
Consolidating ownership |
| Glitter Lake |
Disposed, NSR retained |
|
| Reefton Property, NZ |
Sale to Stevenson Mining Ltd. |
|
The Company is restricting its exploration
activities on these Other projects until financial markets recover. The Company intends to continue its efforts to seek a venture
partner either through a joint venture or sales of its other projects.
In fiscal 2014, the Company recognized an impairment
on its Grease River, Poplar, Lake Athabasca, Hodgson and Carswell claims for approximately $357,000 as it did not renew certain
of its claims on these properties.
In May 2014, Golden Fern Resources Limited,
the Company's wholly owned subsidiary in New Zealand, began liquidation proceedings. The New Zealand subsidiary is being liquidated
after the sale of the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. and there are no significant assets or liabilities remaining in
the entity.
CanAlaska maintains 12 other projects
in the Athabasca basin; one project in Alaska and four projects in British Columbia. These other projects have value to the Company
but are not being actively explored, other than reviews and reporting. A number of these projects are being marketed for sale or
joint venture, and the company hopes to realize increased value in the future.
All of the samples from the CanAlaska exploration
programs have been submitted to one of two qualified Canadian Laboratories for analysis. Samples submitted to Saskatchewan Research
Laboratories were analyzed for multi-element geochemistry and including uranium by tri-acid digestion and ICP. Samples submitted
for assay for trace element geochemistry to Acme Laboratories in Vancouver BC, were analyzed by aqua regia digestion and ICP analysis.
The samples were collected by CanAlaska field geologists under the supervision of Dr. Karl Schimann, and were shipped in secure
containment to the laboratories noted above.
Our exploration activities requires permitting
in the Province of Saskatchewan. For our projects in Saskatchewan, the Company applies for surface exploration permits from the
Ministry of Environment, a letter of advice from the Heritage Resources Branch of the Ministry of Tourism, Parks, Culture and Sport,
and a Right to Use Water from the Saskatchewan Water Authority. For our exploration projects in the Province of Manitoba, the Company
applies for a Prospecting License, a Work Permit from the Manitoba Department of Conservation, and a notification to the Director
of Mines for airborne surveys. In addition, all exploration activities have to conform to the Fisheries Act in terms of protection
of fish habitat.
Project Expenditure Summary
Details of life to date (“LTD”)
exploration and evaluation expenditures:
| ($000’s) |
2014 Fiscal Expenditures |
Life to Date - April 30, 2014 |
| Project |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net YTD |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net LTD |
| Athabasca Basin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cree East |
- |
223 |
- |
223 |
- |
19,150 |
- |
19,150 |
| West McArthur |
- |
37 |
(19) |
18 |
65 |
19,578 |
(14,227) |
5,416 |
| Fond Du Lac |
- |
11 |
- |
11 |
120 |
4,427 |
- |
4,547 |
| NW Manitoba |
- |
3 |
- |
3 |
16 |
7,311 |
- |
7,327 |
| Poplar |
- |
- |
(35) |
(35) |
166 |
3,637 |
(3,245) |
558 |
| Grease River |
- |
1 |
(57) |
(56) |
133 |
3,495 |
(2,907) |
721 |
| Key Lake |
- |
- |
- |
- |
24 |
1,027 |
(1,047) |
4 |
| Helmer |
- |
1 |
- |
1 |
107 |
5,047 |
- |
5,154 |
| Lake Athabasca |
- |
- |
(20) |
(20) |
118 |
5,966 |
(20) |
6,064 |
| Hodgson |
7 |
- |
(109) |
(102) |
116 |
1,561 |
(109) |
1,568 |
| Collins Bay |
- |
10 |
- |
10 |
- |
1,319 |
- |
1,319 |
| McTavish |
- |
- |
- |
- |
74 |
687 |
(108) |
653 |
| Ruttan |
- |
33 |
- |
33 |
15 |
67 |
- |
82 |
| Carswell |
- |
1 |
(137) |
(136) |
137 |
754 |
(137) |
754 |
| Other |
0 |
1 |
- |
1 |
57 |
2,568 |
(1,616) |
1,009 |
| New Zealand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Reefton, NZ |
- |
25 |
(24) |
1 |
24 |
811 |
(505) |
330 |
| Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Projects, Various |
12 |
17 |
- |
29 |
86 |
692 |
(425) |
353 |
| Total |
19 |
363 |
(401) |
(19) |
1,258 |
78,097 |
(24,346) |
55,009 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ($000’s) |
2013 Fiscal Expenditures |
Life to Date - April 30, 2013 |
| Project |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net YTD |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net LTD |
|
| Athabasca Basin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cree East |
- |
184 |
- |
184 |
- |
18,927 |
- |
18,927 |
|
| West McArthur |
- |
406 |
(213) |
193 |
65 |
19,541 |
(14,208) |
5,398 |
|
| Poplar |
- |
- |
- |
- |
166 |
3,637 |
(3,210) |
593 |
|
| Fond Du Lac |
- |
17 |
- |
17 |
120 |
4,415 |
- |
4,535 |
|
| Grease River |
- |
- |
- |
- |
133 |
3,494 |
(2,850) |
777 |
|
| Cree West |
- |
- |
(48) |
(48) |
- |
1,112 |
(1,112) |
- |
|
| Key Lake |
- |
- |
- |
- |
24 |
1,027 |
(1,047) |
4 |
|
| NW Manitoba |
- |
36 |
- |
36 |
16 |
7,308 |
- |
7,324 |
|
| Helmer |
- |
14 |
- |
14 |
107 |
5,046 |
- |
5,153 |
|
| Lake Athabasca |
- |
- |
- |
- |
118 |
5,966 |
- |
6,084 |
|
| Alberta |
- |
2 |
(11) |
(9) |
- |
2,331 |
- |
2,331 |
|
| Hodgson |
- |
81 |
- |
81 |
109 |
1,561 |
- |
1,670 |
|
| Arnold |
- |
- |
(35) |
(35) |
- |
1,341 |
- |
1,341 |
|
| Collins Bay |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1,309 |
- |
1,309 |
|
| McTavish |
- |
4 |
- |
4 |
74 |
687 |
(108) |
653 |
|
| Carswell |
- |
23 |
(37) |
(14) |
136 |
753 |
- |
889 |
|
| Ruttan |
15 |
32 |
- |
47 |
15 |
34 |
- |
49 |
|
| Other |
4 |
2 |
- |
6 |
57 |
2,870 |
(1,919) |
1,008 |
|
| New Zealand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Reefton, NZ |
- |
6 |
- |
6 |
24 |
786 |
(481) |
329 |
|
| Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Projects, Various |
1 |
194 |
(82) |
113 |
74 |
675 |
(425) |
324 |
|
| Total |
20 |
1,001 |
(426) |
595 |
1,238 |
82,820 |
(25,360) |
58,698 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITEM 4A | | - UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
| ITEM 5. | | OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS |
This discussion should be read in conjunction
with the consolidated financial statements of the Company for the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014 and the Management Discussion
and Analysis dated August 7, 2014 as filed herewith.
Significant Accounting Policies
The complete list of the Company’s
significant accounting policies are set out in Note 3 of the consolidated financial statements for the year ended April 30, 2014,
filed herewith.
Financial assets and liabilities
Financial assets held are cash and cash equivalents,
trade and other receivables and available-for-sale securities. Financial liabilities are trade and other payables.
These are classified into the following specified
categories: available-for-sale (“AFS”) financial assets, loans and receivables and other liabilities. The classification
depends on the nature and purpose of the financial assets and is determined at the time of initial recognition. Available-for-sale
securities held by the Company that are traded in an active market are classified as being AFS and are stated at fair value. Gains
and losses arising from changes in fair value are recognized directly in other comprehensive income ("OCI”) in the investments
revaluation reserve with the exception of significant or prolonged losses which are
recognized in profit or loss. Where the investment is disposed of or is determined to be impaired, the cumulative gain or loss
previously recognized in the investments revaluation reserve is included in the consolidated statement of net loss and comprehensive
loss for the period.
The fair value of AFS monetary assets denominated
in a foreign currency is determined in that foreign currency and translated at the spot rate at the financial position reporting
date. The change in fair value attributable to translation differences that result from a change in amortized cost of the asset
is recognized in profit or loss. Trade and other receivables that have fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an
active market are classified as loans and receivables. Loans and receivables are measured at amortized cost using the effective
interest method, less any impairment. Interest income is recognized by applying the effective interest rate, except for short-term
receivables when the recognition of interest would be immaterial. Other financial liabilities are measured at amortized cost.
The Company has classified its financial instruments as follows:
| Cash and cash equivalents |
Loans and receivables |
| Available-for-sale securities |
Available-for-sale |
| Trade and other receivables |
Loans and receivables |
| Trade and other payables |
Other financial liabilities |
Financial instruments recorded at fair
value on the consolidated statement of financial position are classified using a fair value hierarchy that reflects the significance
of the inputs used in making the measurements. The fair value hierarchy has the following levels:
- Level 1 - valuation based on quoted prices
(unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities;
- Level 2 - valuation techniques based on
inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e. as prices)
or indirectly (i.e. derived from prices);
- Level 3 - valuation techniques using inputs
for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs).
The Company’s available for
sale investments are classified as Level 1 financial instruments. There have been no transfers between fair value levels during
the reporting period.
| | Exploration and evaluation expenditures |
Exploration and evaluation expenditure include
the costs of acquiring licenses, costs associated with exploration and evaluation activity, and the fair value (at acquisition
date) of exploration and evaluation assets acquired in a business combination. Exploration and evaluation expenditures are expensed
as incurred as mineral property expenditures. Costs incurred before the Company has obtained the legal rights to explore an area
are recognized in the statement of comprehensive loss.
Acquisition costs are capitalized to the extent
that these costs can be related directly to the acquisition of a specific area of interest where it is considered likely to be
recoverable by future exploitation or sale.
Once the technical feasibility and commercial
viability of the extraction of mineral resources in an area of interest are demonstrable, exploration and evaluation assets attributable
to that area of interest are first tested for impairment and then reclassified to mining property and development assets within
property and equipment. Subsequent costs are capitalized to the respective mineral property interests.
Recoverability of the carrying amount of the
exploration and evaluation assets is dependent on successful development and commercial exploitation, or alternatively, sale of
the respective areas of interest.
The Company is in
the exploration stage with respect to its investment in mineral properties and accordingly follows the practice of expensing all
costs relating to exploration for and development of mineral claims and crediting all proceeds received for option or farm-out
arrangements or recovery of costs against the mineral expenditures.
Option payments made
by an interested acquirer are recorded as a reduction of the value of the asset, with any excess over the carrying value of the
asset recorded into income.
| | Impairment of financial assets |
Financial assets are assessed for indicators
of impairment at each financial position reporting date. Financial assets are impaired where there is objective evidence that,
as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition of the financial asset, the estimated future cash
flows of the investment have been impacted. For unlisted shares classified as AFS, a significant or prolonged decline in the fair
value of the security below its cost is considered to be objective evidence of impairment. For all other financial assets objective
evidence of impairment could include:
- significant financial difficulty of the issuer
or counterparty; or
- default or delinquency in interest or principal
payments; or
- it becoming probable that the borrower will
enter bankruptcy or financial re-organization.
For certain categories of financial assets,
such as trade and other receivables, assets that are assessed not to be impaired individually are subsequently assessed for impairment
on a collective basis. The carrying amount of the financial asset is reduced by the impairment loss directly for all financial
assets with the exception of accounts receivable, where the carrying amount is reduced through the use of an allowance account.
When an accounts receivable is considered uncollectible, it is written off against the allowance account. Subsequent recoveries
of amounts previously written off are credited against the allowance account. Changes in the carrying amount of the allowance account
are recognized in the consolidated statement of net loss and comprehensive loss. With the exception of AFS equity instruments,
if, in a subsequent period, the amount of the impairment loss decreases and the decrease can be related objectively to an event
occurring after the impairment was recognized, the previously recognized impairment loss is reversed through profit or loss to
the extent that the carrying amount of the investment at the date the impairment is reversed does not exceed what the amortized
cost would have been had the impairment not been recognized. In respect of AFS equity securities, impairment losses previously
recognized through profit or loss are not reversed through profit or loss. Any increase in fair value subsequent to an impairment
loss is recognized directly in equity.
| | Impairment of non-financial assets |
At each reporting date, the carrying amounts
of the Company’s non-financial assets are reviewed to determine whether there is any indication that those assets are impaired.
If any such indication exists, the recoverable amount of the asset is estimated in order to determine the extent of the impairment,
if any. The recoverable amount is the higher of fair value less costs to sell and value in use. Fair value is determined as the
amount that would be obtained from the sale of the asset in an arm’s length transaction between knowledgeable and willing
parties. In assessing value in use, the estimated future cash flows are discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount
rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset. If the recoverable
amount of an asset is estimated to be less than its carrying amount, the carrying amount of the asset is reduced to its recoverable
amount and the impairment loss is recognized in the profit or loss for the period. For the purposes of impairment testing, exploration
and evaluation assets are allocated to cash-generating units to which the exploration activity relates, generally by mineral property
interests. For an asset that does not generate largely independent cash inflows, the recoverable amount is determined for the cash
generating unit to which the asset belongs. For exploration and evaluation assets, indication of impairment includes but is not
limited to expiration of the rights to explore, substantive expenditure in the specific area is neither budgeted or planned, and
if the entity has decided to discontinue exploration activity in the specified area.
Where an impairment loss subsequently reverses,
the carrying amount of the asset (or cash-generating unit) is increased to the revised estimate of its recoverable amount, but
so that the increased carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined had no impairment loss
been recognized for the asset (or cash-generating unit) in prior years. A reversal of an impairment loss is recognized immediately
in profit or loss.
Management considers both external and internal
sources of information in assessing whether there are any indications that the Company’s non-financial assets are impaired.
External sources of information management considers include changes in market, economic and legal environment in which the Company
operates that are not within its control and affect the recoverable amount of its non-financial assets. Internal sources of information
management consider include the manner in which non-financial assets are being used or are expected to be used and indications
of economic performance of the assets.
Decommissioning liabilities
Obligations associated with the
decommissioning of tangible non-current assets are recorded as provisions when those obligations are incurred, with the amount
of the liability initially measured at management’s best estimates. These obligations are capitalized in the accounts of
the related non-current assets and are amortized over the useful lives of the related assets. It is possible that the Company's
estimates of its ultimate decommissioning liabilities could change as a result of changes in regulations, the extent of environmental
remediation required and the means of reclamation or costs estimates. Changes in estimates
are accounted for prospectively from the period these estimates are revised. There are no decommissioning liabilities obligations
as at April 30, 2014 and April 30, 2013.
Income taxes
Income tax expense consists of current and
deferred tax expense. Income tax is recognized in the consolidated statement of net loss and comprehensive loss except to the extent
it relates to items recognized directly in equity, in which case the related taxes are recognized in equity.
Current tax expense is the expected tax payable
on the taxable income for the year, using tax rates substantially enacted at period end, adjusted for amendments to tax payable
with regards to previous years.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized
for deferred tax consequences attributable to unused tax loss carry forwards, unused tax credits and differences between the financial
statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. Deferred tax assets and liabilities
are measured using the enacted or substantially enacted tax rates expected to apply when the asset is realized or the liability
settled.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities
of a change in tax rates is recognized in income or loss in the period that substantive enactment occurs.
A deferred tax asset is recognized to the extent
that it is probable that future taxable income will be available against which the asset can be utilized. To the extent that the
Company does not consider it probable that deferred tax asset will be recovered, the deferred tax asset is reduced.
The following temporary differences do
not result in deferred tax assets or liabilities:
| · | the initial recognition of assets or liabilities, not arising in
a business combination, that does not affect accounting or taxable income; |
| · | initial recognition of goodwill; |
| · | investments in subsidiaries, associates and jointly controlled entities
where the timing of reversal of the temporary differences can be controlled and reversal in the foreseeable future is not probable. |
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset
when there is a legally enforceable right to the set off current tax assets against current tax liabilities and when they relate
to income taxes levied by the same taxation authority and the Company intends to settle its current tax assets and liabilities
on a net basis.
Share-based payments
The Company operates an equity-settled, share-based
compensation plan, under which the entity receives services from employees and non-employees as consideration for equity instruments
(options) of the Company. The total amount to be expensed is determined by reference to the fair value of the options granted.
The fair value of share-based compensation
is determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and management’s assumptions as disclosed in note 10 of the Company’s
audited financial statements for the year ended April 30, 2014 and 2013. When a stock option is exercised, the Company recognizes
an increase in its share capital equivalent to the consideration paid by the option holder and the fair value amount previously
recognized in equity reserve. The fair value of any stock options granted to directors, officers and employees of the Company is
recorded as an expense over the vesting period of the options with a corresponding increase in equity reserve.
Flow-through shares
Under Canadian income tax legislation, a company
is permitted to issue flow-through shares whereby a company agrees to incur qualifying expenditures and renounce the related income
tax deductions to the investors. The Company has adopted a policy to (i) allocate the proceeds between the offering of the shares
and the sale of tax benefits when the shares are offered and (ii) recognize an income tax provision upon filing of appropriate
renunciation forms with the Canadian taxation authorities for qualifying expenditures previously incurred.
The allocation of the proceeds is made based
on the residual difference between the quoted price of the shares and the amount the investor pays for the flow-through shares.
A liability is recognized for the premium paid by the investors. The liability is reduced and the reduction of premium liability
is recorded in other income when the Company has the intention to renounce the expenditures with the Canadian taxation authorities
for qualifying expenditures previously incurred. The deferred tax impact, if any, is recorded at the same time.
New accounting standards adopted
The following standards were adopted effective
May 1, 2013.
(i) IFRS 10, Consolidated Financial Statements,
requires an entity to consolidate an investee when it has power over the investee, is exposed, or has rights, to variable returns
from its involvement with the investee and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the investee. Under existing
IFRS, consolidation was required when an entity has the power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as
to obtain benefits from its activities. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
(ii) IFRS 11, Joint Arrangements, requires
a venturer to classify its interest in a joint arrangement as a joint venture or joint operation. Joint ventures will be accounted
for using the equity method of accounting whereas for a joint operation the venturer will recognize its share of the assets, liabilities,
revenue and expenses of the joint operation. Under previous IFRS, entities had the choice to proportionately consolidate or equity
account for interests in jointly controlled entities. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated
financial statements.
(iii) IFRS 12, Disclosure of Interests in Other
Entities, outlines the disclosure requirements for interests in subsidiaries and other entities to enable users to evaluate the
risks associated with interests in other entities and the effects of those interests on an entity's financial position, financial
performance and cash flow. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
(iv) IFRS 13, Fair Value Measurement, provides
a single framework for measuring fair value. The measurement of the fair value of an asset or liability is based on assumptions
that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability under current market conditions, including assumptions about
risk. The Company adopted IFRS 13 on May 1, 2013 on a prospective basis. The adoption of IFRS 13 did not require any adjustments
to the valuation techniques used by the Company to measure fair value and did not result in any measurement adjustments as at May
1, 2013.
(v) The Company has adopted the amendments
to IAS 1 effective May 1, 2013. These amendments required the Company to group other comprehensive income by those that will be
reclassified subsequently to profit or loss and those that will not be reclassified. The adoption of this standard had no effect
on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Future Accounting pronouncements
Unless otherwise noted, the following new or
revised standards will be effective for the Company in future periods.
(i) IFRS 9 Financial Instruments, was issued
in November 2009 and addresses classification and measurement of financial assets. It replaces the multiple category and measurement
models in IAS 39 for debt instruments with a new mixed measurement model having only two categories: amortized cost and fair value
through profit or loss. IFRS 9 also replaces the models for measuring equity instruments. Such instruments are either recognized
at fair value through profit or loss or at fair value through other comprehensive income. Where equity instruments are measured
at fair value through other comprehensive income, dividends are recognized in profit or loss to the extent that they do not clearly
represent a return of investment; however, other gains and losses (including impairments) associated with such instruments remain
in accumulated comprehensive income indefinitely.
Requirements for financial liabilities were
added to IFRS 9 in October 2010 and they largely carried forward existing requirements in IAS 39, Financial Instruments - Recognition
and Measurement, except that fair value changes due to credit risk for liabilities designated at fair value through profit and
loss are generally recorded in other comprehensive income. In February 2014, the IASB tentatively determined that the revised effective
date for IFRS 9 would be January 1, 2018. The Company has not yet completed an assessment of the impact of adopting IFRS 9.
(ii) IFRIC 21, Accounting for Levies imposed
by Governments, clarifies that the obligating event giving rise to a liability to pay a levy is the activity described in the relevant
legislation that triggers payment of the levy. IFRIC 21 is effective for the Company beginning on May 1, 2014. The Company is currently
assessing the impact of this guidance.
|
Results of Operations –
Consolidated Statements of Net Loss
and Comprehensive Loss |
|
|
|
| For the years ending April 30 |
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
| |
($000’s) |
($000’s) |
($000’s) |
| |
|
|
|
| EXPENSED EXPLORATION COSTS |
|
|
|
| Mineral property expenditures |
271 |
632 |
4,825 |
| Mineral property write-offs |
357 |
137 |
451 |
| Equipment rental income |
(12) |
(3) |
(157) |
| Recoveries on option payment received |
(746) |
- |
- |
| Write-down on reclamation bonds |
3 |
110 |
- |
| |
(127) |
876 |
5,119 |
| OTHER EXPENSES |
|
|
|
| Consulting, labour and professional fees |
402 |
834 |
1,255 |
| Depreciation and amortization |
80 |
108 |
136 |
| Loss (gain) on disposal of property and equipment |
5 |
4 |
(7) |
| Foreign exchange loss (gain) |
1 |
(1) |
(4) |
| Insurance, licenses and filing fees |
98 |
85 |
115 |
| Interest income |
(10) |
(24) |
(119) |
| Other corporate costs |
33 |
67 |
164 |
| Investor relations and presentations |
22 |
52 |
132 |
| Rent |
26 |
127 |
134 |
| Share-based payments |
125 |
176 |
319 |
| Travel and accommodation |
9 |
19 |
68 |
| Management fees |
(30) |
(46) |
(363) |
| Impairment of available-for-sale securities |
74 |
83 |
122 |
| Premium on flow-through shares |
- |
- |
(202) |
| |
835 |
1,484 |
1,750 |
| |
|
|
|
| Net loss for the year |
(708) |
(2,360) |
(6,869) |
| |
|
|
|
| Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
| Items that may be subsequently reclassified to profit or loss: |
|
|
|
| Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities |
23 |
54 |
214 |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year |
(731) |
(2,414) |
(7,083) |
| |
|
|
|
| Basic and diluted loss per share ($ per share) |
(0.03) |
(0.11) |
(0.34) |
| A. | | Operating Results - Narrative Discussion |
In the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014, the
Company spent $0.5 million on exploration costs and recovered $0.2 million from our exploration partners for a net
mineral property expenditure of $0.3 million.
For the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014, the
Company recognized mineral property impairments on the Grease River, Poplar, Lake Athabasca, Hodgson and Carswell projects for
approximately $357,000 as the Company did not renew certain of its permits for these projects.
Camp and other miscellaneous exploration equipment
owned by the Company is maintained at our La Ronge warehouse. Equipment rental income is comprised of income (cost recapture) from
charging exploration projects for the rental of this equipment. In Q412, the equipment rental income is related to the winter drill
programs for the Cree East and West McArthur projects. In Q1 and Q2, 2013, the rental income is related to the summer work program
on the BC Copper project. In Q3 and Q4 2014, the rental income is related to the rental of tents and camp supplies to a 3rd party.
Consulting, labour, and professional fees are
lower than the same comparative prior period. The decrease is primarily attributed to a decrease in the salaries expense from the
re-negotiated employment agreements for senior staff and management which began effective August 2012. The Company has terminated
some staff and re-negotiated employment agreements with senior staff and management in efforts to minimize the Company’s
operating costs. The Company also reduced it usage of professionals and consultants in Q414 compared to Q413. As of January 1,
2013, the independent directors of the Company have not received directors’ fees in the form of cash, in order to assist
the Company in its plans to control its operation costs.
Insurance, licenses and filing fees are higher
for fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013. The increase is primarily due to the TSX Venture listing fees incurred in Q314 as the
Company’s shares began trading on the TSX Venture Exchange on December 30, 2013. In Q1, Q2 and Q4 2014, insurance, license
and filing fees were consistent relative to the same comparative prior periods.
Interest income was lower in 2014 compared
to 2013. The decrease was attributed to the decreased cash balances held during the year.
Investor relations expenses were lower in 2014
compared to 2013. The decrease is primarily attributed to the decrease in services provided by a Canadian investor relations firm.
The Company received contract services from the Canadian investor relations firm which started in June of 2011 and terminated in
July 2012.
Rent expense was lower in Q414 compared to
Q314 as a Company sublet its office space in its effort to reduce it cash burn and operating costs going forward. The Company is
however committed to the full lease amount, not the net for the head lease on the Vancouver office space.
The share-based payments amount for the year
is lower than the amount for the previous year. The decrease was primarily due to the decrease in the fair value calculation on
the options granted in fiscal 2014 relative to fiscal 2013. During fiscal 2014, there were 1,591,750 options granted with an average
fair value of $0.07 per option compared to 1,357,500 option granted with an average fair value of $0.13 per option in fiscal 2013.
A write-down on available-for-sale securities
of approximately $74,000 was recorded in fiscal 2014. This was attributed to a significant or prolonged impairment on a number
of investments. The Company wrote the balances down to their market values due to the significant decline in market value that
was viewed as other than a temporary impairment.
Management fees were lower in fiscal 2014 compared
to fiscal 2013. This was primarily due to the decrease in our exploration activities relative to last year. During fiscal 2014,
the Company spent $0.5 million on exploration, of which $0.3 million were related to our joint venture projects where management
fees were generated. During fiscal 2013, the Company spent $1.0 million on exploration, of which $0.6 million were related to joint
venture projects.
| B. | | Liquidity and Capital Resources |
As of April 30, 2014, the Company had $1.0
million in cash and cash equivalents and working capital of $1.1 million and as of April 30, 2013, the Company had $1.3 million
in cash and cash equivalents and working capital of $1.2 million.
The Company’s operating activities resulted
in net cash outflows of $0.6 million and $3.2 million for the fiscal years ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 respectively. Operating
activities and costs for fiscal 2014 are lower than fiscal 2013 as the Company reduced its exploration activities and option or
sold several of its projects during the year, as well as continued its efforts to minimize it operating costs to conserve its cash
reserves.
Financing activities resulted in net cash outflows
of approximately $1,000 and $5,000 for the fiscal years ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 respectively. During the fiscal year ended
April 30, 2014, the Company paid finders fees related to a prior financing in March 2012. In fiscal 2013, the Company incurred
TSX listing fees related to the Company’s share compensation plan. Currently, junior uranium exploration companies are finding
it difficult to seek financing. The Company is working to sell option or joint venture non core assets.
Investing activities resulted in net cash inflow
of approximately $396,000 and $72,000 for fiscal year ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 respectively. During the year ended April 30,
2014, the Company received cash option payments of approximately $385,000. The Company also staked the Hansen project for approximately
$10,000, the Hodgson project for approximately $7,000 and the Big Creek project for approximately $1,000. The Company also recovered
approximately $10,000 of reclamation bonds deposited with the Manitoba Mines Branch and the Company also sold the Reefton project
for $20,000 to Stevenson Mining during the year. During the year ended April 30, 2013, the Company acquired the Ruttan property
and the Patterson Lake property by staking five blocks of claims totalling 7,742 hectares for approximately $20,000 and received
$75,000 in option payments from Discovery Ventures Ltd. The Company also received approximately $19,000 from the sale of certain
property and equipment.
Cash and Working Capital
|
($000’s)
Cash and Working Capital |
|
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
1,044 |
1,265 |
| Trade and other receivables |
|
|
|
|
52 |
58 |
| Available-for-sale securities |
|
|
|
|
414 |
86 |
| Trade and other payables |
|
|
|
|
(382) |
(195) |
| Working capital |
|
|
|
|
1,128 |
1,214 |
For analysis and discussion of the movement
in cash and cash equivalents reference should be made to section 5 of this MD&A. Included within cash and cash equivalents
are $0.2 million in funds from the CKU Partnership which are dedicated to the Cree East project. Reference should be made to note
5 of the consolidated financial statements for further details.
As at April 30, 2014, included within trade
and other receivables is approximately $13,000 in Goods and Services Tax ("GST") refunds. The increase in available-for-sale
securities is primarily a result of receiving 1,000,000 shares from Makena Resources Inc. for our Patterson project in Q314, 500,000
shares from Copper Reef for our Hanson project and 2,250,000 shares from MPVC Inc. for our NW Manitoba project in Q414. The decrease
in trade and other receivables for April 30, 2014 is due primarily to a reduction its exploration expenditures in winter 2014 compared
to winter 2013.
The increase in trade and other payables is
due primarily to our exploration activities at our Cree East project compared with the fourth quarter of 2013. The Company intends
to operate an extensive geophysics program at our Cree East project in winter 2014.
| 3.1 | | Other Assets and Liabilities |
|
($000’s)
Other Assets and Liabilities |
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Reclamation bonds |
|
|
|
189 |
203 |
| Property and equipment |
|
|
|
294 |
375 |
| Mineral property interests (section 2.2) |
|
|
|
813 |
1,238 |
During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014,
the Company received approximately $10,000 cash from a refund of a reclamation bond from the Manitoba Mines Branch and also wrote
down approximately $3,000 of reclamation bonds.
During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014,
exploration and evaluation expenditures were made primarily on the West McArthur, Cree East, Hodgson and BC Copper (section 2).
During fiscal 2014, the Company acquired the
Hanson property by staking 14 blocks of claims totalling 17,272 hectares for approximately $10,000. The Company also re-staked
three blocks of claims totally 11,492 hectares of the Hodgson property for approximately $7,000 to maintain its interest in the
property. The Company also staked two block of claims totalling 723 hectares in south central British Columbia for approximately
$1,000. In addition, the Company recognized an impairment on its Grease River, Poplar, Lake Athabasca, Hodgson and Carswell claims
for approximately $357,000 as it did not renew certain of its permit for these properties.
|
($000’s)
Equity |
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Common shares |
|
|
|
73,205 |
73,205 |
| Equity reserve |
|
|
|
10,807 |
10,682 |
| Investment revaluation reserve |
|
|
|
(24) |
(1) |
| Deficit |
|
|
|
(81,564) |
(80,856) |
| Total equity |
|
|
|
2,424 |
3,030 |
|
(000’s)
Equity Instruments |
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
22,068 |
22,058 |
| Options outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
| Number |
|
|
|
3,851 |
3,598 |
| Weighted average price |
|
|
|
$0.20 |
$0.55 |
| Warrants outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
| Number |
|
|
|
- |
72 |
| Weighted average price |
|
|
|
- |
$0.55 |
Equity instruments
As of July 29, 2014, the Company
had the following securities outstanding. Common shares - 22,068,136; Stock options – 4,125,500; and Warrants – nil.
On June 12, 2013, the Company issued
10,000 common shares under the option agreement for the Collins Bay Extension project.
In March 2012, the Company issued
283,000 common shares for gross proceeds of $121,690. A finder’s fee of $4,867 in cash and 11,320 warrants were issued in
connection with the financing. Each finder’s warrant entitles the holder to purchase on additional common share for a period
of 18 months from the closing date, at a price of $0.55 per warrant share. The share purchase warrants issued as part of this placement
have been recorded at a fair value of $1,825 using the Black Scholes model.
In March 2012, the Company issued
1,522,000 flow-through common shares for gross proceeds of $776,220. A finder’s fee of $31,049 in cash and 60,880 warrants
were issued in connection with the financing. $68,490 was allocated to premium as the market value on the date of close was less
than the offering price associated with this offering. Each finder’s warrant entitles the holder to purchase one additional
common share for a period of 18 months from the closing date at a price of $0.55 per warrant share. The share purchase warrants
issued as part of this placement have been recorded at a fair value of $9,816 using the Black Scholes model.
In July 2011, the Company issued 5,000 common
shares under the option agreement for the Black Lake project.
In May 2011, the Company issued 418,141 flow-through
common shares for gross proceeds of $472,500, of which $133,805 was allocated to the flow-through share premium as the market value
on the date of close was less than the offering price associated with this offering.
| Proceeds from Financings |
|
|
| Date |
Type |
Intended Use |
Actual Use |
| March 2012 |
$0.1 million – 283,000 common shares |
Uranium exploration in Saskatchewan |
As Intended |
| March 2012 |
$0.8 million – 1,522,000 flow-through common shares |
Uranium exploration in Saskatchewan |
As Intended |
| C. | | Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, etc. |
As the Company is a mineral exploration company
with no research and development, the information required by this section is not applicable.
As the Company is a mineral exploration company
with no producing properties, the information required by this section is not applicable.
| E. | | Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements |
The Company does not have any off-balance sheet
arrangements.
| F. | | Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations |
The Company has the following commitments
in respect of operating leases for office space, land, or computer equipment:
| $000’s |
Payments due by period |
| Contractual Obligations: |
Total |
< 1 year |
1 – 3 years |
3 – 5 years |
> 5 years |
| Operating Lease Obligations |
290 |
150 |
133 |
7 |
- |
| TOTAL |
290 |
150 |
133 |
7 |
- |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company has outstanding future commitments
under mineral property agreements to issue common shares of the Company. Reference should be made to Note 8 of the consolidated
financial statements filed herewith.
| ITEM 6. | | DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES |
| A. | | Directors and Senior Management |
The following table the name, province or state
and country of residence for each director and executive officer of the Company, their principle occupation over the past five
years, years of service and the number of securities held. Each director will hold office until the next annual general meeting
of the shareholders and until such director’s successor is elected and qualifies, or until the director’s earlier death,
resignation or removal. The executive officers and committee members of the Company are elected annually at the first directors’
meeting immediately following the annual general meeting of shareholders.
|
Name, Residence and Current Position(s)
with the Company |
Principle Occupation
|
Director of the Company Since |
Number of Securities Held |
|
Peter Dasler
Tsawwassen,
BC, Canada
President, Chief Executive
Officer & Director
|
President and CEO since 2004; Mr. Dasler has
over 35 years’ experience in exploration geology including 20 years of geological consulting and contracting for junior and
senior companies based out of Vancouver, BC. Mr. Dasler holds Bachelor’s (1974) and Master’s (1981) degrees from Canterbury
University, New Zealand, and is a member of the professional Engineers and Geoscientists Association of BC. His background includes
senior geological positions in New Zealand, and Mine Manager of the 10 million ton per annum Taharoa Irons and Mine, as well as
management of junior exploration companies in Canada. |
Sept 20, 2006
|
286,538 (6)
Common shares
800,000
Stock Options |
|
Amb. Thomas Graham, Jr.
(2)(3)(5)
Bethesda, MD, United States
Chairman & Director |
Chairman of the Board since June 3, 2011); Member
of the International Advisory Board for the nuclear program of the United Arab Emirates since 2010; Chairman of the Board of Mexco
Energy Corporation (July 1997-2012); Executive Chairman of Lightbridge Corporation (formerly Thorium Power, Ltd.) (2006-present).
Ambassador Graham is one of the world's leading experts in nuclear non-proliferation. He has served under four successive U.S.
Presidents as a senior U.S. diplomat involved in the negotiation of every major international arms control and non-proliferation
agreement for the past 35 years. This includes the SALT, START, ABM, INF, NPT, CFE and CTBT Treaties. Amb. Graham has served with
the U.S. Arms Control and Disarmament Agency and as the Special Representative of the President of the United States for Arms Control,
Non-Proliferation, and Disarmament, in which role he successfully led U.S. government efforts to achieve the permanent extension
of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
|
Mar 30, 2007
|
20,000
Common shares
425,000
Stock Options
|
|
Jean Luc Roy (1)(2)(4)
Burkina
Faso, Africa
Director |
Independent Director of the Company (2007-present);
Former President and CEO of El Nino Ventures Inc.(2006-2009); Manager for SOMISY SA (2008 – 2009); COO of Ampella Mining
Limited (2009 – present). Mr. Roy has over 20 years’ experience in the mining industry. The majority of his experience
has been in Africa for companies such as International Gold Resources, Ashanti Goldfields Inc., Senafo, and First Quantum Minerals.
Mr. Roy has managed projects from exploration through to production in three different countries. As Managing Director for First
Quantum Minerals, Jean Luc played a crucial role in securing extensive land positions and by successfully placing a mining operation
into production in the Democratic Republic of Congo during a period of major unrest in the country. Mr. Roy is presently a resident
of Burkina Faso where he is the COO of Ampella Mining Ltd., an Australian listed company focused on gold exploration in West Africa
with their flagship property, Batie West.
|
Oct 31, 2007
|
425,000
Stock Options
|
|
Name, Residence and Current Position(s)
with the Company |
Principle Occupation
|
Director of the Company Since |
Number of Securities Held |
|
Victor Fern (1)(2)(3)
Fond du Lac, SK, Canada
Director |
Independent Director of the Company (2008-present);
Road Maintenance Supervisor for Athabasca Development Corporation (2009-present); Mill Training Foreman and a Mill Process Operator
for Cameco Corporation; former Chief of the Fond Du Lac Denesuline First Nation (2005–2007). |
Mar 25, 2008
|
425,000
Stock Options
|
|
Karl Schimann (3)
Vancouver, BC, Canada
Vice-President Exploration and Director
|
Vice-President Exploration since June 28, 2007.
Dr. Schimann holds a Ph.D. from the University of Alberta, and is member of the Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists
of British Columbia, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy, and Petroleum, the Geological Association of Canada, and the
Association of Exploration Geochemists. |
Sept 26, 2013
|
423,375
Common shares
800,000
Stock Options |
|
Kathleen K. Townsend (1)
Shady Side, Maryland, USA
Director |
Independent
Director of the Company. Member of the Bar, State of Maryland, USA. Managing Director, The Rock Creek Group, a Washington, D.C.-based
investor adviser, since 2007; Director, Lightbridge Corporation since 2013. |
Jan 7, 2014 |
425,000
Stock Options |
|
Harry Chan
Vancouver, BC, Canada
Chief Financial Officer |
Certified General Accountant. Mr. Chan has over
20 years of experience working in several different industries ranging from public practice, sports entertainment, wholesale distribution
and telecommunications. |
Jan 1, 2013
|
250,000
Stock Options |
Notes:
| (1) | Member of Audit Committee |
| (2) | Member of Compensation Committee |
| (3) | Member of Governance Committee |
| (4) | Chair of the Audit Committee and the Compensation Committee |
| (5) | Chair of the Governance Committee |
| (6) | Of these shares, 179,380 are held indirectly in the name of Bay Geological Inc., a private company
controlled by Mr. Dasler. |
Cease Trade Orders, Bankruptcies, Penalties or Sanctions
None of the directors or officers of the Company:
| (a) | is, as at the date of this Form 20-F, or has been, within ten years before the date of this Form
20-F, a director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer of any company (including the Company) that: |
| (i) | was subject to a cease trade order or similar order or an order that
denied the relevant company access to any exemption under securities legislation, which order was in effect for a period of more
than 30 |
consecutive days (an “Order”)
that was issued while the proposed director was acting in the capacity as director, chief executive officer or chief financial
officer;
| (ii) | was subject to an Order that was issued after the proposed director
ceased to be a director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer and which resulted from an event that occurred while
that person was acting in the capacity as director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer, |
| (b) | is, as at the date of this Form 20-F, or has been, within ten years
before the date of this Form 20-F, a director or executive officer of any company (including the Company) that, while that person
was acting in that capacity, or within a year of that person ceasing to act in that capacity, became bankrupt, made a proposal
under any legislation relating to bankruptcy or insolvency or was subject to or instituted any proceedings, arrangement or compromise
with creditors or had a receiver, receiver manager or trustee appointed to hold its assets; |
| (c) | has, within the ten years before the date of this Form 20-F, become
bankrupt, made a proposal under any legislation relating to bankruptcy or insolvency, or become subject to or instituted any proceedings,
arrangement or compromise with creditors, or had a receiver, receiver manager or trustee appointed to hold the assets of the proposed
director. |
Other Principle Directorships
In addition to their positions on the Board,
the following Directors also serve as Directors of the following reporting issuers or reporting issuer equivalents:
| Name of Director |
Reporting Issuer(s) or Equivalent(s) |
| Amb. Thomas Graham Jr. |
Lightbridge Corporation (LTBR) |
| Kathleen K. Townsend |
Lightbridge Corporation (LTBR) |
In this Form 20-F:
Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”)
means an individual who acted as chief executive officer of the Company, or acted in a similar capacity, for any part of the most
recently completed financial year;
Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”)
means an individual who acted as chief financial officer of the Company, or acted in a similar capacity, for any part of the most
recently completed financial year;
Named Executive Officer (“NEO”)
means each of the following individuals:
| (c) | each of the three most highly compensated executive officers of the
company including any of its subsidiaries, or the three most highly compensated individuals acting in a similar capacity, other
than CEO and CFO, at the end of the most recently completed financial year whose total compensation was, individually, more than
$150,000, as determined in accordance with subsection 1.3(6), for that financial year; and |
| (d) | each individual who would be an NEO under paragraph (c) but for the
fact that the individual was neither an executive officer of the Company or its subsidiaries, nor acting in a similar capacity,
at the end of that financial year; |
Named Executive Officers
During the financial year ended April 30, 2014,
the Company had the following NEOs: Peter Dasler, President and CEO, and Harry Chan, CFO.
Compensation Discussion & Analysis
Due to increasingly difficult conditions facing
junior uranium exploration, in April 2012 the Company’s management and Board of Directors, approved a plan to significantly
reduce the overhead of the Company. Employment and consulting contracts with all of the Company’s NEOS were amended or terminated
as discussed below.
Dasler Employment Agreement
The Company entered into an employment agreement
dated August 1, 2012 (the “Dasler Employment Agreement”) with Peter Dasler, President, CEO and a director of the Company.
Pursuant to the terms of the Dasler Employment Agreement, Mr. Dasler was paid a monthly retainer fee of $10,000 for approximately
60% of his professional time on a monthly basis. Commencing June 27, 2014 the Company entered into an employment agreement with
Mr. Dasler for the payment of a monthly retainer fee of $15,000 (the “Fee”) for approximately 90% of his professional
time on a monthly basis. The Fee shall be increased annually at the discretion of the Company’s Compensation Committee, which
increase shall be not less than the greater of: (a) the annual percentage rate of inflation; (b) five per cent (5%).
The Dasler Employment Agreement may be terminated
for any reason upon provision of 90 days written notice. The Company may also, in its sole discretion, waive this notice requirement
if Mr. Dasler terminates the Dasler Employment Agreement.
In addition to the Dasler Employment Agreement,
the Company and Mr. Dasler have also entered into a Contingency Agreement dated June 27, 2014. The Contingency Agreement governs
the termination or modification of Mr. Dasler’s consulting agreement in the event that a change of control of the Company
occurs during the term of the Dasler Employment Agreement.
Chan Consulting Agreement
The Company entered into an employment
agreement dated February 1, 2013 (the “Chan Employment Agreement”) with Harry Chan, CFO of the Company. Pursuant to
the terms of the Chan Employment Agreement, Mr. Chan is paid a monthly retainer fee of $8,333 for approximately 80% of his professional
time on a monthly basis. The Fee shall be increased annually at the discretion of the Company’s Compensation Committee, which
increase shall be not less than the greater of: (a) the annual percentage rate of inflation; (b) five per cent (5%).
Performance Graph
The common shares of
the Company commenced trading on the TSX on June 21, 2011 under the symbol “CVV” until December 27, 2013. On December
30, 2013 the Company’s shares were delisted from the TSX and commenced trading on the TSX Venture Exchange. The following
chart compares the total cumulative shareholder return for CDN $100 invested in common shares of the Company on April 30, 2010,
with the cumulative total return of the S&P/TSX Composite Index (formally the TSE 300 Composite Index) for the period from
April 30, 2010 to April 30, 2014. The performance of common shares of the Company as set out in the graph does not necessarily
indicate future price performance.

| |
Apr. 2010 |
Apr. 2011 |
Apr. 2012 |
Apr. 2013 |
Apr. 2014 |
| S&P/TSX Composite Index |
$100.00 |
$114.20 |
$100.67 |
$102.01 |
$119.99 |
| CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. |
$100.00 |
$56.00 |
$28.67 |
$9.33 |
$14.67 |
Share Based and Option Based Awards
The Company maintains a stock option plan to
provide additional long-term incentives to the Company’s executive officers, as well as its directors, employees and consultants.
The Compensation Committee reviews the level of incentive options periodically and makes any new issuance recommendations to the
Board for approval. Previous grants of option-based awards are taken into account when considering new grants. See “Narrative
Discussion” under “Incentive Plan Awards” below for details of the Company’s stock option plan.
Compensation Governance
Compensation of the
NEOs of the Company is set by the Board as recommended by the Company’s compensation committee (the “Compensation Committee”).
The Compensation Committee consists of three independent directors namely Jean Luc Roy (Chair), Victor Fern, and Amb. Thomas Graham,
Jr.
The Compensation Committee
reviews, on an annual basis, the cash compensation, performance and overall compensation package for each NEO. The Compensation
Committee then presents its findings and any recommendations to the Board for consideration and approval, if acceptable to the
Board . The Compensation Committee recognizes the need to provide a total compensation package that will attract and retain qualified
and experienced executives as well as align the compensation level of each of the NEOs.
The Company’s
executive compensation practices are intended to provide both current and long term rewards to its NEOs that are competitive within
the compensation practices of the industry and consistent with their individual performance and contribution to the Company’s
objectives. Compensation components include base salary, bonus and long term incentives in the form of stock options.
In determining the appropriate base salary
of an executive officer, the Compensation Committee considers the responsibilities of the individual, comparable salaries in the
industry, the experience level of the individual and overall performance. Once the base salary has been established, it is reviewed
by the Compensation Committee on an annual basis. The Committee meets at least annually or more frequently if required. On an annual
basis, the Compensation Committee will report to the Board that it is compliant with its Charter.
The Compensation committee has formulated polices
that are flexible and reflective of current market conditions, while limiting any risks arising out of compensation practices.
Summary Compensation
Table
The following table
sets out compensation of the NEOs of the Company for the three most recently completed financial years of the Company:
|
Name and principal position
(a) |
Year
Ended April 30
(b) |
Salary
($)
(c) |
Option-based awards ($)
(2)
(e) |
Non-equity incentive plan compensation
($)
(f) |
All other compensation
($)
(h) |
Total compensation
($)
(i) |
|
Annual incentive plans
(f1)
|
Long-term incentive plans
(f2) |
|
Peter Dasler
President, CEO and Director |
2014
2013
2012
|
120,000
158,885
191,016 |
14,584
31,238
48,213 |
Nil
Nil
Nil |
Nil
Nil
Nil |
Nil
Nil
Nil |
134,584
190,123
239,229 |
|
Harry Chan
CFO (1) |
2014
2013
2012 |
100,000
33,333
N/A |
4,199
12,640
N/A |
Nil
Nil
N/A |
Nil
Nil
N/A |
Nil
Nil
N/A |
104,199
45,973
N/A |
Notes:
| (1) | Mr. Chan was appointed CFO of the Company on January 1, 2013. Mr. Chan’s compensation was
paid as a management fee. |
| (2) | In determining the fair value of the options granted, the Company followed the principles established
under International Financial Reporting Standards, which requires the determination of the fair value of options granted using
the Black-Scholes methodology. The Black-Scholes methodology requires making estimates of the risk free rate, expected life
of the options, expected volatility and expected dividends. The Company used the following assumptions in determining the
fair value of the options: |
Forfeiture
rate: 15.4%
Risk-free
rate: 1.12% to 1.15%
Expected
Life 2.21 to 2.24 years
Expected
volatility 113.4% to 118.2%
Expected
dividends 0%
Outstanding Share-Based and Option-Based Awards
The following table
sets forth details of all awards outstanding for the Company’s NEOs as at the year ended April 30, 2014, and includes awards
granted to the NEOs in prior years.
| |
Option-based Awards |
Share-based Awards |
| Name |
Number of securities underlying unexercised options
(#) |
Option exercise price
($) |
Option expiration date |
Value of unexercised in-the-money options
($) |
Number of shares or units of shares that have not vested
(#) |
Market or payout value of share-based awards that have not vested
($) |
|
Peter Dasler
President, CEO and Director
|
90,000
200,000
45,000
5,000
200,000
144,000 |
$0.10
$0.50
$0.25
$0.25
$0.25
$0.12 |
Dec 3/14
Nov 7/14
Aug 13/17
Oct 3/17
Feb 1/18
Nov 5/18 |
10,350
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
13,680 |
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil |
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil |
| |
656,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Harry Chan
CFO |
20,000
17,500
100,000
62,500
|
$0.10
$0.25
$0.25
$0.12
|
Oct 28/14
Nov 7/14
Feb 1/18
Nov 5/18
|
2,300
(1)
(1)
5,938
|
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
|
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
|
| |
200,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
| (1) | The Company’s common shares closed at $0.215 per share on April 30, 2014, therefore these
options were not in the money as at that date. |
The following table
sets forth details of the value vested or earned by the Company’s NEOs for all incentive plan awards during the year ended
April 30, 2014:
|
Name |
Option-based awards –
Value vested during the year
($)(1) |
Share-based awards –
Value vested during the year ($) |
Non-equity incentive plan compensation
–
Value earned during the year ($) |
| Peter Dasler |
Nil |
Nil |
Nil |
| Harry Chan |
Nil |
Nil |
Nil |
| (1) | The value of the option-based awards – vested during the year
is calculated by using the number of fully vested options at the financial year end and multiplying that number of options by the
difference between the market price and the exercise price of the option. The market value of $0.215 per share is the closing price
of the Company’s shares at April 30, 2014. |
Stock Option Plan - Narrative Discussion
The Company adopted a stock option plan (the
“Plan”) dated September 30, 2010 (which was last approved by the shareholders of the Company at an annual general meeting
on September 26, 2013). On November 8, 2010 the Company consolidated its share capital on a ten old for one new basis resulting
in the maximum shares issuable under the Plan having been reduced to a maximum issuable of 3,400,000 shares and the exercise price
of the outstanding stock options were adjusted accordingly to the exercise price of $1.00 per share. At the Company’s annual
general meeting held September 27, 2012, shareholders approved that the Plan be increased to the maximum aggregate number of common
shares of the Company which may be reserved for issuance under the Plan to 4,400,000 common shares, which represented approximately
20% of the issued and outstanding common shares of the Company. In addition, the exercise price of all of the qualified stock options
outstanding under the Plan as at September 23, 2010 was adjusted to the minimum exercise price permitted by the TSX-V of $0.10
per share.
The principal purpose of the Plan is to give
directors, officers, employees and consultants the opportunity to participate in the profitability and growth of the Company by
granting to such individuals options, exercisable over periods of up to ten years as determined by the Board, to buy shares of
the Company at a price not less than the closing market price of the Company’s shares on the day preceding the date of granting
of the option.
The Plan provides that the maximum aggregate
number of common shares reserved for issuance under the Plan and all other share compensation arrangements of the Company is 4,400,000
common shares, representing approximately 20% of the Company’s issued and outstanding share capital.
The Plan is administered by the Compensation
Committee of the Company. Management will make recommendations to the Compensation Committee for proposed allocations. Once the
Compensation Committee approves the allotment, the proposed issuance is forwarded to the Board of Directors for acceptance.
The full text of the Plan is available by contacting
the Company and has been posted on SEDAR at www.sedar.com and EDGAR at www.edgar.com.
The current status of the
Plan is as follows:
|
Shares reserved for issuance pursuant to unexercised
incentive stock options
Unallocated shares available for future grants
of incentive stock options |
|
4,225,500
174,500 |
| TOTAL |
|
4,400,000 |
Management believes that incentive plan awards
are an effective means of rewarding corporate and individual performance and that they are a necessary component of compensation
packages that are currently an industry standard.
Director Compensation Table
The following table
sets forth the details of compensation provided to the directors, other than the NEOs, during the Company’s most recently
completed financial year:
|
Name |
Fees
Earned
($) |
Share-based Awards
($) |
Option-based Awards (1)
($) |
Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation
($) |
All Other Compensation
($) |
Total
($) |
| Amb. Thomas Graham, Jr. |
Nil |
Nil |
11,334 |
Nil |
Nil |
11,334 |
| Jean Luc Roy |
Nil |
Nil |
11,174 |
Nil |
Nil |
11,174 |
| Victor Fern |
Nil |
Nil |
14,017 |
Nil |
Nil |
14,017 |
| Michael Riley |
Nil |
Nil |
2,667 |
Nil |
Nil |
2,667 |
| Karl Schimann |
81,808 |
Nil |
21,425 |
Nil |
Nil |
103,233 |
| Kathleen Townsend |
Nil |
Nil |
36,786 |
Nil |
Nil |
36,786 |
| (1) | In determining the fair value of the options granted, the Company
followed the principles established under International Financial Reporting Standards, which requires the determination of the
fair value of options granted using the Black-Scholes methodology. The Black-Scholes methodology requires making estimates
of the risk free rate, expected life of the options, expected volatility and expected dividends. The Company used the following
assumptions in determining the fair value of the options: |
Forfeiture rate: 15.4%%
Risk-free rate: 1.12% to 1.15%
Expected Life 2.21 to 2.24
years
Expected volatility 113.4%
to 118.2%
Expected dividends 0%
Director Compensation - Narrative Discussion
During the year ended April 30, 2014, the directors
did not receive directors’ fees in the form of cash in order to assist the Company in its plans to control its operation
costs.
Pension Plan Benefits
As at the year ended April 30, 2014, the Company
did not maintain any defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans or deferred compensation plans for the NEOs or the other
Directors.
Termination and Change of Control Benefits
As of July 19, 2014, all senior management
contracts may be terminated by providing the required 90 day working notice. In addition, all change of control compensatory provisions
will be terminated at that time.
Directors and Officers Insurance
The
Company subscribes to a Directors and Officers Liability Insurance to a limit of $5,000,000 per claim. The policy insures the Company
against any wrongful act committed by its Directors and Officers, including any actual or alleged breach of duty, neglect, error,
omission, misstatement, misrepresentation, or act done or attempted by the Directors and Officers of the Company in their capacity
to act for the Company. In addition, the Company has further indemnified its Directors and Officers, to the fullest extent of the
law, by entering into personal indemnity agreements with all of the Company’s Directors and Officers. The Directors are also
compensated through the grant of incentive stock options.
1.
The election and retirement of our directors
are provided for in the Company’s Articles. An election of directors takes place at each annual meeting of shareholders.
A director retains office only until the election of his successor. The number of directors to be elected at such meeting is the
number of directors then in office, unless the directors or the shareholders otherwise determine. The election is by ordinary resolution
of shareholders. If an election of directors is not held at the proper time, the incumbent directors continue in office until their
successors are elected. The last annual general meeting was held on September 26, 2013. Company Articles permit the directors to
add additional directors to the board between annual general meetings as long as the number appointed does not exceed one-third
of the number directors elected at the last annual general meeting. Individuals appointed as directors to fill casual vacancies
created on the board or added as additional directors hold office like any other director until the next annual general meeting
at which time they may be re-elected or replaced.
The officers of the Company are re-appointed
at a directors' meeting following each annual general meeting.
2. As at August 27, 2014 the Company did
not, nor any of its subsidiaries, have service contracts with any of its directors providing for benefits upon termination of employment.
3. The members of our audit committee included
Jean Luc Roy (Chair), Kathleen K. Kennedy and Victor Fern. The audit committee reviews and approves the scope of the audit procedures
employed by our independent auditors, reviews the results of the auditor's examination, the scope of audits, the auditor's opinion
on the adequacy of internal controls and quality of financial reporting and our accounting and reporting principles, policies and
practices, as well as the accounting, financial and operating controls. The audit committee also reports to the Board of Directors
with respect to such matters and recommends the selection of independent auditors. Before financial statements that are to be submitted
to the shareholders at an annual general meeting are considered by the Board of Directors, such financial statements are submitted
to the audit committee for review with the independent auditors, following which the report of the audit committee on the financial
statements is submitted to the Board of Directors.
The members of the nominating
and corporate governance committee included Amb. Thomas Graham, Jr (Chair), Victor Fern and Karl Schimann. The mandate of the nominating
and corporate governance committee is to identify individuals qualified to be nominated for election as directors of the Company
or any of the Board's committees, evaluate the qualifications and independence of each member of the Board and its committees and
recommend to the Board any appropriate changes in the composition of the Board and any of its committees, evaluate the performance
of the Board and its committees; and develop and recommend to the Board corporate governance principles.
The members of the compensation
committee included Jean Luc Roy (Chair), Victor Fern and Amb. Thomas Graham, Jr. The compensation committee reviews and approves
the total compensation package for the Company’s senior executives including, without limitation, their base salaries, annual
incentives, deferred compensation and stock options.
At the fiscal year end April 30, 2014, the
Company employed four part-time and one fixed term personnel. The Company also engages contractors and consultants from time to
time to work on specific projects and for administration, legal and other services that are required. Management continues to reduce
the staffing requirements of the Company in response to the downturn in the financial markets and the decrease in exploration activity
for the Company. Management intends to satisfy the staffing requirements on a consulting or fixed term basis.
The following
tables set forth the share ownership of those persons listed in Subsection 6B above and include details of warrants, options to
purchase shares of the Company and common shares beneficially owned by such persons for the most recently completed fiscal year
ending April 30, 2014:
Common Shares and Stock Options
|
Name and Position
|
Number
of Common
Shares
Beneficially
Owned
# |
Number of
Securities
underlying unexercised
Options
#
|
Option
Issue
Date
|
Option
Exercise
price
($)
|
Option
Expiration
Date
|
Number
of
Warrants |
Exercise
Price
($) |
Warrant
Expiry
Date |
|
Peter Dasler
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director
|
|
90,000
200,000
45,000
5,000
200,000
144,000 |
Dec 4/09
Nov 8/11
Aug 13/12
03-Oct-12
01-Feb-13
05-Nov-13 |
$0.10
$0.50
$0.25
$0.25
$0.25
$0.12 |
Dec 3/14
Nov 7/14
Aug 13/17
Oct 3/17
Feb 1/18
Nov 5/18 |
|
|
|
| |
286,538 |
684,000 |
|
|
|
Nil |
|
|
|
Harry Chan
Chief Financial Officer |
|
20,000
17,500
100,000
62,500 |
Oct 29/09
Nov 8/10
Feb 1/13
Nov 5/13 |
$0.10
$0.25
$0.25
$0.12 |
Oct 28/14
Nov 7/14
Feb 1/18
Nov 5/18 |
|
|
|
| |
Nil |
200,000 |
|
|
|
Nil |
|
|
Share Option Plan
Management believes that incentive plan awards
are an effective means of rewarding corporate and individual performance and that they are a necessary component of compensation
packages that are currently an industry standard. For a description of the share option plan please refer to Item 6. Directors,
Senior Management and Employees; Subsection B. Compensation.
| ITEM 7. | | MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTION, |
1. (a)
To
the knowledge of the directors and executive officers of the Company, and based upon the Company’s review of the records
maintained by CST Trust Company and insider reports filed with System for Electronic Disclosure by Insiders (SEDI), as at April
30, 2014, the Company had 22,068,136 shares issued and there are no shareholders beneficially owning, directly or indirectly, or
exercised control or direction over, shares carrying more than 5% of the voting rights attached to all outstanding shares of the
Company.
(b) Not
applicable.
(c) No shareholders have any special
voting rights, one common share, one vote.
| 2. | The most recent records show that the Company has approximately 551
shareholders of record, holding 22,068,136 common shares of the Company. Approximately 82% of the shareholders are located in Canada,
16% in the United States, and the balance in Asia, Africa, New Zealand and Europe. |
| 3. | To the extent known to the Company, the Company is not owned or controlled
directly or indirectly by another corporation, by any foreign government, or any other legal person(s) severally or jointly. |
| 4. | There are no arrangements known to the Company of which may at a
subsequent date result in a change of control of the Company. |
| B. | | Related Party Transactions |
There were no material related party transactions
from the last fiscal year end April 30, 2013, to the current date of this report. There are no proposed material related party
transactions between the Company or any of its subsidiaries, except as previously disclosed in the audited year ended April 30,
2013 consolidated financial statements filed herewith.
| C. | | Interests of Experts and Counsel |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
| ITEM 8. | | FINANCIAL INFORMATION |
| A. | | Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information |
This Form 20-F contains consolidated financial
statements for the Company for fiscal year end April 30, 2014 which contains an audit report dated July 24, 2014 filed herewith
under Item 19.
There have been no significant changes since
the financial year ended April 30, 2014, other than disclosed in this Form 20-F.
| ITEM 9. | | THE OFFER AND LISTING |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act, and as such provides information called for by items 9.A.4 and 9.C.
| 1. | | TSX Venture Exchange and Toronto Stock Exchange Trading Activity |
(a) The annual high and low market prices
for the five most recent financial years as quoted on the TSX Venture Exchange and the Toronto Stock Exchange:
| Year Ended |
High |
Low |
|
May 2013 – April 2014
May 2012 – April 2013
May 2011 – April 2012
May 2010 – April 2011
May 2009 – April 2010 |
0.28
0.43
0.83
1.79
1.95 |
0.09
0.12
0.30
0.84
1.45 |
(b) The two most recent full financial years
and any subsequent period: the high and low market prices for each full financial quarter as quoted on the TSX or the TSX Venture
Exchange:
| TSX Venture Exchange |
High |
Low |
| 2014 |
|
|
| First Quarter |
0.15 |
0.09 |
| Second Quarter |
0.16 |
0.09 |
| Third Quarter |
0.28 |
0.10 |
| Fourth Quarter |
0.26 |
0.18 |
| 2013 |
|
|
| First Quarter |
0.43 |
0.25 |
| Second Quarter |
0.26 |
0.15 |
| Third Quarter |
0.32 |
0.15 |
| Fourth Quarter |
0.25 |
0.12 |
(c) The high and low market prices for the
most recent six months as quoted on the Toronto Stock Exchange:
| 2014 |
High |
Low |
| February |
0.23 |
0.19 |
| March |
0.26 |
0.18 |
| April |
0.24 |
0.20 |
| May |
0.24 |
0.16 |
| June |
0.20 |
0.14 |
| July |
0.17 |
0.15 |
The Company’s common shares commenced trading on the Vancouver
Stock Exchange (now the TSX Venture Exchange) on January 4, 1988 under the trading symbol “CVV”. On June 21, 2011 the
shares of the Company were delisted from the TSX Venture Exchange and commenced trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange under the
same symbol “CVV”. On December 27, 2013 the Company’s shares were delisted from the Toronto Stock Exchange and
commenced trading on the TSX Venture Exchange on December 30, 2013.
| 2. | | Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board Trading Activity |
(a) The annual high and low market prices
for the five most recent financial years as quoted on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board:
| Year Ended |
High |
Low |
|
May 2013 – April 2014
May 2012 – April 2013
May 2011 – April 2012
May 2010 – April 2011
May 2009 – April 2010 |
0.26
0.44
0.87
1.79
2.00 |
0.08
0.11
0.30
0.70
1.30 |
(b)
The two most recent full financial years
and any subsequent period: the high and low market prices for each full financial quarter as quoted on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin
Board:
| Quarter Ended |
High |
Low |
| 2014 |
|
|
| First Quarter |
0.15 |
0.08 |
| Second Quarter |
0.14 |
0.09 |
| Third Quarter |
0.26 |
0.10 |
| Fourth Quarter |
0.24 |
0.16 |
| 2013 |
|
|
| First Quarter |
0.44 |
0.25 |
| Second Quarter |
0.27 |
0.16 |
| Third Quarter |
0.30 |
0.15 |
| Fourth Quarter |
0.24 |
0.11 |
(c) The high and low market prices for the
most recent six months as quoted on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board:
| 2014 |
High |
Low |
| February |
0.22 |
0.17 |
| March |
0.24 |
0.16 |
| April |
0.22 |
0.19 |
| May |
0.20 |
0.18 |
| June |
0.18 |
0.13 |
| July |
0.15 |
0.13 |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
The Company’s common shares commenced
trading on the Vancouver Stock Exchange (now theTSX Venture Exchange) on January 4, 1988 under the trading symbol “CVV”;
have been listed on the OTCBB since December 3, 1999 under the trading symbol of “CVVUF”, and on the Frankfurt Stock
Exchange, Open Market, under the trading symbol DH7N. On June 21, 2011, the shares of the Company were delisted from the TSX Venture
Exchange and commenced trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange under its existing symbol “CVV”. On December 27, 2013
the Company’s shares were delisted from the Toronto Stock Exchange and commenced trading on the TSX Venture Exchange on December
30, 2013 under the same symbol, “CVV”.
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
| ITEM 10. | | ADDITIONAL INFORMATION |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
| B. | | Memorandum and Articles of Association |
1. The
Company is permitted to conduct any lawful business, that it is not restricted from conducting by its Memorandum and Articles,
neither of which contain any restriction on the lawful business that the Company may conduct. CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. executive,
registered and records office is located at 1020 – 625 Howe Street, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, V6C 2T6, telephone
number 604.688.3211.
| | The Company was incorporated on May 22, 1985 under the laws of the Province of British Columbia,
Canada under the name Canadian Gravity Recovery Group Ltd. On June 14, 1985, the Company changed its name to CanAlaska Resources
Ltd. On September 15, 1993, the Company consolidated its share capital on a four for one basis and changed its name to International
CanAlaska Resources Ltd. On October 19, 1999, the Company consolidated its share capital on a five for one basis and changed its
name to CanAlaska Ventures Ltd. The Company was transitioned under the Business Corporations Act (British Columbia) on September
24, 2004. The Company changed its name to CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. on October 11, 2006. |
The Company’s common stock
(the “Common Shares”) havebeen listed on the Vancouver Stock Exchange (now the TSX Venture Exchange) (since January
4, 1988 as a Tier 1 Company. The Company has been trading on the OTC Bulletin Board in the United States under the symbol ICSKF
from July 20, 1999 and under the symbol CVVUF since December 3, 1999, and on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange, Open Market, under the
trading symbol DH7. On June 21, 2011, the shares of the Company were delisted from the TSX Venture Exchange and commenced trading
on the Toronto Stock Exchange under its existing symbol “CVV”. On December 27, 2013 the Company’s shares were
delisted from the Toronto Stock Exchange and commenced trading on the TSX Venture Exchange as a Tier 2 Company on December 30,
2013 under the same symbol, “CVV”.
The Company is a reporting company
in British Columbia, Alberta, Ontario and Labrador and Newfoundland. The Company is extra-provincially registered in Labrador and
Newfoundland, Saskatchewan, Northern Manitoba, and Alberta, Canada.
| 2. | A director who is, in any way, directly or indirectly interested in an existing proposal or contract
or transaction with the Company, where a conflict of interest is declared, the nature and extent of the conflict which must be
disclosed as required by the Business Corporations Act (British Columbia), may not vote in respect to the approval of the
transaction. |
| 3. | All of the shares of common stock of the Company are of the same
class and, once issued, rank equally as to dividends, voting powers, and participation in assets and in all other respects, on
liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary. The holders of the common shares are entitled
to one vote for each common share on all matters to be voted on by the shareholders. There are no sinking fund provisions. All
common shares must be fully paid prior to issue and are thereafter subject to no further capital calls by the Company. There exists
no discriminatory provision affecting any existing or prospective holder of common shares as a result of such shareholder owning
a substantial number of shares. |
| 4. | The rights of the shareholders may be changed only by the shareholders passing a special resolution
approved by members holding two thirds of the votes cast. |
5.
The
Board of Directors must call an annual general meeting once each calendar year, not later than 15 months after the last such meeting.
The Board may call an extraordinary meeting of shareholders at any time. Notice of such meetings must be accompanied by an Information
Circular describing the proposed business to be dealt with and disclosures as prescribed by statute. Not less than 21 days’
notice shall be given for any meeting. A quorum shall be two members in person or proxy not representing less than 5% of the issued
shares.
| 6. | The Articles of the Company contain no limitations on the rights of non-resident or foreign shareholders. |
| 7. | There are no provisions in the Company’s Articles that would have an effect of delaying,
deferring or preventing a change in control of the Company and that would operate only with respect to a merger, acquisition or
corporate restructuring involving the Company or its subsidiaries. |
| 8. | There are no provisions in the Company’s Articles governing ownership threshold. |
| 9. | With respect to items 2 through 8 above, the law applicable to the Company in these areas is not
significantly different from that in the host country. |
10. Conditions
imposed by the Memorandum and Articles governing changes in the capital require a special resolution of shareholders requiring
two-thirds of the votes cast.
A copy of our Articles of Incorporation
are incorporated by reference as Exhibit 1.1 to this Annual Report on Form 20-F.
During the two years immediately preceding
April 30, 2014, there were no material contracts entered into by the Company other than during the normal course of business as
disclosed in Item 4, Section D, Property, Plant and Equipment and Item 5 Section F, Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations.
There is no law or governmental decree or regulation
in Canada that restricts the export or import of capital, or affects the remittance of dividends, interest or other payments to
a non-resident holder of common shares, other than withholding tax requirements.
There is no limitation imposed by Canadian
law or by the constituent documents of the Company on the right of a non-resident to hold or vote common shares, other than are
provided in the Investment Canada Act (Canada). The following summarizes the material features of the Investment Canada
Act (Canada).
The Investment Canada Act (Canada)
requires certain "non-Canadian" individuals, governments, corporations or other entities who wish to acquire a "Canadian
business" (as defined in the Investment Canada Act), or establish a "new Canadian business" (as defined in
the Investment Canada Act) to file either a notification or an application for review with a governmental agency known as
"Investment Canada". The Investment Canada Act requires that certain acquisitions of control of a Canadian business
by a "non-Canadian" must be reviewed and approved by the Minister responsible for the Investment Canada Act on
the basis that the Minister is satisfied that the acquisition is "likely to be of net benefit to Canada", having regard
to criteria set forth in the Investment Canada Act. Only acquisitions of control are reviewable under the Investment
Canada Act; however, the Investment Canada Act provides detailed rules for the determination of whether control has been
acquired and, pursuant to those rules, the acquisition of one-third or more of the voting shares of a corporation may, in some
circumstances, be considered to constitute an acquisition of control. Certain reviewable acquisitions of control may not be implemented
before being approved by the Minister; if the Minister does not ultimately approve a reviewable acquisition which has been completed,
the acquired Canadian business be divested. Failure to comply with the review provisions of the Investment Canada Act could
result in, among other things, an injunction or a court order directing disposition of assets or shares.
CERTAIN UNITED STATES
FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following is
a general summary of certain material U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to a U.S. Holder (as defined below)
arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. This summary is for general
information purposes only and does not purport to be a complete analysis or listing of all potential U.S. federal income tax
considerations that may apply to a U.S. Holder arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of
common shares. In addition, this summary does not take into account the individual facts and circumstances of any particular
U.S. Holder that may affect the U.S. federal income tax consequences to such U.S. Holder, including specific tax consequences
to a U.S. Holder under an applicable tax treaty. Accordingly, this summary is not intended to be, and should not be construed
as, legal or U.S. federal income tax advice with respect to any U.S. Holder. This summary does not address the U.S. federal
alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences to U.S. Holders of the
acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. Each prospective U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor
regarding the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign
tax consequences relating to the acquisition, ownership and disposition of common shares. No legal opinion from U.S. legal
counsel or ruling from the Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”) has been requested, or will be obtained,
regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. This
summary is not binding on the IRS, and the IRS is not precluded from taking a position that is different from, and contrary
to, the positions taken in this summary. In addition, because the authorities on which this summary is based are subject to
various interpretations, the IRS and the U.S. courts could disagree with one or more of the conclusions described in this
summary.
Scope of this Summary
Authorities
This summary is based
on the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), Treasury Regulations (whether final, temporary, or proposed),
published rulings of the IRS, published administrative positions of the IRS, the Convention Between Canada and the United States
of America with Respect to Taxes on Income and on Capital, signed September 26, 1980, as amended (the “Canada-U.S. Tax Convention”),
and U.S. court decisions that are applicable and, in each case, as in effect and available, as of the date of this document. Any
of the authorities on which this summary is based could be changed in a material and adverse manner at any time, and any such change
could be applied on a retroactive or prospective basis which could affect the U.S. federal income tax considerations described
in this summary. This summary does not discuss the potential effects, whether adverse or beneficial, of any proposed legislation
that, if enacted, could be applied on a retroactive or prospective basis.
U.S. Holders
For purposes
of this summary, the term "U.S. Holder" means a beneficial owner of common shares that is for U.S. federal income tax
purposes:
| · | an individual who is a citizen or resident
of the U.S.; |
| · | a corporation (or other entity taxable as
a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes) organized under the laws of the U.S., any state thereof or the District of
Columbia; |
| · | an estate whose income is subject to U.S.
federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| · | a trust that (1) is subject to the primary
supervision of a court within the U.S. and the control of one or more U.S. persons for all substantial decisions or (2) has a valid
election in effect under applicable Treasury Regulations to be treated as a U.S. person. |
Non-U.S. Holders
For purposes of this
summary, a “non-U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of common shares that is not a U.S. Holder. This summary does not
address the U.S. federal income tax consequences to non-U.S. Holders arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and
disposition of common shares. Accordingly, a non-U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S.
federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences (including the potential
application of and operation of any income tax treaties) relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares.
U.S. Holders Subject
to Special U.S. Federal Income Tax Rules Not Addressed
This summary does not
address the U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to U.S. Holders that are subject to special provisions under the
Code, including, but not limited to, the following: (a) U.S. Holders that are tax-exempt organizations, qualified retirement plans,
individual retirement accounts, or other tax-deferred accounts; (b) U.S. Holders that are financial institutions, underwriters,
insurance companies, real estate investment trusts, or regulated investment companies; (c) U.S. Holders that are broker-dealers,
dealers, or traders in securities or currencies that elect to apply a mark-to-market accounting
method; (d) U.S. Holders that have a “functional currency” other than the U.S. dollar; (e) U.S. Holders that own common
shares as part of a straddle, hedging transaction, conversion transaction, constructive sale, or other arrangement involving more
than one position; (f) U.S. Holders that acquired common shares in connection with the exercise of employee stock options or otherwise
as compensation for services; (g) U.S. Holders that hold common shares other than as a capital asset within the meaning of Section
1221 of the Code (generally, property held for investment purposes); or (h) U.S. Holders that own or have owned (directly, indirectly,
or by attribution) 10% or more of the total combined voting power of the outstanding shares of the Company. This summary also does
not address the U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to U.S. Holders who are: (a) U.S. expatriates or former long-term
residents of the U.S.; (b) persons that have been, are, or will be a resident or deemed to be a resident in Canada for purposes
of the Income Tax Act (Canada) (the “Tax Act”); (c) persons that use or hold, will use or hold, or that are or will
be deemed to use or hold common shares in connection with carrying on a business in Canada; (d) persons whose common shares constitute
“taxable Canadian property” under the Tax Act; or (e) persons that have a permanent establishment in Canada for the
purposes of the Canada-U.S. Tax Convention. U.S. Holders that are subject to special provisions under the Code, including, but
not limited to, U.S. Holders described immediately above, should consult their own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S.
federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences relating to the acquisition,
ownership and disposition of common shares.
If an entity or arrangement
that is classified as a partnership (or other “pass-through” entity) for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds common
shares, the U.S. federal income tax consequences to such entity and the partners (or other owners) of such entity generally will
depend on the activities of the entity and the status of such partners (or owners). This summary does not address the tax consequences
to any such owner. Partners (or other owners) of entities or arrangements that are classified as partnerships or as “pass-through”
entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes should consult their own tax advisors regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences
arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares.
Passive Foreign
Investment Company Rules
If the Company were
to constitute a “passive foreign investment company” under the meaning of Section 1297 of the Code (a “PFIC”,
as defined below) for any year during a U.S. Holder’s holding period, then certain potentially adverse rules will affect
the U.S. federal income tax consequences to a U.S. Holder resulting from the acquisition, ownership and disposition of common shares.
The Company believes that it was classified as a PFIC during the tax year ended April 30, 2014, and may be a PFIC in future tax
years. The determination of whether any corporation was, or will be, a PFIC for a tax year depends, in part, on the application
of complex U.S. federal income tax rules, which are subject to differing interpretations. In addition, whether any corporation
will be a PFIC for any tax year depends on the assets and income of such corporation over the course of each such tax year and,
as a result, cannot be predicted with certainty as of the date of this document. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that the
IRS will not challenge any determination made by the Company (or any subsidiary of the Company) concerning its PFIC status. Each
U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the PFIC status of the Company and any subsidiary of the Company.
In addition, in any
year in which the Company is classified as a PFIC, such holder would be required to file an annual report with the IRS containing
such information as Treasury Regulations and/or other IRS guidance may require. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors
regarding the requirements of filing such information returns under these rules, including the requirement to file a IRS Form 8621.
PFIC Status of the
Company
The Company generally
will be a PFIC if, for a tax year, (a) 75% or more of the gross income of the Company is passive income (the “income test”)
or (b) 50% or more of the value of the Company’s assets either produce passive income or are held for the production of passive
income, based on the quarterly average of the fair market value of such assets (the “asset test”). “Gross income”
generally includes all sales revenues less the cost of goods sold, plus income from investments and from incidental or outside
operations or sources, and “passive income” generally includes, for example, dividends, interest, certain rents and
royalties, certain gains from the sale of stock and securities, and certain gains from commodities transactions.
Active business gains
arising from the sale of commodities generally are excluded from passive income if substantially all (85% or more) of a foreign
corporation’s commodities are stock in trade or inventory, depreciable property used in a trade or business, or supplies
regularly used or consumed in a trade or business and certain other requirements are satisfied. For purposes of the PFIC income
test and asset test described above, if the Company owns, directly or indirectly, 25% or more of the total value of the outstanding
shares of another corporation, the Company will be treated as if it (a) held a proportionate share of the assets of such other
corporation and (b) received directly a proportionate share of the income of such other corporation. In addition, for purposes
of the PFIC income test and asset test described above, and assuming certain other requirements are met, “passive income”
does not include certain interest, dividends, rents, or royalties that are received or accrued
by the Company from certain “related persons” (as defined in Section 954(d)(3) of the Code), to the extent such items
are properly allocable to the income of such related person that is not passive income.
Under certain attribution
rules, if the Company is a PFIC, U.S. Holders will generally be deemed to own their proportionate share of the Company’s
direct or indirect equity interest in any company that is also a PFIC (a ‘‘Subsidiary PFIC’’), and will
be subject to U.S. federal income tax on their proportionate share of (a) any “excess distributions,” as described
below, on the stock of a Subsidiary PFIC and (b) a disposition or deemed disposition of the stock of a Subsidiary PFIC by the Company
or another Subsidiary PFIC, both as if such U.S. Holders directly held the shares of such Subsidiary PFIC. In addition, U.S. Holders
may be subject to U.S. federal income tax on any indirect gain realized on the stock of a Subsidiary PFIC on the sale or disposition
of common shares. Accordingly, U.S. Holders should be aware that they could be subject to tax even if no distributions are received
and no redemptions or other dispositions of common shares are made.
Default PFIC Rules Under Section 1291 of
the Code
If the Company is a
PFIC for any tax year during which a U.S. Holder owns common shares, the U.S. federal income tax consequences to such U.S. Holder
of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares will depend on whether and when such U.S. Holder makes an election
to treat the Company and each Subsidiary PFIC, if any, as a “qualified electing fund” or “QEF” under Section
1295 of the Code (a “QEF Election”) or makes a mark-to-market election under Section 1296 of the Code (a “Mark-to-Market
Election”). A U.S. Holder that does not make either a QEF Election or a Mark-to-Market Election will be referred to in this
summary as a “Non-Electing U.S. Holder.” A Non-Electing U.S. Holder will be subject to the rules of Section 1291 of
the Code (described below) with respect to (a) any gain recognized on the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares and
(b) any excess distribution received on the common shares. A distribution generally will be an “excess distribution”
to the extent that such distribution (together with all other distributions received in the current tax year) exceeds 125% of the
average distributions received during the three preceding tax years (or during a U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common
shares, if shorter). Under Section 1291 of the Code, any gain recognized on the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares
(including an indirect disposition of the stock of any Subsidiary PFIC), and any excess distribution” received on
common shares or with respect to the stock of a Subsidiary PFIC, must be ratably allocated to each day in a Non-Electing U.S. Holder’s
holding period for the respective common shares. The amount of any such gain or excess distribution allocated to the tax year of
disposition or distribution of the excess distribution and to years before the entity became a PFIC, if any, would be taxed as
ordinary income. The amounts allocated to any other tax year would be subject to U.S. federal income tax at the highest tax rate
applicable to ordinary income in each such year, and an interest charge would be imposed on the tax liability for each such year,
calculated as if such tax liability had been due in each such year. A Non-Electing U.S. Holder that is not a corporation must treat
any such interest paid as “personal interest,” which is not deductible. If the Company is a PFIC for any tax year during
which a Non-Electing U.S. Holder holds common shares, the Company will continue to be treated as a PFIC with respect to such Non-Electing
U.S. Holder, regardless of whether the Company ceases to be a PFIC in one or more subsequent tax years. A Non-Electing U.S. Holder
may terminate this deemed PFIC status by electing to recognize gain (which will be taxed under the rules of Section 1291 of the
Code discussed above), but not loss, as if such common shares were sold on the last day of the last tax year for which the Company
was a PFIC.
QEF Election
A U.S. Holder that makes a timely
and effective QEF Election for the first tax year in which its holding period of its common shares begins generally will not be
subject to the rules of Section 1291 of the Code discussed above with respect to its common shares. A U.S. Holder that makes a
timely and effective QEF Election will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on such U.S. Holder’s pro rata share of (a)
the net capital gain of the Company, which will be taxed as long-term capital gain to such U.S. Holder, and (b) the ordinary earnings
of the Company, which will be taxed as ordinary income to such U.S. Holder. Generally, “net capital gain” is the excess
of (a) net long-term capital gain over (b) net short-term capital loss, and “ordinary earnings” are the excess of (a)
“earnings and profits” over (b) net capital gain. A U.S. Holder that makes a QEF Election will be subject to U.S. federal
income tax on such amounts for each tax year in which the Company is a PFIC, regardless of whether such amounts are actually distributed
to such U.S. Holder by the Company. However, for any tax year in which the Company is a PFIC and has no net income or gain, U.S.
Holders that have made a QEF Election would not have any income inclusions as a result of the QEF Election. If a U.S. Holder that
made a QEF Election has an income inclusion, such a U.S. Holder may, subject to certain limitations, elect to defer cash payment
of current U.S. federal income tax on such amounts, subject to an interest charge. If such U.S. Holder is not a corporation, any
such interest paid will be treated as “personal interest,” which is not deductible
.
A U.S. Holder that makes a timely and
effective QEF Election with respect to the Company generally (a) may receive a tax-free distribution from the Company to the extent
that such distribution represents “earnings and profits” of the Company that were previously included in income by
the U.S. Holder because of such QEF Election and (b) will adjust such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the common shares to reflect
the amount included in income or allowed as a tax-free distribution because of such QEF Election.
In addition, a U.S. Holder that makes a QEF Election generally will recognize capital gain or loss on the sale or other taxable
disposition of common shares.
The procedure for making a QEF Election,
and the U.S. federal income tax consequences of making a QEF Election, will depend on whether such QEF Election is timely. A QEF
Election will be treated as “timely” if such QEF Election is made for the first year in the U.S. Holder’s holding
period for the common shares in which the Company was a PFIC. A U.S. Holder may make a timely QEF Election by filing the appropriate
QEF Election documents at the time such U.S. Holder files a U.S. federal income tax return for such year. If a U.S. Holder does
not make a timely and effective QEF Election for the first year in the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares,
the U.S. Holder may still be able to make a timely and effective QEF Election in a subsequent year if such U.S. Holder meets certain
requirements and makes a “purging” election to recognize gain (which will be taxed under the rules of Section 1291
of the Code discussed above) as if such common shares were sold for their fair market value on the day the QEF Election is effective.
If a U.S. Holder owns PFIC stock indirectly through another PFIC, separate QEF Elections must be made for the PFIC in which the
U.S. Holder is a direct shareholder and the Subsidiary PFIC for the QEF rules to apply to both PFICs.
A QEF Election will apply to the tax
year for which such QEF Election is timely made and to all subsequent tax years, unless such QEF Election is invalidated or terminated
or the IRS consents to revocation of such QEF Election. If a U.S. Holder makes a QEF Election and, in a subsequent tax year, the
Company ceases to be a PFIC, the QEF Election will remain in effect (although it will not be applicable) during those tax years
in which the Company is not a PFIC. Accordingly, if the Company becomes a PFIC in another subsequent tax year, the QEF Election
will be effective and the U.S. Holder will be subject to the QEF rules described above during any subsequent tax year in which
the Company qualifies as a PFIC.
U.S. Holders should be aware that there
can be no assurances that the Company will satisfy the record keeping requirements that apply to a QEF, or that the Company will
supply U.S. Holders with information that such U.S. Holders are required to report under the QEF rules, in the event that the Company
is a PFIC. Thus, U.S. Holders may not be able to make a QEF Election with respect to their common shares. Each U.S. Holder should
consult its own tax advisor regarding the availability of, and procedure for making, a QEF Election.
A U.S. Holder makes a QEF Election by
attaching a completed IRS Form 8621, including a PFIC Annual Information Statement, to a timely filed United States federal income
tax return. However, if the Company cannot provide the required information with regard to the Company or any of its Subsidiary
PFICs, U.S. Holders will not be able to make a QEF Election for such entity and will continue to be subject to the rules discussed
above that apply to Non-Electing U.S. Holders with respect to the taxation of gains and excess distributions.
Mark-to-Market Election
A U.S. Holder may make a Mark-to-Market
Election only if the common shares are marketable stock. The common shares generally will be “marketable stock”
if the common shares are regularly traded on (a) a national securities exchange that is registered with the Securities and
Exchange Commission, (b) the national market system established pursuant to section 11A of the Securities and Exchange Act of
1934, or (c) a foreign securities exchange that is regulated or supervised by a governmental authority of the country in
which the market is located, provided that (i) such foreign exchange has trading volume, listing, financial disclosure, and
surveillance requirements, and meets other requirements and the laws of the country in which such foreign exchange is
located, together with the rules of such foreign exchange, ensure that such requirements are actually enforced and (ii) the
rules of such foreign exchange effectively promote active trading of listed stocks. If such stock is traded on such a
qualified exchange or other market, such stock generally will be “regularly traded” for any calendar year during
which such stock is traded, other than in de minimis quantities, on at least 15 days during each calendar quarter. A U.S.
Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election with respect to its common shares generally will not be subject to the rules of
Section 1291 of the Code discussed above with respect to such common shares. However, if a U.S. Holder does not make a
Mark-to-Market Election beginning in the first tax year of such U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares or
such U.S. Holder has not made a timely QEF Election, the rules of Section 1291 of the Code discussed above will apply to
certain dispositions of, and distributions on, the common shares. A U.S. Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election
will include in ordinary income, for each tax year in which the Company is a PFIC, an amount equal to the excess, if any, of
(a) the fair market value of the common shares, as of the close of such tax year over (b) such U.S. Holder’s tax
basis in such common shares. A U.S. Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election will be allowed a deduction in an amount
equal to the excess, if any, of (a) such U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the common shares, over (b) the fair
market value of such common shares (but only to the extent of the net amount of previously included income as a result of the
Mark-to-Market Election for prior tax years). A U.S. Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election generally also will
adjust such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the common shares to reflect the amount included in gross income or allowed as a
deduction because of such Mark-to-Market Election. In addition, upon a sale or other
taxable disposition of common shares, a U.S. Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election will recognize ordinary income or ordinary
loss (not to exceed the excess, if any, of (a) the amount included in ordinary income because of such Mark-to-Market Election for
prior tax years over (b) the amount allowed as a deduction because of such Mark-to-Market Election for prior tax years). Losses
that exceed this limitation are subject to the rules generally applicable to losses provided in the Code and Treasury Regulations.
A Mark-to-Market Election applies to
the tax year in which such Mark-to-Market Election is made and to each subsequent tax year, unless the common shares cease to be
“marketable stock” or the IRS consents to revocation of such election. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax
advisor regarding the availability of, and procedure for making, a Mark-to-Market Election.
Although a U.S. Holder may be eligible
to make a Mark-to-Market Election with respect to the common shares, no such election may be made with respect to the stock of
any Subsidiary PFIC that a U.S. Holder is treated as owning, because such stock is not marketable. Hence, the Mark-to-Market Election
will not be effective to eliminate the application of the default rules of Section 1291 of the Code described above with respect
to deemed dispositions of Subsidiary PFIC stock or excess distributions from a Subsidiary PFIC.
Other PFIC Rules
Under Section 1291(f) of the Code, the
IRS has issued proposed Treasury Regulations that, subject to certain exceptions, would cause a U.S. Holder that had not made a
timely QEF Election to recognize gain (but not loss) upon certain transfers of common shares that would otherwise be tax-deferred
(e.g., gifts and exchanges pursuant to corporate reorganizations). However, the specific U.S. federal income tax consequences to
a U.S. Holder may vary based on the manner in which common shares are transferred.
Certain additional adverse rules may
apply with respect to a U.S. Holder if the Company is a PFIC, regardless of whether such U.S. Holder makes a QEF Election. For
example, under Section 1298(b)(6) of the Code, a U.S. Holder that uses common shares as security for a loan will, except as may
be provided in Treasury Regulations, be treated as having made a taxable disposition of such common shares.
Special rules also apply to the amount
of foreign tax credit that a U.S. Holder may claim on a distribution from a PFIC. Subject to such special rules, foreign taxes
paid with respect to any distribution in respect of stock in a PFIC are generally eligible for the foreign tax credit. The rules
relating to distributions by a PFIC and their eligibility for the foreign tax credit are complicated, and a U.S. Holder should
consult with its own tax advisor regarding the availability of the foreign tax credit with respect to distributions by a PFIC.
The PFIC rules are
complex, and each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the PFIC rules and how the PFIC rules may affect the
U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares.
Ownership and Disposition
of Common Shares
The following discussion is subject
to the rules described above under the heading “Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules.”
Distributions on
Common Shares
A U.S. Holder that
receives a distribution, including a constructive distribution, with respect to a common share will be required to include the
amount of such distribution in gross income as a dividend (without reduction for any Canadian income tax withheld from such distribution)
to the extent of the current or accumulated “earnings and profits” of the Company, as computed for U.S. federal income
tax purposes. A dividend generally will be taxed to a U.S. Holder at ordinary income tax rates if the Company is a PFIC. To the
extent that a distribution exceeds the current and accumulated “earnings and profits” of the Company, such distribution
will be treated first as a tax-free return of capital to the extent of a U.S. Holder's tax basis in the common shares and thereafter
as gain from the sale or exchange of such common shares. (See “Sale or Other Taxable Disposition of common shares”
below). However, the Company may not maintain the calculations of earnings and profits in accordance with U.S. federal income tax
principles, and each U.S. Holder should therefore assume that any distribution by the Company with respect to the common shares
will constitute ordinary dividend income. Dividends received on common shares generally will not be eligible for the “dividends
received deduction”. In addition, the Company does not anticipate that its distributions will constitute qualified dividend
income eligible for the preferential tax rates applicable to long-term capital gains. The dividend rules are complex, and each
U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the application of such rules.
Sale or Other Taxable
Disposition of Common Shares
Upon the sale or other
taxable disposition of common shares, a U.S. Holder generally will recognize capital gain or loss in an amount equal to the difference
between the U.S. dollar value of cash received plus the fair market value of any property received and such U.S. Holder's tax basis
in such common shares sold or otherwise disposed of. A U.S. Holder’s tax basis in common shares generally will be such holder’s
U.S. dollar cost for such common shares. Gain or loss recognized on such sale or other disposition generally will be long-term
capital gain or loss if, at the time of the sale or other disposition, the common shares have been held for more than one year.
Preferential tax rates
currently apply to long-term capital gain of a U.S. Holder that is an individual, estate, or trust. There are currently no preferential
tax rates for long-term capital gain of a U.S. Holder that is a corporation. Deductions for capital losses are subject to significant
limitations under the Code.
Additional Considerations
Additional Tax on Passive
Income
For tax years beginning after
December 31, 2012, certain individuals, estates and trusts whose income exceeds certain thresholds will be required to pay a 3.8%
Medicare surtax on “net investment income” including, among other things, dividends and net gain from dispositions
of property (other than property held in a trade or business). U.S. Holders should consult with their own tax advisors regarding
the effect, if any, of this tax on their ownership and disposition of common shares.
Receipt of Foreign
Currency
The amount of any distribution
paid to a U.S. Holder in foreign currency, or on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of common shares, generally will
be equal to the U.S. dollar value of such foreign currency based on the exchange rate applicable on the date of receipt (regardless
of whether such foreign currency is converted into U.S. dollars at that time). A U.S. Holder will have a basis in the foreign currency
equal to its U.S. dollar value on the date of receipt. Any U.S. Holder who converts or otherwise disposes of the foreign currency
after the date of receipt may have a foreign currency exchange gain or loss that would be treated as ordinary income or loss, and
generally will be U.S. source income or loss for foreign tax credit purposes. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own U.S. tax
advisor regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of receiving, owning, and disposing of foreign currency.
Foreign Tax Credit
Subject to the PFIC
rules discussed above, a U.S. Holder that pays (whether directly or through withholding) Canadian income tax with respect to dividends
paid on the common shares generally will be entitled, at the election of such U.S. Holder, to receive either a deduction or a credit
for such Canadian income tax. Generally, a credit will reduce a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability on a dollar-for-dollar
basis, whereas a deduction will reduce a U.S. Holder’s income subject to U.S. federal income tax. This election is made on
a year-by-year basis and applies to all foreign taxes paid (whether directly or through withholding) by a U.S. Holder during a
year.
Complex limitations
apply to the foreign tax credit, including the general limitation that the credit cannot exceed the proportionate share of a U.S.
Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability that such U.S. Holder’s “foreign source” taxable income bears
to such U.S. Holder’s worldwide taxable income. In applying this limitation, a U.S. Holder’s various items of income
and deduction must be classified, under complex rules, as either “foreign source” or “U.S. source.” Generally,
dividends paid by a foreign corporation should be treated as foreign source for this purpose, and gains recognized on the sale
of stock of a foreign corporation by a U.S. Holder should be treated as U.S. source for this purpose, except as otherwise provided
in an applicable income tax treaty, and if an election is properly made under the Code. However, the amount of a distribution with
respect to the common shares that is treated as a “dividend” may be lower for U.S. federal income tax purposes than
it is for Canadian federal income tax purposes, resulting in a reduced foreign tax credit allowance to a U.S. Holder. In addition,
this limitation is calculated separately with respect to specific categories of income. The foreign tax credit rules are complex,
and each U.S. Holder should consult its own U.S. tax advisor regarding the foreign tax credit rules.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
Under U.S. federal
income tax law and Treasury Regulations, certain categories of U.S. Holders must file information returns with respect to their
investment in, or involvement in, a foreign corporation. For example, recently enacted legislation generally imposes new U.S. return
disclosure obligations (and related penalties) on individuals who are U.S. Holders that hold certain specified foreign financial
assets in excess of $50,000. The definition of specified foreign financial assets includes not only financial accounts maintained
in foreign financial institutions, but also, unless held in accounts maintained by a financial institution, any stock or security
issued by a non-U.S. person, any financial instrument or contract held for investment that has an issuer or counterparty other
than a U.S. person and any interest in a foreign entity. U.S. Holders may be subject to these reporting requirements unless their
common shares are held in an account at a domestic financial
institution. Penalties for failure to file certain of these information returns are substantial. U.S. Holders should consult with
their own tax advisors regarding the requirements of filing information returns, including the requirement to file an IRS Form
8938. Payments made within the U.S. or by a U.S. payor or U.S. middleman, of dividends on, and proceeds arising from the sale or
other taxable disposition of, common shares will generally be subject to information reporting and backup withholding tax, at the
rate of 28% (and increasing to 31% for payments made after December 31, 2012), if a U.S. Holder (a) fails to furnish such U.S.
Holder’s correct U.S. taxpayer identification number (generally on Form W-9), (b) furnishes an incorrect U.S. taxpayer identification
number, (c) is notified by the IRS that such U.S. Holder has previously failed to properly report items subject to backup withholding
tax, or (d) fails to certify, under penalty of perjury, that such U.S. Holder has furnished its correct U.S. taxpayer identification
number and that the IRS has not notified such U.S. Holder that it is subject to backup withholding tax. However, certain exempt
persons generally are excluded from these information reporting and backup withholding rules. Backup withholding is not an additional
tax. Any amounts withheld under the U.S. backup withholding tax rules will be allowed as a credit against a U.S. Holder’s
U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, or will be refunded, if such U.S. Holder furnishes required information to the IRS in
a timely manner. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the information reporting and backup withholding
rules.
| F. | | Dividends and Paying Agents |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
Any statement in this annual report about any
of the Company's contracts or other documents is not necessarily complete. If the contract or document is filed as an exhibit to
this annual report, the contract or document is deemed to modify the description contained in this annual report. Readers must
review the exhibits themselves for a complete description of the contract or document.
Readers may review a copy of the Company's
filings with the SEC, including exhibits and schedules filed with it, at the SEC's public reference facilities at 100 F Street,
N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. Readers may call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the public reference rooms.
The SEC maintains a Web site (http://www.sec.gov) that contains reports, submissions and other information regarding registrants
that file electronically with the SEC. The Company also files electronically through the EDGAR system.
Readers may read and copy any reports, statements
or other information that the Company files with the SEC at the address indicated above and may also access them electronically
at the Web site set forth above. These SEC filings are also available to the public from commercial document retrieval services.
Any documents referred to in this annual report
may be inspected at the head office of the Company, 1020 – 625 Howe Street, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6C 2T6, Canada,
during normal business hours.
There is no information relating to the Company’s
subsidiaries which must be provided in Canada and which are not otherwise called for by the body of generally accepted accounting
principles used in preparing the consolidated financial statements.
| ITEM 11. | | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURE ABOUT MARKET RISK |
The Company anticipates its primary market
risk, if any, to be related to fluctuations in exchange rates. Exchange rate risk may arise if the Company is required to use different
currencies for various aspects of its operations. At present, the functional currency for the Company is the Canadian dollar. Based
on the Company’s overall exchange rate risk as at April 30, 2013, the Company believes that a 10% change in exchange rates
would not have a material adverse effect on its financial position, financial performance, or changes in financial position. The
Company intends to monitor its exchange rate risk and take reasonable steps to reduce its exposure. The Company does not intend
to purchase or sell derivative instruments for speculative purposes.
| ITEM 12. | | DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES |
This Form 20-F is being filed as an annual
report under the Exchange Act and, as such, there is no requirement to provide any information under this section.
PART
II
| ITEM 13. | | DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARS AND DELINQUENCIES |
There has not been a material default in the
payment of principal, interest, a sinking or purchase fund installment, or any other material default not cured within thirty days,
relating to indebtedness of the Company or any of its significant subsidiaries. There are no payments of dividends by the Company
in arrears, nor has there been any other material delinquency relating to any class of preference shares of the Company.
| ITEM 14. | | MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS |
Not applicable.
| ITEM 15. | | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
At the end of the period covered by this annual
report on Form 20-F, an evaluation was carried out under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management,
including the Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and the Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), of the effectiveness
of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a - 15(e)and 15d - 15(e) under the Exchange Act).
Based on that evaluation, the CEO and the CFO have concluded that as of the end of the period covered by this annual report on
Form 20-F, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective in ensuring that: (i) information required to
be disclosed by the Company in reports that it files or submits to the SEC under the Exchange Act was recorded, processed, summarized
and reported within the time periods specified in applicable rules and forms and (ii) material information required to be disclosed
in the Company’s reports filed under the Exchange Act was accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management,
including the CEO and the CFO, as appropriate, to allow for accurate and timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial
Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible
for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)
under the Exchange Act. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable
assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements for
external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
The Company’s management, including its
CEO and CFO, does not expect that its disclosure controls and procedures or internal controls and procedures will prevent all error
and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance
that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are
resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs.
Because of the inherent limitations in all
control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any,
within the Company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be
faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual
acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of
controls is also based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that
any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions; over time, controls may become inadequate
because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of the inherent
limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
With the participation of the CEO and CFO,
management conducted an evaluation of the design and operation of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting
as of April 30, 2014, based on the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992) issued
by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. This evaluation included review of the documentation of
controls, evaluation of the design effectiveness of controls, testing of the operating effectiveness of controls and a conclusion
on this evaluation. Based on this evaluation, management concluded in its report that the Company’s internal control over
financial reporting was effective as of April 30, 2014.
Attestation Report of the Independent Registered Public Accounting
Firm
This annual report does not include an attestation
report of our independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management’s
report was not subject to attestation by our registered public accounting firm pursuant the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer
Protection Act of 2010, which permits the company to provide only management’s report in this annual report. The Dodd-Frank
Act permits a “non-accelerated filer” to provide only management’s report on internal control over financial
reporting in an annual report and omit an attestation report of the issuer’s registered public accounting firm regarding
management’s report on internal control over financial reporting.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
During the period covered by this annual report
on Form 20-F, no changes occurred in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that have materially affected,
or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| ITEM 16A. | | AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT |
Composition of the Audit Committee
The Company’s audit committee members
are Jean Luc Roy, Victor Fern and Kathleen K. Townsend. All of the audit committee members are independent directors, as such term
is defined by the listing standards of the NYSE MKT. The board of directors has determined that the Chairman of the Company’s
audit committee, Jean Luc Roy, qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as that term is defined in Item 16A(b)
of Form 20-F. As a result of their education and experience, each member of the audit committee has familiarity with, and understanding
of, or experience in accounting principles used by the Company to prepare its financial statements, in reviewing and evaluating
the financial statements and are familiar with internal controls and procedures for financial reporting.
Mr. Roy is Chairman and an independent member
of the audit committee and is financially literate. Mr. Roy has an understanding of IFRS and financial statements. He has the ability
to assess the general application of such principles in connection with accounting for estimates, accruals and reserves. In addition
he has the background and experience to deal with the complexity of accounting issues that can be reasonably raised by the registrant’s
financial statements. Mr. Roy has an understanding of internal controls and the functioning of the audit committee and has experience
overseeing the financial reporting function. Mr. Roy has been a director or executive officer of several exploration and mining
companies for the past 20 years. Mr. Roy was the past President and CEO of El Nino Ventures Inc. Mr. Roy is presently a resident
of Burkina Faso where is he COO of Ampella Mining Ltd., an Australian-listed company focused on gold exploration in West Africa,
with their flagship property, Batie West.
Victor Fern is an independent member of the
audit committee and is financially literate. Mr. Fern has the ability to assess the general application of such principles in connection
with accounting for estimates, accruals and reserves.
Kathleen Townsend is an independent member
of the audit committee and is financially literate. Ms. Townsend has the ability to assess the general application of such principles
in connection with accounting for estimates, accruals and reserves. She is a Managing Director at the Rock Creek Group, an investment
management company. Ms. Townsend founded the Center for Retirement Initiatives at the McCourt School of Public Policy at Georgetown
University, where she is a Research Professor. As the State of Maryland’s first woman Lieutenant Governor, Ms. Townsend was
in charge of a multimillion dollar budget and had oversight of major cabinet departments, including Economic Development and Transportation,
State Police, Public Safety and Correction and Juvenile Justice. Prior to being elected Lt. Governor, Ms. Townsend served as Deputy
Assistant Attorney General of the United States.
A copy of the audit committee charter is available
on the Company’s website and is available by contacting the Company directly. The Audit Committee Charter is filed herewith.
The Company has adopted a Code of Ethics (“COE”)
which defines certain fundamental principles, policies and procedures that govern the directors, officers, employees, advisors
and contractors. The Company is committed to conducting its business in accordance with
applicable laws, rules and regulations and to the highest standard of business ethics. A copy of the COE is provided to all individuals
associated with the Company including outside contractors.
The COE establishes a level of awareness and
expectations in certain areas of behaviour such as conflicts of interest, gifts and entertainment, competitive practices, disclosure
policies, legal compliance, financial reporting, records, company assets, workplace environment and Health and Safety. A whistle
blower system for reporting violations to the COE has been established and is routinely revisited during regular employee meeting
and orientations.
The COE is posted on the Company’s website,
and has been posted on SEDAR and EDGAR. A copy of the COE may be requested by contacting the head office at #1020 –
625 Howe Street, Vancouver, BC, V6C 2T6, by telephone 604.688.3211, fax 604.688.3217 or via e-mail at dszigety@canalaska.com. The
Code of Ethics is included as Exhibit 11.1 herewith.
|
ITEM 16C.
| | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
The following table discloses the aggregate
fees billed for each of the last two financial years for professional services rendered by the Company’s audit firm, Deloitte
LLP, for various services in Canadian Dollars.
| Financial Year Ended |
Audit Fees |
Audit-Related Fees |
Tax Advisory Fees |
All Other Fees |
| 2014 |
$45,000 |
$20,910 |
$28,623 |
$Nil |
| 2013 |
$40,000 |
$24,610 |
$17,280 |
$Nil |
From time to time,
management of the Company recommends to and requests approval from the audit committee for non-audit services to be provided by
the Company’s auditors. The audit committee routinely considers such requests at committee meetings, and if acceptable to
a majority of the audit committee members, pre-approves such non-audit services by a resolution authorizing management to engage
the Company’s auditors for such non-audit services, with set maximum dollar amount for each itemized service. During such
deliberations, the audit committee assesses, among other factors, whether the services requested would be considered “prohibited
services” as contemplated by the US Securities and Exchange Commission, and whether the services requested and the fees related
to such services could impair the independence of the auditors.
| ITEM 16D. | | EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES |
None.
| ITEM 16E. | | PURCHASE OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS |
There have been
no purchases made on behalf of the issuer or any affiliate issuer during this reporting period.
| ITEM 16F. | | CHANGE IN REGISTRANTS CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT |
None.
| ITEM 16G. | | CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Not applicable.
| ITEM 16H. | | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE |
Not applicable
PART III
| ITEM 17. | | CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
Not applicable.
| ITEM 18. | | CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
See the consolidated financial statements and
Exhibits listed in Item 19 hereof and filed as part of this Annual Report.
The audited consolidated financial statements
of the Company and exhibits listed below are filed with this annual report on Form 20-F in the United States. The financial statements
appear on Pages F-1 through F-41. The following financial statements are attached to and form a part of this report filed with
the SEC:
Consolidated
Financial Statements of the Company:
| · | Report of Independent Registered Public
Accounting Firm on Consolidated Financial Statements for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012 . |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Financial Position
as at April 30, 2014 and 2013. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Loss, Comprehensive
Loss and Deficit for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012. |
| · | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for
the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012. |
| · | Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
EXHIBIT INDEX
The following exhibits are attached to and form part of this Annual Report:
Exhibit |
| 1.1 |
Articles of Incorporation* |
| 11.1 |
Code of Ethics |
| 12.1 |
Section 302 Certification of the Company's Chief Executive Officer |
| 12.2 |
Section 302 Certification of the Company's Chief Financial Officer |
| 13.1 |
Section 906 Certification of the Company's Chief Executive Officer |
| 13.2 |
Section 906 Certification of the Company's Chief Financial Officer |
| 14.1 |
Management Discussion and Analysis dated July 29, 2014 |
| 14.2 |
Audit Committee Charter |
| 14.3 |
Corporate Governance Policy |
* Previously filed and incorporated by reference
from our Form 20-F filed with the SEC on September 14, 2010
SIGNATURES
The Company hereby certifies that it meets
all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this annual
report on its behalf.
Date: August 27, 2014
CANALASKA URANIUM LTD.
“Peter
Dasler”
President & CEO
“Harry
Chan”
Chief Financial Officer

CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Consolidated Financial Statements
April 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars, except where
indicated)
Deloitte LLP
2800 - 1055 Dunsmuir Street
4 Bentall Centre
P.O. Box 49279
Vancouver BC V7X 1P4
Canada
Tel: 604-669-4466
Fax: 778-374-0496
www.deloitte.ca
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated financial statements
of CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. and subsidiaries (the “Company”), which comprise the consolidated statements of financial
position as at April 30, 2014 and April 30, 2013, and the consolidated statements of loss and comprehensive loss, changes in equity,
and cash flows for each of the years in the three year period ended April 30, 2014, and a summary of significant accounting policies
and other explanatory information.
Management's Responsibility for the Consolidated Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation
of these consolidated financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International
Accounting Standards Board, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of consolidated
financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
Auditor's Responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated
financial statements based on our audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with Canadian generally accepted auditing standards
and the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we comply with
ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements
are free from material misstatement. We were not engaged
to perform an audit of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal
control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for
the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly,
we express no such opinion.
An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence
about the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the auditor's judgment,
including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to fraud or
error. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates
made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements.
We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained in our audits
is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly,
in all material respects, the financial position of CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. and subsidiaries as at April 30, 2014 and April 30,
2013, and their financial performance and their cash flows for each of the years in the three year period ended April 30, 2014
in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Emphasis of Matter
Without qualifying our opinion, we draw attention to Note 2 in
the consolidated financial statements which indicates that the Company does not earn revenues from its operations, incurred a net
loss of $0.7 million during the year ended April 30, 2014, and has a deficit of $81.6 million at April 30, 2014. Accordingly, the
Company depends on its ability to raise financing in order to discharge its commitments and liabilities in the normal course of
business. These matters, along with the other matters set forth in Note 2, indicate the existence of material uncertainties that
cast substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
/s/Deloitte LLP
Chartered Accountants
July 29, 2014
Vancouver, Canada
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Financial Position
As at April 30, 2014 and 2013
(Expressed in Canadian dollars
except where indicated)
| |
|
|
April 30
2014
$000’s |
April 30
2013
$000’s |
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Current assets |
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents (note 5) |
|
|
1,044 |
1,265 |
| Trade and other receivables |
|
|
52 |
58 |
| Available-for-sale securities (note 6) |
|
|
414 |
86 |
| Total current assets |
|
|
1,510 |
1,409 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Non-current assets |
|
|
|
|
| Reclamation bonds |
|
|
189 |
203 |
| Property and equipment (note 7) |
|
|
294 |
375 |
| Mineral property interests (note 8) |
|
|
813 |
1,238 |
| Total assets |
|
|
2,806 |
3,225 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Trade and other payables |
|
|
382 |
195 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Equity |
|
|
|
|
| Common shares (note 9) |
|
|
73,205 |
73,205 |
| Equity reserve (note 10) |
|
|
10,807 |
10,682 |
| Investment revaluation reserve |
|
|
(24) |
(1) |
| Deficit |
|
|
(81,564) |
(80,856) |
| |
|
|
2,424 |
3,030 |
| |
|
|
2,806 |
3,225 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Going Concern (note 2) |
|
|
|
|
| Commitments (note 13) |
|
|
|
|
| Subsequent Events (note 17) |
|
|
|
|
Approved by the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors
| “Peter Dasler” |
|
|
“Jean Luc Roy” |
|
| Director |
|
Director |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated
financial statements.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Net Loss and Comprehensive Loss
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30,
2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars
except where indicated)
| |
|
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
| |
|
($000's) |
($000's) |
($000's) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| EXPLORATION COSTS |
|
|
|
|
| Mineral property expenditures |
|
271 |
632 |
4,825 |
| Mineral property write-offs (note 8) |
|
357 |
137 |
451 |
| Write-down on reclamation bonds |
|
3 |
110 |
- |
| Equipment rental income |
|
(12) |
(3) |
(157) |
| Recoveries on option payments received (note 8) |
|
(746) |
- |
- |
| |
|
(127) |
876 |
5,119 |
| OTHER EXPENSES (INCOME) |
|
|
|
|
| Consulting, labour and professional fees |
|
402 |
834 |
1,255 |
| Depreciation and amortization (note 7) |
|
80 |
108 |
136 |
| Loss (gain) on disposal of property and equipment |
|
5 |
4 |
(7) |
| Foreign exchange loss (gain) |
|
1 |
(1) |
(4) |
| Insurance, licenses and filing fees |
|
98 |
85 |
115 |
| Interest income |
|
(10) |
(24) |
(119) |
| Other corporate costs |
|
33 |
67 |
164 |
| Investor relations and presentations |
|
22 |
52 |
132 |
| Rent |
|
26 |
127 |
134 |
| Share-based payments (note 10) |
|
125 |
176 |
319 |
| Travel and accommodation |
|
9 |
19 |
68 |
| Management fee income |
|
(30) |
(46) |
(363) |
| Impairment of available-for-sale securities (note 6) |
|
74 |
83 |
122 |
| Premium on flow-through shares (note 9) |
|
- |
- |
(202) |
| |
|
835 |
1,484 |
1,750 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Net loss for the year |
|
(708) |
(2,360) |
(6,869) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
|
| Items that may be subsequently reclassified to profit or loss: |
|
|
|
|
| Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities (note 6) |
|
23 |
54 |
214 |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year |
|
(731) |
(2,414) |
(7,083) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Basic and diluted loss per share ($ per share) |
|
(0.03) |
(0.11) |
(0.34) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average common
shares outstanding
(000's) |
|
22,066 |
22,058 |
20,425 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated
financial statements.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30,
2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars
except where indicated)
| |
|
|
|
Investment Revaluation Reserve
$000’s |
Accumulated
Deficit
$000’s |
Total
Equity
$000’s |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Common Shares |
Equity
Reserve
$000’s |
| |
|
Shares
000’s |
Amount
$000’s |
| Balance-May 1, 2011 |
|
19,830 |
72,108 |
10,170 |
267 |
(71,627) |
10,918 |
| Issued on private placement for cash |
|
2,223 |
1,168 |
- |
- |
- |
1,168 |
| Warrants issued on private placement |
|
- |
- |
12 |
- |
- |
12 |
| Issued to acquire mineral property interest |
|
5 |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
4 |
| Share issuance costs |
|
- |
(70) |
- |
- |
- |
(70) |
| Share-based payments |
|
- |
- |
324 |
- |
- |
324 |
| Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities |
|
- |
- |
- |
(214) |
- |
(214) |
| Net loss for the year |
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
(6,869) |
(6,869) |
| Balance-April 30, 2012 |
|
22,058 |
73,210 |
10,506 |
53 |
(78,496) |
5,273 |
| Share issuance costs |
|
- |
(5) |
- |
- |
- |
(5) |
| Share-based payments |
|
- |
- |
176 |
- |
- |
176 |
| Change in fair value of available-for-sale securities |
|
- |
- |
- |
(137) |
- |
(137) |
| Reclassification of losses on available-for-sale securities to earnings |
|
- |
- |
- |
83 |
- |
83 |
| Net loss for the year |
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
(2,360) |
(2,360) |
| Balance-April 30, 2013 |
|
22,058 |
73,205 |
10,682 |
(1) |
(80,856) |
3,030 |
| Issued to acquire mineral property interest |
|
10 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
| Share issuance costs |
|
- |
(1) |
- |
- |
- |
(1) |
| Share-based payments |
|
- |
- |
125 |
- |
- |
125 |
| Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities |
|
- |
- |
- |
(23) |
- |
(23) |
| Loss for the year |
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
(708) |
(708) |
| Balance-April 30, 2014 |
|
22,068 |
73,205 |
10,807 |
(24) |
(81,564) |
2,424 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated
financial statements.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30,
2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars
except where indicated)
| |
|
|
|
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
| |
|
|
|
$000’s |
$000’s |
$000’s |
| Cash flows used in operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Net loss for the year |
|
|
|
(708) |
(2,360) |
(6,869) |
| Items not affecting cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Impairment of available-for-sale securities (note 6) |
|
|
|
74 |
83 |
122 |
| Loss (gain) on disposal of property and equipment |
|
|
|
5 |
4 |
(7) |
| Depreciation and amortization (note 7) |
|
|
|
80 |
108 |
136 |
| Premium on flow-through shares (note 9) |
|
|
|
- |
- |
(202) |
| Mineral property write-offs |
|
|
|
357 |
137 |
451 |
| Write-down on reclamation bonds |
|
|
|
3 |
110 |
- |
| Other |
|
|
|
- |
- |
10 |
| Recoveries on option payments received |
|
|
|
(746) |
- |
- |
| Share-based payments (note 10) |
|
|
|
125 |
176 |
319 |
| Interest income |
|
|
|
(10) |
(24) |
(119) |
| |
|
|
|
(820) |
(1,766) |
(6,159) |
| Interest received |
|
|
|
15 |
30 |
118 |
| Change in non-cash operating working capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Decrease in trade and other receivables |
|
|
|
2 |
180 |
181 |
| Increase (decrease) in trade and other payables |
|
|
|
187 |
(1,640) |
(670) |
| |
|
|
|
(616) |
(3,196) |
(6,530) |
| Cash flows from/used in financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common shares (net of share issue costs) |
|
|
|
(1) |
(5) |
1,311 |
| |
|
|
|
(1) |
(5) |
1,311 |
| Cash flows from/used in investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Additions to mineral property interests |
|
|
|
(19) |
(20) |
(10) |
| Acquisition of property and equipment |
|
|
|
- |
(2) |
(43) |
| Option payments received |
|
|
|
385 |
75 |
- |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment |
|
|
|
20 |
19 |
26 |
| Reclamation bond |
|
|
|
10 |
- |
(2) |
| |
|
|
|
396 |
72 |
(29) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
(221) |
(3,129) |
(5,248) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents - beginning of year (note 5) |
|
|
|
1,265 |
4,394 |
9,642 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents - end of year (note 5) |
|
|
|
1,044 |
1,265 |
4,394 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated
financial statements.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. (the “Company”
or “CanAlaska”) and its subsidiaries are principally engaged in the exploration of uranium properties. The Company
may brings the properties to production, structures joint ventures with others, option or lease properties to third parties or
sell the properties outright. The Company has not determined whether these properties contain ore reserves that are economically
recoverable and the Company is considered to be in the exploration stage. From time to time, the Company evaluates new properties
and directs exploration on these properties based on the Board of Director’s evaluation of financial and market considerations
at the time. On December 30, 2013, the Company’s shares commenced trading on the TSX Venture Exchange under the symbol “CVV”
and ceased trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange. The Company’s shares are also quoted on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board
(“OTCBB”) in the United States under the symbol “CVVUF” and the Frankfurt Stock Exchange under the symbol
“DH7N”. The Company’s registered office is located at 625 Howe Street, Suite 1020, Vancouver, British Columbia,
V6C 2T6, Canada.
These consolidated financial statements have
been prepared on a going concern basis. The going concern basis of presentation assumes that the Company will continue in operation
for the foreseeable future and be able to realize its assets and discharge its liabilities and commitments in the normal course
of business. These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments to the carrying values of assets and liabilities
and the reported expenses and statement of financial position classification that would be necessary should the Company be unable
to continue as a going concern. These adjustments could be material.
The recoverability of the amounts shown for
mineral properties and related deferred costs is dependent upon the existence of economically recoverable mineral reserves, the
ability of the Company to obtain the necessary financing to complete the development, and upon future profitable production or
proceeds from disposition of the mineral properties. Due to increasingly difficult market conditions facing junior uranium exploration
companies there is no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising additional financing. The amounts shown as mineral
property costs represent acquisition costs incurred to date, net of recoveries.
At April 30, 2014, the Company had
cash and cash equivalents of $1.0 million (April 30, 2013: $1.3 million) (note 5) and working capital of $1.1 million (April 30,
2013: $1.2 million). The Company does not earn revenues from its operations, incurred a net loss of $0.7 million during the year
ended April 30, 2014, and has a deficit of $81.6 million at April 30, 2014. Management believes that the cash on hand is sufficient
to meet corporate, administrative and selected exploration activities for at least the next twelve months and closed a substantial
cash injection transaction following the year end (note 17). Management may either need to dilute its ownership in its properties
or secure additional financing to continue to advance the development of its exploration projects. Management has taken steps to
streamline non-discretionary expenditures and financial overheads and is working to option, joint venture or sell its individual
exploration projects. The above factors may cast substantial doubt regarding the Company’s ability to continue as a going
concern.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
| a) | | Statement of Compliance |
These consolidated financial statements have
been prepared in accordance with and in compliance with International Financial Reporting Standard as issued by the International
Accounting Standards Boards (“IFRS”). The policies applied in these consolidated financial statements are presented
in note 3 and are based on IFRS issued and effective at April 30, 2014. These consolidated financial statements were approved by
the Board of Directors for issue on July 29, 2014.
These consolidated financial statements are
presented in Canadian dollars. The consolidated financial statements are prepared on the historical cost basis except for certain
financial instruments that are measured on the fair value basis.
These consolidated financial statements include the accounts of
CanAlaska and its wholly-owned subsidiaries including:
- CanAlaska Resources Ltd. U.S.A., a Nevada company
- CanAlaska West McArthur Uranium Ltd., a B.C. company
- Golden Fern Resources Limited, a New Zealand company
- Poplar Uranium Limited., a B.C. company
Subsidiaries are entities over which
the Company has the power, directly or indirectly, to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity so as to obtain
benefits from its activities. In assessing control, potential voting rights that are presently exercisable or convertible, are
taken into account in the assessment of whether control exists. Subsidiaries are consolidated from the date on which control is
transferred to the Company. They are deconsolidated from the date on which control ceases. All inter-company transactions, balances,
income and expenses have been eliminated on consolidation.
These consolidated financial statements
also include the Company's share of the jointly held assets, its jointly incurred liabilities, and its share of the revenues and
expenses of the CanAlaska Korean Uranium Limited Partnership (“CKULP” or the “Partnership” or the “CKU
Partnership”) and CanAlaska Korean Uranium Limited.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
The Company operates an equity-settled, share-based
compensation plan, under which the entity receives services from employees and non-employees as consideration for equity instruments
(options) of the Company. The total amount to be expensed is determined by reference to the fair value of the options granted.
The fair value of share-based compensation
is determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and management’s assumptions as disclosed in note 10. When a stock
option is exercised, the Company recognizes an increase in its share capital equivalent to the consideration paid by the option
holder and the fair value amount previously recognized in equity reserve. The fair value of any stock options granted to directors,
officers and employees of the Company is recorded as an expense over the vesting period of the options with a corresponding increase
in equity reserve.
Income tax expense consists of current and
deferred tax expense. Income tax is recognized in the consolidated statement of net loss and comprehensive loss except to the extent
it relates to items recognized directly in equity, in which case the related taxes are recognized in equity.
Current tax expense is the expected tax payable
on the taxable income for the year, using tax rates substantially enacted at period end, adjusted for amendments to tax payable
with regards to previous years.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized
for deferred tax consequences attributable to unused tax loss carry forwards, unused tax credits and differences between the financial
statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. Deferred tax assets and liabilities
are measured using the enacted or substantially enacted tax rates expected to apply when the asset is realized or the liability
settled.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities
of a change in tax rates is recognized in income or loss in the period that substantive enactment occurs.
A deferred tax asset is recognized to the extent
that it is probable that future taxable income will be available against which the asset can be utilized. To the extent that the
Company does not consider it probable that deferred tax asset will be recovered, the deferred tax asset is reduced.
The following temporary differences do not
result in deferred tax assets or liabilities:
| · | the initial recognition of assets or liabilities,
not arising in a business combination, that does not affect accounting or taxable income; |
| · | initial recognition of goodwill; |
| · | investments in subsidiaries, associates
and jointly controlled entities where the timing of reversal of the temporary differences can be controlled and reversal in the
foreseeable future is not probable. |
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset
when there is a legally enforceable right to the set off current tax assets against current tax liabilities and when they relate
to income taxes levied by the same taxation authority and the Company intends to settle its current tax assets and liabilities
on a net basis.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
Under Canadian income tax legislation, a company
is permitted to issue flow-through shares whereby the Company agrees to incur qualifying expenditures and renounce the related
income tax deductions to the investors. The Company has adopted a policy to (i) allocate the proceeds between the offering of the
shares and the sale of tax benefits when the shares are offered and (ii) recognize an income tax provision upon filing of appropriate
renunciation forms with the Canadian taxation authorities for qualifying expenditures previously incurred.
The allocation of the proceeds is made based
on the residual difference between the quoted price of the shares and the amount the investor pays for the flow-through shares.
A liability is recognized for the premium paid by the investors. The liability is reduced and the reduction of premium liability
is recorded in other income when the Company has the intention to renounce the expenditures with the Canadian taxation authorities
for qualifying expenditures previously incurred. The deferred tax impact, if any, is recorded at the same time.
Property and equipment (“PPE”)
are carried at cost, less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses, if any. The cost of an item of PPE consists
of the purchase price, any costs directly attributable to bringing the asset to the location and condition necessary for its intended
use and an initial estimate of the costs of dismantling and removing the item and restoring the site on which it is located. An
item of PPE is derecognized upon disposal or when no future economic benefits are expected to arise from the continued use of the
asset. Any gain or loss arising on disposal of the asset, determined as the difference between the net disposal proceeds and the
carrying amount of the asset, is recognized in profit or loss. Where an item of property and equipment comprises major components
with different useful lives, the components are accounted for as separate items of plant and equipment. Expenditures incurred to
replace a component of an item of property and equipment that is accounted for separately, including major inspection and overhaul
expenditures are capitalized.
The Company provides for amortization of its property and equipment
as follows:
| Automotive |
30% declining balance basis |
| Leasehold improvements |
30% declining balance basis |
| Mining equipment |
30% declining balance basis |
| Office equipment |
20% declining balance basis |
| g) | | Exploration and evaluation expenditures |
Exploration and evaluation expenditure include
the costs of acquiring licenses, costs associated with exploration and evaluation activity, and the fair value (at acquisition
date) of exploration and evaluation assets acquired in a business combination. Exploration and evaluation expenditures are expensed
as incurred as mineral property expenditures. Costs incurred before the Company has obtained the legal rights to explore an area
are recognized in the statement of comprehensive loss.
Acquisition costs are capitalized to the extent
that these costs can be related directly to the acquisition of a specific area of interest where it is considered likely to be
recoverable by future exploitation or sale.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
Once the technical feasibility and commercial
viability of the extraction of mineral resources in an area of interest are demonstrable, exploration and evaluation assets attributable
to that area of interest are first tested for impairment and then reclassified to mining property and development assets within
property and equipment. Subsequent costs are capitalized to the respective mineral property interests.
Recoverability of the carrying amount of the
exploration and evaluation assets is dependent on successful development and commercial exploitation, or alternatively, sale of
the respective areas of interest.
The Company is in
the exploration stage with respect to its investment in mineral properties and accordingly follows the practice of expensing all
costs relating to exploration for and development of mineral claims and crediting all proceeds received for option or farm-out
arrangements or recovery of costs against the mineral expenditures.
Option payments made
by an interested acquirer are recorded as a reduction of the value of the asset, with any excess over the carrying value of the
asset recorded into income.
| h) | | Impairment of non-financial assets |
At each reporting date, the carrying amounts
of the Company’s non-financial assets are reviewed to determine whether there is any indication that those assets are impaired.
If any such indication exists, the recoverable amount of the asset is estimated in order to determine the extent of the impairment,
if any. The recoverable amount is the higher of fair value less costs to sell and value in use. Fair value is determined as the
amount that would be obtained from the sale of the asset in an arm’s length transaction between knowledgeable and willing
parties. In assessing value in use, the estimated future cash flows are discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount
rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset. If the recoverable
amount of an asset is estimated to be less than its carrying amount, the carrying amount of the asset is reduced to its recoverable
amount and the impairment loss is recognized in the profit or loss for the period. For the purposes of impairment testing, exploration
and evaluation assets are allocated to cash-generating units to which the exploration activity relates, generally by mineral property
interests. For an asset that does not generate largely independent cash inflows, the recoverable amount is determined for the cash
generating unit to which the asset belongs. For exploration and evaluation assets, indication of impairment includes but is not
limited to expiration of the rights to explore, substantive expenditure in the specific area is neither budgeted or planned, and
if the entity has decided to discontinue exploration activity in the specified area.
Where an impairment loss subsequently reverses,
the carrying amount of the asset (or cash-generating unit) is increased to the revised estimate of its recoverable amount, but
so that the increased carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined had no impairment loss
been recognized for the asset (or cash-generating unit) in prior years. A reversal of an impairment loss is recognized immediately
in profit or loss.
Management considers both external and internal
sources of information in assessing whether there are any indications that the Company’s non-financial assets are impaired.
External sources of information management considers include changes in market, economic and legal environment in which the Company
operates that are not within its control and affect the recoverable amount of its non-financial assets. Internal sources of information
management consider include the manner in which non-financial assets are being used or are expected to be used and indications
of economic performance of the assets.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
The functional and presentation currency of
the Company and its subsidiaries is the Canadian dollar. Transactions in currencies other than the functional currency are recorded
at the rates of exchange prevailing on dates of transactions. At each reporting date, monetary assets and liabilities that are
denominated in foreign currencies are translated at the spot rates prevailing at the date. Non-monetary items that are measured
in terms of historical cost in a foreign currency are translated at the date of the transaction and not revalued every period.
| j) | | Financial assets and liabilities |
Financial assets held are cash and cash equivalents,
trade and other receivables and available-for-sale securities. Financial liabilities are trade and other payables.
These are classified into the following specified
categories: available-for-sale (“AFS”) financial assets, loans and receivables and other liabilities. The classification
depends on the nature and purpose of the financial assets and is determined at the time of initial recognition. Available-for-sale
securities held by the Company that are traded in an active market are classified as being AFS and are stated at fair value. Gains
and losses arising from changes in fair value are recognized directly in other comprehensive income ("OCI") in the investments
revaluation reserve with the exception of significant or prolonged losses which are recognized in profit or loss. Where the investment
is disposed of or is determined to be impaired, the cumulative gain or loss previously recognized in the investments revaluation
reserve is included in the consolidated statement of net loss and comprehensive loss for the period.
The fair value of AFS monetary assets denominated
in a foreign currency is determined in that foreign currency and translated at the spot rate at the financial position reporting
date. The change in fair value attributable to translation differences that result from a change in amortized cost of the asset
is recognized in profit or loss. Trade and other receivables that have fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an
active market are classified as loans and receivables. Loans and receivables are measured at amortized cost using the effective
interest method, less any impairment. Interest income is recognized by applying the effective interest rate, except for short-term
receivables when the recognition of interest would be immaterial. Other financial liabilities are measured at amortized cost.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
3 Summary of Significant Accounting
Policies (continued)
The Company has classified its financial instruments as follows:
| Cash and cash equivalents |
Loans and receivables |
| Available-for-sale securities |
Available-for-sale |
| Trade and other receivables |
Loans and receivables |
| Trade and other payables |
Other financial liabilities |
Financial instruments recorded at fair value
on the consolidated statement of financial position are classified using a fair value hierarchy that reflects the significance
of the inputs used in making the measurements. The fair value hierarchy has the following levels:
- Level 1 - valuation based on quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical
assets or liabilities;
- Level 2 - valuation techniques based on inputs other than quoted prices included
in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e. as prices) or indirectly (i.e. derived from prices);
- Level 3 - valuation techniques using inputs for the asset or liability that are
not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs).
The Company’s available for
sale investments are classified as Level 1 financial instruments. There have been no transfers between fair value levels during
the reporting period.
Impairment of financial assets
Financial assets are assessed for indicators
of impairment at each financial position reporting date. Financial assets are impaired where there is objective evidence that,
as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition of the financial asset, the estimated future cash
flows of the investment have been impacted. For unlisted shares classified as AFS, a significant or prolonged decline in the fair
value of the security below its cost is considered to be objective evidence of impairment. For all other financial assets objective
evidence of impairment could include:
- significant financial difficulty of the issuer or counterparty; or
- default or delinquency in interest or principal payments; or
- it becoming probable that the borrower will enter bankruptcy or financial re-organization.
For certain categories of financial assets,
such as trade and other receivables, assets that are assessed not to be impaired individually are subsequently assessed for impairment
on a collective basis. The carrying amount of the financial asset is reduced by the impairment loss directly for all financial
assets with the exception of accounts receivable, where the carrying amount is reduced through the use of an allowance account.
When an accounts receivable is considered uncollectible, it is written off against the allowance account. Subsequent recoveries
of amounts previously written off are credited against the allowance account. Changes in the carrying amount of the allowance account
are recognized in the consolidated statement of net loss and comprehensive loss. With the exception of AFS equity instruments,
if, in a subsequent period, the amount of the impairment loss decreases and the decrease can be related objectively to an event
occurring after the impairment was recognized, the previously recognized impairment loss is reversed through profit or loss to
the extent that the carrying amount of the investment at the date the impairment is reversed does not exceed what the amortized
cost would have been had the impairment not been recognized. In respect of AFS equity securities, impairment losses previously
recognized through profit or loss are not reversed through profit or loss. Any increase in fair value subsequent to an impairment
loss is recognized directly in equity.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
| k) | | Investment revaluation reserve |
Investment revaluation reserve includes
unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities, none of which are included in the calculation of net earnings or
losses until realized or until there is a significant or prolonged decline in the investments value.
| l) | | Cash and cash equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents consist
of cash deposits in banks, bankers’ acceptances and certificates of deposits (note 5) and are readily convertible into a
known amount of cash with maturity days of three months or less.
| m) | | Decommissioning liabilities |
Obligations associated with the
decommissioning of tangible non-current assets are recorded as provisions when those obligations are incurred, with the amount
of the liability initially measured at management’s best estimates. These obligations are capitalized in the accounts of
the related non-current assets and are amortized over the useful lives of the related assets. It is possible that the Company's
estimates of its ultimate decommissioning liabilities could change as a result of changes in regulations, the extent of environmental
remediation required and the means of reclamation or costs estimates. Changes in estimates are accounted for prospectively from
the period these estimates are revised. There are no decommissioning liabilities obligations as at April 30, 2014 and April 30,
2013.
An equity instrument is any contract that evidences
a residual interest in the assets of the Company after deducting all of its liabilities. Equity instruments issued by the Company
are recorded at the proceeds received, net of issue costs.
A provision is recognized in the statement
of financial position when the Company has a present legal or constructive obligation as a result of a past event, it is probable
that an outflow of economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation and the amount can be reliably estimated. If the
effect is material, provisions are determined by discounting the expected future cash flows at a pre-tax rate that reflects current
market assessments of the time value of money and, where appropriate, the risks specific to the liability.
Interest income is accrued on a time basis,
by reference to the principal outstanding and at the effective interest rate applicable.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
Basic loss per common share is calculated by
dividing the loss attributed to shareholders for the period by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding in the
period. Diluted loss per common share is calculated by adjusting the weighted average number of common shares outstanding to assume
conversion of all dilutive potential common shares. Stock options, shares to be issued, and warrants outstanding are not included
in the computation of diluted (loss) earnings per share if their inclusion would be anti-dilutive.
A segment is a component of the Company that
is distinguishable by economic activity (business segment), or by its geographical location (geographical segment), which is subject
to risks and rewards that are different from those of other segments. The Company operates in one business segment, the exploration
of mineral property interests.
| s) | | New accounting standards adopted |
The following standards were adopted effective
May 1, 2013.
(i) IFRS 10, Consolidated Financial Statements,
requires an entity to consolidate an investee when it has power over the investee, is exposed, or has rights, to variable returns
from its involvement with the investee and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the investee. Under existing
IFRS, consolidation was required when an entity has the power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as
to obtain benefits from its activities. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
(ii) IFRS 11, Joint Arrangements, requires
a venturer to classify its interest in a joint arrangement as a joint venture or joint operation. Joint ventures will be accounted
for using the equity method of accounting whereas for a joint operation the venturer will recognize its share of the assets, liabilities,
revenue and expenses of the joint operation. Under previous IFRS, entities had the choice to proportionately consolidate or equity
account for interests in jointly controlled entities. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated
financial statements.
(iii) IFRS 12, Disclosure of Interests in Other
Entities, outlines the disclosure requirements for interests in subsidiaries and other entities to enable users to evaluate the
risks associated with interests in other entities and the effects of those interests on an entity's financial position, financial
performance and cash flow. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
(iv) IFRS 13, Fair Value Measurement, provides
a single framework for measuring fair value. The measurement of the fair value of an asset or liability is based on assumptions
that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability under current market conditions, including assumptions about
risk. The Company adopted IFRS 13 on May 1, 2013 on a prospective basis. The adoption of IFRS 13 did not require any adjustments
to the valuation techniques used by the Company to measure fair value and did not result in any measurement adjustments as at May
1, 2013.
(v) The Company has adopted the amendments
to IAS 1 effective May 1, 2013. These amendments required the Company to group other comprehensive income by those that will be
reclassified subsequently to profit or loss and those that will not be reclassified. The adoption of this standard had no effect
on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 3 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
| t) | | Future Accounting Pronouncements |
Unless otherwise noted, the following new or
revised standards will be effective for the Company in future periods.
(i) IFRS 9 Financial Instruments, was issued
in November 2009 and addresses classification and measurement of financial assets. It replaces the multiple category and measurement
models in IAS 39 for debt instruments with a new mixed measurement model having only two categories: amortized cost and fair value
through profit or loss. IFRS 9 also replaces the models for measuring equity instruments. Such instruments are either recognized
at fair value through profit or loss or at fair value through other comprehensive income. Where equity instruments are measured
at fair value through other comprehensive income, dividends are recognized in profit or loss to the extent that they do not clearly
represent a return of investment; however, other gains and losses (including impairments) associated with such instruments remain
in accumulated comprehensive income indefinitely.
Requirements for financial liabilities were
added to IFRS 9 in October 2010 and they largely carried forward existing requirements in IAS 39, Financial Instruments - Recognition
and Measurement, except that fair value changes due to credit risk for liabilities designated at fair value through profit and
loss are generally recorded in other comprehensive income. In February 2014, the IASB tentatively determined that the revised effective
date for IFRS 9 would be January 1, 2018. The Company has not yet completed an assessment of the impact of adopting IFRS 9.
(ii) IFRIC 21, Accounting for Levies imposed
by Governments, clarifies that the obligating event giving rise to a liability to pay a levy is the activity described in the relevant
legislation that triggers payment of the levy. IFRIC 21 is effective for the Company beginning on May 1, 2014. The Company is currently
assessing the impact of this guidance.
| 4 | | Significant Accounting Judgments and Estimates |
The preparation
of these consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts
of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period.
Actual outcomes could differ from these estimates. The consolidated financial statements include estimates which, by their nature,
are uncertain. The impacts of such estimates are pervasive throughout the consolidated financial statements, and may require
accounting adjustments based on future occurrences. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the
estimate is revised and the revision affects both current and future periods.
Significant assumptions about the future and
other sources of estimation uncertainty that management has made at the statement of financial position date, that could result
in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities, in the event that actual results differ from assumptions
made, relate to, but are not limited to, the following:
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 4 | | Significant Accounting Judgments and Estimates (continued) |
| · | The Company believes that the cash on hand at April 30, 2014 is sufficient to meet corporate, administrative
and selected exploration activities for at least the next twelve months and that the presentation of these consolidated financial
statements on a going concern basis is appropriate. |
| · | The Company has determined that it will account for its investment in CKU Partnership as a joint
operation to reflect its joint control with the Korean Consortium. In assessing whether the Company has joint control the Company
assessed whether all the parties, or a group of the parties, control the arrangement. This assessment necessarily involves judgment
as to whether the Korean Consortium and the Company have equal contractual rights and powers in governing the financial and operating
policies of the Partnership or appointing and removing members of the Partnership’s Board of Directors and each of the parties
have rights to the assets and has obligations for the liabilities related to the CKU Partnership. |
| · | The Company decided not to recognize deferred tax assets arising from Canadian
exploration expenses, capital losses and unused tax losses as it considered it not to be probable that taxable income will be available
in the near future to offset the reversal of these items. |
| · | Under IFRS, the Company ;may elect a policy for accounting for costs related
to exploration and evaluation expenditures to either capitalize or expense the costs as incurred until a decision is made that
commercial exploitation is probable, from which point the costs are capitalized. The Company has elected a policy to expense all
costs related to exploration and evaluation expenditures. |
| · | Management assesses each mineral property interest at each reporting period
to determine whether any indication of impairment exists, and if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying
value may not be recoverable. Where an indicator of impairment exists, a formal estimate of the recoverable amount is made which
is considered to be the higher of the fair value less costs to sell and its value in use. These assessments require the use of
estimates and assumptions such as future capital requirements and assessments of preliminary assay results. Fair value is determined
as the amount that would be obtained from the sale of the asset in an arm’s-length transaction between knowledgeable and
willing parties. |
| · | the fair value estimation of share-based
awards included in the consolidated statements of financial position and the inputs used in accounting for stock options and warrants
in the consolidated statements of comprehensive loss; |
| · | the accounting and recognition of income
taxes which is included in the consolidation statement of net loss and comprehensive loss and composition of deferred income tax
asset and liabilities included in the consolidated statement of financial position; and, |
| · | the assessment of indications of impairment
of each mineral properties and related determination of the net realizable value and write-down of those properties where applicable.
|
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 5 | | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
| |
|
April 30, 2014
$000’s |
April 30, 2013
$000’s |
| CKULP funds |
|
176 |
290 |
| Option-in advance |
|
93 |
116 |
| Cash in bank and other short term deposits |
|
775 |
859 |
| Total |
|
1,044 |
1,265 |
CKULP funds are held by the Company
for expenditures on the properties held by the CKULP.
Option-in advance are advance cash
funding by joint venture partners on various exploration properties.
Cash and cash equivalents of the
Company are comprised of bank balances and short-term investments, which are readily convertible to cash, with an original maturity
of 90 days or less as follows:
| |
|
April 30, 2014
$000’s |
April 30, 2013
$000’s |
| Cash |
|
319 |
364 |
| Short-term investments |
|
725 |
901 |
| Total |
|
1,044 |
1,265 |
6 Available-for-Sale Securities
| |
|
April 30, 2014 |
April 30, 2013 |
| |
|
|
Cost
$000’s
|
Fair Value $000’s |
Cost
$000’s
|
Fair Value
$000’s |
| Pacific North West Capital Corp. |
|
|
17 |
17 |
42 |
42 |
| Westcan Uranium Corp. |
|
|
- |
- |
6 |
6 |
| Mega Uranium Ltd. |
|
|
3 |
11 |
6 |
6 |
| Makena Resources Inc. |
|
|
155 |
80 |
- |
- |
| Copper Reef Mining Corp. |
|
|
20 |
10 |
- |
- |
| MPVC Inc. |
|
|
225 |
259 |
- |
- |
| Other available-for-sale securities |
|
|
18 |
37 |
33 |
32 |
| Total |
|
|
438 |
414 |
87 |
86 |
The Company reviewed the carrying
values of its available-for-sale securities, and after considering where the decreases on fair value were significant or prolonged,
the Company recognized an impairment on available-for-sale securities of $74,000 during the year ended April 30, 2014 (2013: $83,000;
2012: $122,000).
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
Property and equipment are comprised of the following:
| |
Automotive
$000’s |
Leasehold improvements
$000’s |
Mining equipment
$000’s |
Office equipment
$000’s |
Total
$000’s |
| Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
| At May 1, 2012 |
82 |
270 |
1,024 |
501 |
1,877 |
| Additions |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
2 |
| Disposals |
(57) |
- |
(2) |
(47) |
(106) |
| At April 30, 2013 |
25 |
270 |
1,022 |
456 |
1,773 |
| Disposals |
- |
- |
- |
(1) |
(1) |
| At April 30, 2014 |
25 |
270 |
1,022 |
455 |
1,772 |
| Accumulated Depreciation and Amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
| At May 1, 2012 |
(67) |
(105) |
(821) |
(380) |
(1,373) |
| Depreciation and amortization |
(4) |
(20) |
(61) |
(23) |
(108) |
| Disposals |
54 |
- |
2 |
27 |
83 |
| At April 30, 2013 |
(17) |
(125) |
(880) |
(376) |
(1,398) |
| Depreciation and amortization |
(3) |
(20) |
(42) |
(15) |
(80) |
| Disposals |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| At April 30, 2014 |
(20) |
(145) |
(922) |
(391) |
(1,478) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Carrying Value |
|
|
|
|
|
| At April 30, 2013 |
8 |
145 |
142 |
80 |
375 |
| At April 30, 2014 |
5 |
125 |
100 |
64 |
294 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 8 | | Mineral Property Interests |
The Company holds approximately 742,000 hectares
of mining claims in the Athabasca region located across the provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba in Canada. The holdings are
through 18 projects which are in various stages of exploration and discovery.
The Company also holds mining claims
in Alaska and British Columbia. The Company held a property in New Zealand which it sold in March 2014 (note 8(k)).
Details of acquisition costs and
mineral property impairments for the years ended April 30, 2014 and April 30, 2013 respectively are as follows:
| Project ($000’s) |
May 1, 2012 |
Additions/
write-offs |
April 31, 2013 |
Additions/
write-offs/Recoveries |
April 30, 2014 |
| Athabasca Basin |
|
|
|
|
|
| Cree East (a) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| West McArthur (b) |
65 |
- |
65 |
- |
65 |
| Fond du Lac |
120 |
- |
120 |
- |
120 |
| Grease River (c) |
133 |
- |
133 |
(57) |
76 |
| Cree West |
48 |
(48) |
- |
- |
- |
| Key Lake |
24 |
- |
24 |
- |
24 |
| NW Manitoba (d) |
16 |
- |
16 |
(8) |
8 |
| Poplar (e) |
166 |
- |
166 |
(35) |
131 |
| Helmer |
107 |
- |
107 |
- |
107 |
| Lake Athabasca (f) |
118 |
- |
118 |
(20) |
98 |
| Alberta |
11 |
(11) |
- |
- |
- |
| Hodgson (g) |
109 |
- |
109 |
(102) |
7 |
| Arnold |
35 |
(35) |
- |
- |
- |
| Collins Bay (h) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| McTavish |
74 |
- |
74 |
- |
74 |
| Carswell (i) |
173 |
(37) |
136 |
(136) |
- |
| Ruttan |
- |
15 |
15 |
- |
15 |
| Patterson (j) |
- |
4 |
4 |
(2) |
2 |
| Other |
53 |
- |
53 |
- |
53 |
| New Zealand |
|
|
|
|
|
| Reefton, NZ (k) |
24 |
- |
24 |
(24) |
- |
| Other |
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Projects, Various (l) |
80 |
(6) |
74 |
(41) |
33 |
| Total |
1,356 |
(118) |
1,238 |
(425)1 |
813 |
1 Includes
mineral property write-offs of approximately $357,000, disposal of the Reefton project of approximately $24,000, net option payments
of approximately $63,000 and additions to mineral property interests of approximately $19,000.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 8 | | Mineral Property Interests (continued) |
| |
Total |
|
Summary of option payments remaining due by
CanAlaska in the
years ending April 30 |
|
|
Cash
$000’s |
Spend1
$000’s |
Shares |
| 2015 |
|
|
|
- |
- |
- |
| 2016 |
|
|
|
|
600 |
30,000 |
| Thereafter |
|
|
|
- |
3,000 |
80,000 |
1 Represents
cumulative spend required not the spend per fiscal year to maintain certain interest in the Company’s mineral property interests.
The cumulative spend is at the Company’s discretion under an option. It may not be the Company’s intention to pay the
option, in which case the expenditure will not be incurred.
| |
|
|
|
Total |
| Summary of option payments receivable by CanAlaska in the years ending April 30 2 |
Cash
$000’s |
Spend 1
$000’s |
Shares |
| 2015 |
|
|
|
25 |
3,475 |
3,500,000 |
| 2016 |
|
|
|
25 |
3,925 |
750,000 |
| Thereafter |
|
|
|
- |
13,025 |
7,500,000 |
1 Represents
cumulative spend required not the spend per fiscal year to maintain certain interest in the Company’s properties.
2 Represents
optionees' commitments to maintain certain interest in the Company’s properties (see note 8(d), note 8(j) and note 8(l)).
| a) | | Cree East, Saskatchewan – Korean Consortium |
Cree East consists of approximately 58,000
hectares of mineral claims in the Athabasca. In December 2007, the Company formed the CKU Partnership with the Korean Consortium
(“Consortium”) to develop Cree East. Under the terms of agreements, the Korean Consortium invested $19.0 million towards
the earn-in of a 50% ownership interest in the CKU Partnership over a four year period (April 30, 2013: 50%; April 30, 2012: 50%).
The Company acts as the operator for the exploration project and earns a management fee of 10% of the exploration expenditures
incurred. The total expenditures on the property for the year ended April 30, 2014 was $223,000 (2013: $184,000; 2012: $2,733,000)
and has a carrying value of $nil.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 8 | | Mineral Property Interests (continued) |
| b) | | West McArthur, Saskatchewan - Mitsubishi |
West McArthur consists of approximately 36,000
hectares of mineral claims in the Athabasca. In April 2007, the Company optioned the claims to Mitsubishi Development Pty Ltd.
(“Mitsubishi”) whereby Mitsubishi could exercise an option to earn a 50% interest in the property by funding expenditures
of $10.0 million and by making a $1.0 million payment upon completion of the $10.0 million funding requirement. In February 2010,
Mitsubishi exercised their option with a payment to the Company of $1.0 million and an unincorporated 50/50 joint venture was formed
between the parties to pursue further exploration and development of the property. The Company acts as project operator and earns
a fee (between 5% and 10%) based on the expenditures incurred. The total expenditures on the property for the year ended April
30, 2014 was $37,000 (2013: $193,000; 2012: $1,633,000) and has a carrying value of approximately $65,000.
| c) | | Grease River, Saskatchewan |
In May and September 2013, the Company
recognized an impairment on certain of its Grease River claims of approximately $57,000 as it did not renew its permits on these
claims.
In September 2013, the Company entered
into an option agreement with NEX-listed MPVC Inc. ("MPVC") for an interest in the NW Manitoba project. The project covers
143,603 hectares along the Saskatchewan/Manitoba border. In January 2014, the option agreement was revised whereby MPVC may earn
an 80% interest in the project by carrying out a three stage $11.6 million exploration program, make a cash payment of $35,000,
issue 12 million common shares and issue 6 million common share purchase warrants. In February 2014, the option agreement with
MPVC was amended to extend the date of certain provisions of the agreement from February 28, 2014 to March 14, 2014. In consideration
for amending the option agreement, MPVC paid a non-refundable deposit in the amount of $50,000 on March 14, 2014 to the Company.
The NW Manitoba property has a carrying value of approximately $8,000.
In May 2013, November 2013 and February
2014, the Company recognized an impairment on certain of its Poplar claims of approximately $35,000 as it did not renew its permits
on these claims.
| f) | | Lake Athabasca, Saskatchewan |
In July 2013 and April 2014, the
Company recognized an impairment on certain of its Lake Athabasca claims of approximately $20,000 as it did not renew its permits
on these claims.
g) Hodgson, Saskatchewan
In May and July 2013, the Company
recognized an impairment on its Hodgson claim of approximately $109,000 as it did not renew its permits on this property. In December
2013, the Company re-acquired through staking three blocks of claims totalling 11,492 hectares west of the Cigar Lake mine for
$6,895.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 8 | | Mineral Property Interests (continued) |
| h) | | Collins Bay, Saskatchewan |
In June 2013, the Collins Bay Extension
option agreement dated July 4, 2009 and subsequently amended on March 29, 2011 with Bayswater Uranium Corporation ("Bayswater")
was amended whereby the option period was extended from six years to eight years. In consideration for the extension, the Company
accelerated its staged common share issuances and issued 10,000 common share on July 12, 2013 (note 8). As a result, in July 2013,
the Company issued an aggregate of 20,000 common shares under the amended option agreement for the Collins Bay Extension project.
In January 2014, the Company recognized
an impairment on its Carswell claim of approximately $136,000 as it did not renew its permits on this property.
| j) | | Patterson – Saskatchewan |
In January 2013, the Company acquired
three block of claims, totalling 6,687 hectares located in the Patterson Lake area of the western Athabasca basin. In August 2013,
the Company optioned the claims to Makena Resources Inc ("Makena"). Makena may earn a 50% interest in the property by
making cash payments totalling $100,000 by June 1, 2015, issuing 2,500,000 common share by June 1, 2015 and incurring exploration
expenditures totalling $1.4 million by September 30, 2016. The Patterson property has a carrying value of approximately $2,000.
In September 2012, Atlantic Industrial
Minerals Inc. (“Atlantic”) entered into an option agreement to acquire 100% interest in the Reefton project, in South
Island, New Zealand by paying $300,000 in staged payments, issuing 300,000 shares of Atlantic to the Company and reimbursing the
Company for the annual permit fees for the property from 2012 to 2015 which are approximately $50,000 per year and drilling 1,500
metres by December 31, 2014. In September 2012 and October 2012, the Company received $50,000 from Atlantic for the 2012/2013 annual
permit fee as part of an operating agreement. On August 21, 2013, the option agreement with Atlantic was terminated.
In March 2014, the Company entered
into a purchase agreement to sell the exploration permit for the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. ("Stevenson")
for aggregate purchase consideration of $20,000. The Company recognized a loss on disposal of the Reefton project of approximately
$4,000.
BC Copper, British Columbia
BC Copper is comprised of approximately
7,000 hectares located in south central British Columbia. In March 2012, the Company optioned the claims to Tyrone Docherty. Tyrone
Docherty may earn a 50% interest in the property by making exploration expenditures of $470,000 by July 2014. In May 2012 the Company
amended the agreement where a third party, Discovery Ventures Ltd and Docherty could earn 50% interest for the expenditure of $250,000
by July 1 2014. No amounts were received. On July 2, 2013, the option agreement with Tyrone Docherty and Discovery Venture Ltd.
was terminated.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 8 | | Mineral Property Interests (continued) |
Hanson, Saskatchewan
In July, August and November 2013,
the Company staked the Hanson project which consists of fourteen blocks of claims in the area of the Pikoo kimberlite discovery,
totalling 17,272 hectares located in Saskatchewan for $10,374.
In January 2014, the Company entered
into a purchase agreement for two claim blocks in the Hanson project to Copper Reef Mining Corp. ("Copper Reef") for
aggregate purchase consideration of $50,000 (received) in cash and the issuance of 1,000,000 (500,000 common shares received) common
shares in the capital of Copper Reef and completion of $50,000 of exploration expenditures. The Company retains a 2% net smelter
royalty in the agreement. The Hanson property has a carrying value of $nil.
Kasmere, Manitoba
In March 2014, the Company entered
into a binding agreement to sell its interest in its Kasmere South project in northwestern Manitoba to private company East Resources
Ltd. for an aggregate cash payment totalling $1.8 million. The Company retains a 2.5% net smelter royalty on any future production.
On March 28, 2014, the Company received a non-refundable cash payment of $200,000 from East Resources Ltd. Subsequent to year end,
the Company also received the remaining cash instalments of $100,000 and $1.5 million on May 30, 2014 and June 26, 2014 respectively.
The Company has authorized capital
consisting of an unlimited amount of common shares without par value.
Share Issuances
In July 2013, the Company issued
10,000 common shares under the option agreement for the Collins Bay Extension project (see note 8(h)).
In March 2012, the Company issued
283,000 common shares for gross proceeds of $121,690. A finder’s fee of $4,867 in cash and 11,320 warrants were issued in
connection with the financing. Each finder’s warrant entitles the holder to purchase on additional common share for a period
of eighteen months from the closing date, at a price of $0.55 per warrant share. The share purchase warrants issued as part of
this placement have been recorded at a fair value of $1,825 which was determined using the Black Scholes model.
In March 2012, the Company issued
1,522,000 flow-through common shares for gross proceeds of $776,220. A finder’s fee of $31,049 in cash and 60,880 warrants
were issued in connection with the financing. $68,490 was allocated to the flow-through share premium as the market value on the
date of close was less than the offering price associated with this offering. Each finder’s warrant entitles the holder to
purchase one additional common share for a period of eighteen months from the closing date at a price of $0.55 per warrant share.
The share purchase warrants issued as part of this placement have been recorded at a fair value of $9,816 using the Black Scholes
model.
In May and October 2012, the Company
incurred share issuance costs totalling approximately $5,000.
In July 2011, the Company issued
5,000 common shares under the option agreement for the Black Lake project.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 9 | | Share Capital (continued) |
In May 2011, the Company issued
418,141 flow-through common shares for gross proceeds of $472,500. $133,805 was allocated to the flow-through share premium as
the market value on the date of close was less than the offering price associated with this offering.
| 10 | | Share Stock Options and Warrants |
The Company has a stock option plan
that permits the granting of stock options to directors, officers, key employees and consultants. Terms and pricing of options
are determined by management at the date of grant. A total of 4,400,000 common shares of the Company may be allotted and reserved
for issuance under the stock option plan.
| |
|
Number of options
000’s |
Weighted average
exercise price $ |
| Outstanding - May 1, 2011 |
|
1,790 |
1.03 |
| Granted |
|
1,340 |
0.54 |
| Expired |
|
(191) |
1.00 |
| Forfeited |
|
(15) |
1.00 |
| Outstanding – April 30, 2012 |
|
2,924 |
0.81 |
| Granted |
|
1,358 |
0.26 |
| Expired |
|
(661) |
1.09 |
| Forfeited |
|
(23) |
1.21 |
| Outstanding – April 30, 2013 |
|
3,598 |
0.55 |
| Granted |
|
1,592 |
0.12 |
| Expired |
|
(753) |
0.69 |
| Forfeited |
|
(586) |
0.34 |
| Outstanding – April 30, 2014 |
|
3,851 |
0.20 |
As at April 30, 2014, the following stock options
were outstanding:
| |
Number of options outstanding 000’s |
Number of options exercisable 000’s |
Exercise
price |
Expiry date
(Fiscal Year) |
| |
971 |
971 |
$0.25 |
2015 |
| |
1,288 |
1,288 |
$0.25 |
2018 |
| |
1,592 |
1,592 |
$0.12 |
2019 |
| Total |
3,851 |
3,851 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
On September 26, 2013, the Company,
after receipt of regulatory and shareholder approvals, repriced an aggregate of 1,502,500 previously granted stock options, from
original exercise prices ranging from $0.42 to $1.00 per share, to a revised price of $0.25 per share. All other terms of the stock
options remained unchanged. The incremental fair value of these repriced options were $19,834 was recognized as an expense during
the year ended April 30, 2014.
For the year ended April 30, 2014,
total share-based compensation expense was $124,363 (2013: $175,981; 2012: $324,295), which was recognized as share-based payments
expense in the year.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 10 | | Share Stock Options and Warrants (continued) |
Warrants
| |
|
Number of warrants
000’s |
Weighted average
exercise price $ |
| Outstanding - May 1, 2011 |
|
3,439 |
2.44 |
| Granted |
|
72 |
0.55 |
| Expired |
|
(2,200) |
2.74 |
| Outstanding – April 30, 2012 |
|
1,311 |
1.83 |
| Expired |
|
(1,239) |
1.90 |
| Outstanding – April 30, 2013 |
|
72 |
0.55 |
| Expired |
|
(72) |
0.55 |
| Outstanding – April 30, 2014 |
|
- |
- |
Option and warrant pricing models
require the input of highly subjective assumptions including the expected volatility. Changes in the assumptions can materially
affect the fair value estimate, and therefore, the existing models do not necessarily provide a reliable measure of the fair value
of the Company’s stock options and warrants. The Company’s expected volatility is based on the historical volatility
of the Company’s share price on the Toronto Stock Exchange or the TSX Venture Exchange. The following assumptions were used
in the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate the compensation expense for the year ended April 30, 2014:
| |
|
|
Options |
| Weighted average fair value |
|
|
$0.07 |
| Forfeiture rate |
|
|
15.4% |
| Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
1.12% - 1.15% |
| Expected life |
|
|
2.21 – 2.24 years |
| Expected volatility |
|
|
113.4% - 118.2% |
| Expected dividend |
|
|
0% |
The following assumptions were used
in the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate the compensation expense for the year ended April 30, 2013:
| |
|
|
Options |
| Weighted average fair value |
|
|
$0.13 |
| Forfeiture rate |
|
|
15.4% |
| Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
1.1% - 1.26% |
| Expected life |
|
|
2.4 – 2.54 years |
| Expected volatility |
|
|
78.7% - 93.8% |
| Expected dividend |
|
|
0% |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 10 | | Share Stock Options and Warrants (continued) |
The following assumptions were used
in the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate the compensation expense for the year ended April 30, 2012:
| |
|
Warrants |
Options |
| Weighted average fair value |
|
$0.16 |
$0.24 |
| Forfeiture rate |
|
0% |
15.40% - 15.42% |
| Risk-free interest rate |
|
1.28% |
1.08% - 1.74% |
| Expected life |
|
1.5 years |
1.48 – 2.79 years |
| Expected volatility |
|
84% |
82% - 94% |
| Expected dividend |
|
0% |
0% |
| 11 | | Related Party Transactions |
Related parties include the Board of Directors
and Officers of the Company and enterprises which are controlled by these individuals.
The remuneration of directors and key management
of the Company for the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April 30, 2012 were as follows. Certain compensation is paid
to Schimann Consultants, a company controlled by the VP of Exploration.
| ($000’s) |
|
2014
$ |
2013
$ |
2012
$ |
| Employment benefits |
|
220 |
272 |
450 |
| Schimann Consultants |
|
82 |
131 |
160 |
| Directors fees |
|
- |
80 |
95 |
| Share-based compensation |
|
118 |
129 |
242 |
The directors and key management were awarded the following share
options under the employee share option plan during the year ended April 30, 2014:
| Date of grant |
Number of options |
Exercise price |
Expiry |
| November 5, 2013 |
1,103,750 |
$0.12 |
November 5, 2018 |
| January 7, 2014 |
400,000 |
$0.12 |
January 7, 2019 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
Income tax expense differs from the amount
computed by applying the combined Canadian federal and provincial income tax rates, applicable to CanAlaska Uranium Ltd., to the
income (loss) before tax provision due to the following:
| |
2014
$000’s |
2013
$000’s |
2012
$000’s |
| Loss before income taxes |
(708) |
(2,360) |
(6,869) |
| Canadian federal and provincial income tax rates |
26.00% |
25.40% |
26.39% |
| Income tax (recovery)/ expense based on Canadian federal and provincial income tax rates |
(184) |
(599) |
(1,813) |
| Increase (decrease) attributable to: |
|
|
|
| Non-deductible expenditures |
72 |
84 |
465 |
| True-up of tax provisions in respect of prior years |
335 |
(65) |
117 |
| Flow-through shares renounced |
- |
- |
329 |
| Tax losses expired |
110 |
- |
- |
| Changes in unrecognized deferred tax assets |
51 |
474 |
861 |
| Changes in deferred tax rates and other |
(384) |
106 |
41 |
| Income tax expense (recovery) |
- |
- |
- |
Unrecognized deductible temporary differences,
unused tax losses, and unused tax credits are attributable to the following:
| |
|
2014
$000’s |
2013
$000’s |
| Non-capital loss carry forwards |
|
11,853 |
12,066 |
| Available for sale investments |
|
373 |
324 |
| Excess tax value of property and equipment over book value |
|
1,529 |
1,448 |
| Mineral property interests |
|
22,226 |
21,813 |
| Share issuance costs |
|
63 |
173 |
| Investment tax credit |
|
563 |
1,020 |
| |
|
36,607 |
36,844 |
The Company has income tax loss carry-forwards
of approximately $9,679,126 (April 30, 2013 - $10,088,893) for Canadian tax purposes. These un-recognized tax losses will expire
between 2015 to 2034.
The Company has investment tax credits of approximately
$563,095 (April 30, 2013 - $1,019,763) for Canadian tax purposes. These un-recognized investment tax credits will expire between
2030 to 2034.
The Company has income tax loss carry-forwards
of approximately $101,103 (April 30, 2013 - $99,818) for the United States tax purposes. These un-recognized tax losses will expire
between 2026 to 2034.
The Company has income tax loss carry-forwards
of approximately $2,072,762 (April 30, 2013 - $1,877,789) for New Zealand tax purposes. These un-recognized tax losses are carried
forward indefinitely.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
The Company has the following commitments
in respect of operating leases for office space, land, or computer equipment:
|
Fiscal Year Ending
|
|
|
|
|
Total
$000’s |
| 2015 |
|
|
|
|
150 |
| 2016 |
|
|
|
|
133 |
| Thereafter |
|
|
|
|
7 |
| Total |
|
|
|
|
290 |
The Company has outstanding and
future commitments under mineral properties option agreements to pay cash and/or issue common shares of the Company (note 8).
The Company has sub leased its Vancouver
office space to reduce its operating costs. However, the Company is committed for the full office lease amount.
The fair value of the Company’s
cash and cash equivalent, trade and other receivables, available-for-sale securities and trade and other payables approximate their
carrying values due to the short-term nature of these instruments.
The Company’s financial instruments
are exposed to certain financial risks, including currency risk, credit risk, liquidity risk and interest risk.
The Company’s presentation
and functional currency is the Canadian dollar. The Company is therefore exposed to the financial risk related to the fluctuation
of foreign exchange rates, both in the New Zealand dollar relative to the Canadian dollar , and in the US$ relative to the Canadian
dollar. A 10% change in either of these currencies would not have a significant impact on the comprehensive loss.
The Company does not use any derivative
instruments to reduce its exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates.
.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 14 | | Financial Instruments (continued) |
Financial instruments that potentially
subject the Company to credit risk consist of cash and cash equivalents and trade and other receivables. To mitigate exposure to
credit risk, the Company deposits cash and cash equivalents with high quality large Canadian financial institutions as determined
by rating agencies.
As at April 30, 2014, the Company’s
maximum exposure to credit risk is the carrying value of its cash and cash equivalents and trade and other receivables.
Liquidity risk is the risk that
the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due. The Company is reliant upon equity issuances as
it source of cash. The Company manages liquidity risk by maintaining an adequate level of cash and cash equivalents to meet its
ongoing obligations. The Company continuously reviews its actual expenditures and forecast cash flows and matches the maturity
dates of its cash and cash equivalents to capital and operating needs. For further information related to liquidity refer to note
2.
The Company’s interest income
earned on cash and cash equivalents is exposed to interest rate risk. A decrease in interest rates would result in lower relative
interest income and an increase in interest rates would result in higher relative interest income.
The Company considers its capital
to consist of common shares, stock options and warrants. The Company’s objectives when managing capital are to safeguard
the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern in order to pursue the exploration of its mineral properties and to
maintain a flexible capital structure which optimizes the costs of capital at an acceptable risk.
The Company manages the capital
structure and makes adjustments to it in light of changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying
assets. To maintain or adjust the capital structure, the Company may attempt to issue new shares and, acquire or dispose of assets.
In order to maximize ongoing exploration
efforts, the Company does not pay out dividends. The Company’s investment policy is to invest its short-term excess cash
in highly liquid short-term interest bearing investments with short term maturities, selected with regards to the expected timing
of expenditures from continuing operations.
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended April 30, 2014, April 30, 2013 and April
30, 2012
(Expressed in Canadian dollars except where indicated)
| 16 | | Geographic Segmented Information |
The Company operates in one business
segment, the exploration of mineral property interests. The following summarizes the Company’s operations based on the geographic
areas in which it operates:
| April 30, 2014 ($000’s) |
|
Canada |
|
U.S.A. |
|
New Zealand |
|
Total |
| Non-current assets |
|
1,290 |
|
6 |
|
- |
|
1,296 |
| Total assets |
|
2,771 |
|
6 |
|
29 |
|
2,806 |
| Total liabilities |
|
380 |
|
- |
|
2 |
|
382 |
| Loss for the year |
|
669 |
|
2 |
|
37 |
|
708 |
| April 30, 2013 ($000’s) |
|
Canada |
|
U.S.A. |
|
New Zealand |
|
Total |
| Non-current assets |
|
1,786 |
|
6 |
|
24 |
|
1,816 |
| Total assets |
|
3,185 |
|
6 |
|
34 |
|
3,225 |
| Total liabilities |
|
193 |
|
- |
|
2 |
|
195 |
| Loss for the year |
|
2,342 |
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
2,360 |
| April 30, 2012 ($000’s) |
|
Canada |
|
U.S.A. |
|
New Zealand |
|
Total |
| Non-current assets |
|
2,174 |
|
6 |
|
24 |
|
2,205 |
| Total assets |
|
7,009 |
|
6 |
|
50 |
|
7,065 |
| Total liabilities |
|
1,784 |
|
- |
|
8 |
|
1,792 |
| Loss for the year |
|
6,454 |
|
10 |
|
405 |
|
6,869 |
On May 20, 2014, Golden Fern Resources Limited,
the Company's wholly owned subsidiary in New Zealand, began liquidation proceedings. The New Zealand subsidiary is being liquidated
after the sale of the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd and there are no significant assets or liabilities remaining in the
entity.
On June 26, 2014, the Company received the
final cash instalment of $1.5 million from East Resources for the purchase of the Kasmere South project.
On June 30, 2014, the option agreement
with Makena Resources Inc. for the Patterson project was amended whereby in exchange for a six month extension on the work program,
Makena agreed to return the Patterson Lake North project and the Patterson Lake East project to the Company.

CANALASKA URANIUM LTD.
CODE OF ETHICS
SCOPE OF POLICY
Purpose of the Code of Ethics
The purpose of a Code of Ethics (“COE”)
is to define certain fundamental principles, policies and procedures that will govern the directors, officers, consultants, advisors,
contractors and employees (the “Representatives”) of CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. (the “Company”).
This COE will assist to:
| · | Establish a framework for accepted/unacceptable behaviours |
| · | Prompt high standards of business conduct and practice |
| · | Promote accountability and adherence to this COE |
| · | Develop a corporate culture steeped in honest and ethical conduct |
Principles of the COE
The Company is committed to conducting its
business in accordance with applicable laws, rules and regulations and to the highest standard of business ethics. It is intended
that the Company’s business practices are compatible with the economic, environmental and social priorities of the areas
in which we operate. Any Representative of the Company is expected to comply with this COE in all aspects of their business activities.
Where uncertainty exists in certain applications of the COE, you are expected to seek guidance through the channels provided. Violators
of this COE will be subject to disciplinary action.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Explained
The Company’s Representatives have an
obligation to give their complete loyalty to the best interest of the Company. They must avoid any action that may involve or appear
to involve a conflict of interest with the Company. These Representatives should not have any financial or other business relationships
with suppliers, customers or competitors that might impair the independence of any judgement they may need to make on behalf of
the Company. Any potential conflict of interest must be reported to the appropriate person as outlined in the reporting of violators
section of the COE.
Gifts and Entertainment
Business gifts and entertainment are customary
courtesies designed to build goodwill among business partners. These courtesies include such things as meals, tickets to sporting
or cultural events, discounts, travel, accommodation, merchandise or services. In some cultures these gifts play an important role
in business relationships. However, a problem may occur when such courtesies compromise or appear to compromise your ability to
make objective and fair business decisions.
Offering or receiving a gift that may be perceived
to unfairly influence a business relationship should be avoided. No gift or entertainment should be given, provided or accepted
by any Representative of the Company unless it is not a cash gift, is consistent
with customary practices, is not excessive in value, cannot be construed to be a bribe or payoff, and does not violate any applicable
laws or regulations.
Competitive Practices
The Company believes that fair competition
is one of its core values. In this regard the Company complies with and supports laws of which prohibit restraints of trade, unfair
practices, or abuses of economic power. Therefore the Company will not enter into arrangements that would restrict its ability
to compete with other businesses or the ability of any other business to compete fairly with the Company.
The COE prohibits its Representatives from
entering into understandings that may result in unfair business practices or anticompetitive behaviour. To never offer, or promise
to pay or give anything of value, directly or indirectly, to any official for the purposes of influencing and act or a decision
related to retaining or obtaining business directly or directing business to any other person, company or organization.
Public Relations
The Company’s Chief Executive Officer
(CEO) is responsible for public relations, including all contact with media. To the extent that there is a vacancy in either position,
then the acting individual shall be responsible for public relations and media contact. All other Representatives may not respond
to inquiries or requests for information unless specifically authorized to do so. If contacted by the media, representatives must
refer the contact to the CEO or VP.
Representatives must be careful not to disclose
confidential, personal or business information through public or casual discussions and must have read and are familiar with the
Company’s Disclosure Policy.
LEGAL COMPLIANCE
Compliance with Laws, Rules, and Regulations
All Company Representatives are expected to
comply in good faith at all times with all applicable laws, rules, and regulations are to behave in an ethical manner. Representatives
are required to educate themselves on laws, rules and regulations that govern their work. When an individual has questions or is
uncertain of the laws that govern them, they should seek assistance in understanding these laws from a member of the Corporate
Governance Committee or the Corporate Secretary.
All Company Representatives are subject to
Insider Trading Regulations. Security Laws prohibit the trading in securities of any company while in possession of material, non-public
information regarding such company. Each Representative will receive a copy of the Company’s Disclosure Policy
upon hiring or appointment. The policy will be updated periodically and it is up to the individual to ensure that they thoroughly
understand the policy and any changes or updates. Informational sessions will be held from time to time and Representatives are
encouraged to continuously educate themselves about these laws, rules and regulations.
Additional Conditions for Directors and
Senior Officers
The following additional conditions apply to
directors and senior officers of the Company. A director or senior officer of the Company must file an insider report with the
Canadian provincial and territorial securities regulations within 5 days of a purchase or sale of the Company’s securities
or grant of stock option. In order to reduce the likelihood of the violation of these trading and tipping restrictions, the Company
has adopted the following policy:
| i. | Trading in the Company’s securities, or related securities
such as options, must not take place during blackout periods. Each blackout period begins one business day before the issuance
of a news release and ends at the end of the second business day after the day the Company issues the release
publically. If there
are any doubts whether or not any particular day is within a blackout period contact the CEO or Corporate Secretary. In addition,
when the |
director or senior officer is aware
of a material fact that has not yet been disclosed to the public, they must remain in blackout until the material change has been
reported publically.
| ii. | Each year the Company holds an annual shareholder meeting. In connection
with these meetings, it mails out a proxy circular to its shareholders giving notice of the shareholder meeting and providing information
to shareholders with respect to matters of business to be dealt with at the meeting. A director or senior officer must not trade
from the date of mailing until the end of the fifth business day following the date of mailing of a proxy circular to shareholders.
This restriction also applies to special or extraordinary shareholder meetings. If there are any doubts as to when this period
applies, contact the CEO or Corporate Secretary. |
| iii. | Directors and senior officers are encouraged to give prior notice
to the CEO or Corporate Secretary of their intention to exercise a stock option and obtain confirmation that any sale of securities
in connection with the exercise of a stock option will not occur during a blackout period. |
Notification of Blackout Periods
The CEO, Corporate Secretary or the Vice President
of Corporate Development will endeavour to notify the appropriate parties by e-mail of any blackout periods. If you are not certain
of the current blackout status please confirm by contacting the above individuals prior to engaging in activities involving the
Company’s securities.
Confidential Information
During the normal course of business, Representatives
will have access to business information and records of a confidential nature. Confidential information is described as: “information
which has not been made public by the Company through its public channels”. Confidential business information is not to be
disclosed externally or used for inappropriate purposes. See the Company’s Disclosure Policy. This requirement
applies both during and after termination of employment or services.
Financial Reporting and Records
The Company maintains accurate and complete
records. Honest and accurate recording and reporting of information is critical to our financial reporting and our ability to make
business decisions. Transactions between the Company and outside individuals and organizations are promptly and accurately entered
in our books in accordance with generally accepted accounting practices and principles.
All Representatives who have control over the
Company’s assets and transactions are responsible for establishing or maintaining a system of internal controls in their
area of responsibility designed to prevent unauthorized, unrecorded transactions, and permit the preparation of financial statements
according to acceptable accounting principles.
No one shall rationalize or even consider misrepresenting
facts or falsifying records. All Representatives have a responsibility to ensure that the Company’s records, including accounting
records, do not contain any false or misleading entries or omissions.
No Representative shall exert any influence
over, coerce, mislead or in any way manipulate or attempt to manipulate the independent auditors of the Company.
Records Retention
Records should be retained and destroyed in
accordance with any existing legal requirements.
COMPANY ASSETS
Use of Company Property
All Company Representatives are required to
protect the assets and opportunities and ensure their efficient use. Assets (information, technology, intellectual property, property,
buildings, equipment, machines, software and cash) must be used for legitimate business purposes only. Company assets may not be
used for illegal purposes.
Destruction or Theft of Property
Theft, carelessness and waste have a direct
impact on the Company’s operations. All Company Representatives shall not damage, destroy or misplace any property of the
Company.
Intellectual Property of Others
Company Representatives may not reproduce,
distribute or alter copyrighted materials without permission of the copyright owner. Software used in connection with the Company’s
operations must be properly licensed and used only in accordance with that license.
Information Technology
Email systems and internet services are provided
to help us perform our duties. Occasional personal use is permitted, but not for personal gain or improper use. Your messages including
voice mail and computer information are considered to be the property of the Company and therefore you will not be entitled to
any privacy in regard to these messages. Employees will be provided with a copy of the Employee Handbook which more
clearly details the rights and responsibilities of utilizing the Company’s information technology.
Corporate Opportunities
Company Representatives are not allowed to
take for themselves opportunities that arise through the use of corporate property, information or position, or from using corporate
property information or position for personal gain. Representatives have a duty to advance the interests of the Company and when
opportunities arise they are obligated to use these opportunities for corporate advancement.
WORKPLACE
Harassment or Discrimination
All Company Representatives deserve a workplace
where they are respected, satisfied, and appreciated. The Company respects cultural diversity and will not tolerate harassment
or discrimination prohibited by law. We are committed to equal opportunity in all aspects of employment.
Providing an environment that supports honesty,
integrity, respect, trust, and responsibility permits us the opportunity to achieve excellence in the workplace. While everyone
who works with the Company must contribute to the creation and maintenance of such an environment, our executives and management
assume the special responsibility for fostering a work environment that is free from the fear of retribution and will bring out
the best in all of us. Managers must be careful in words and deeds to avoid placing or seeming to place pressure on subordinates
that could cause them to deviate from acceptable ethical behaviour. See the Respectful Work Environment policy located in the Employee
Handbook, Operations Manual and on the Company Server. The Respectful Work Environment policy is posted at all office, warehouse
and camp locations operated by the Company.
Environment, Health and Safety
The Company is committed to providing a healthy
and safe workplace in compliance with applicable laws, rules and regulations and has developed a Environment, Health, Safety and
Community Policy (“HSE&C”) All Company Representatives must report any safety issues as they arise so that corrective
action may be taken. The Company’s Operations Manual outlines detailed specific expectations and behaviours
in connection with its HSE&C policies in the field. Each Field Employee or Company Representative is expected to be educated
and aware of the policies that are applicable to their particular job description.
Employee Handbook
Upon hiring, you will receive a copy of the
current Employee Handbook. This handbook details among other things, our corporate structure, environment, policies,
procedures and our expectations from you. It is your responsibility to read and understand these policies. The policies will be
reviewed and amended from time to time as required. If you have any questions or problems feel free to contact your immediate supervisor,
the CEO or the Corporate Secretary.
WAIVERS OF THE COE
Any waiver of this Code of Ethics with respect
to any Representative may only be made by the Board of Directors and or the Corporate Governance Committee. Any such waiver will
be promptly disclosed as required by applicable laws or regulatory policies.
REPORTING VIOLATIONS
The Company has a serious commitment to conduct
our business in a lawful and ethical manner. Representatives are encouraged to talk to their immediate supervisors or alternate
when in doubt about the best course of action in connection with a particular situation or a direct violation of the Code of Ethics.
When it is not appropriate or comfortable to report suspected violations to your immediate supervisor or alternate, report to the
Chair of the Corporate Governance Committee or the Chair of the Audit Committee.
If you observe or become aware of an actual
or potential violation of this COE or any law or regulation, it is your responsibility to report the incident. The COE is designed
to provide a safe environment, without reprisal, for the reporting of any incident.
The disciplinary measures are to be conducted
by the Board of Directors for the Company. Measures that may be invoked could include counselling, oral or written reprimand, warnings,
probation or suspension without pay, demotions, termination of employment and restitution.
ANNUAL ACKNOWLEDGEMENT AND CONFIRMATION
All Representatives will acknowledge and confirm
in writing on an annual basis that they are fully compliant with the COE or will report in writing to the Governance Chair the
details where they are not compliant.
CERTIFICATIONS
I, Peter Dasler, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on
Form 20-F of CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.;
| 2. | Based on my knowledge, this annual report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact
or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements
were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this annual report; |
| 3. | Based on my knowledge, the financial statements and other financial information included in this
report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Company as
of, and for, the periods presented in this annual report; |
| 4. | The Company’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining
disclosure controls and procedures for the company (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control
over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the Company and have: |
| (a) | Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures
to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the Company, including its consolidated subsidiaries,
is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
| (b) | Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial
reporting to be designed under supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and
the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
| (c) | Evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented
in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered
by this report based on such evaluation; and |
| (d) | Disclosed in this report any change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting
that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially
affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
| 5. | The Company’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our more recent evaluation
of internal control over financial reporting, to the Company’s auditors and the audit committee of the Company’s board
of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
| (a) | All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control
over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the Company’s ability to record, process, summarize
and report financial information; and |
| (b) | Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant
role in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. |
Date: August 29, 2014
CANALASKA URANIUM LTD
“Peter Dasler”
Peter Dasler
Chief Executive Officer
CERTIFICATIONS
I, Harry Chan, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on
Form 20-F of CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.;
| 2. | Based on my knowledge, this annual report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact
or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements
were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this annual report; |
| 3. | Based on my knowledge, the financial statements and other financial information included in this
report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the company as
of, and for, the periods presented in this annual report; |
| 4. | The company’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining
disclosure controls and procedures for the company (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control
over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the Company and have: |
| (a) | Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures
to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the Company, including its consolidated subsidiaries,
is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
| (b) | Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial
reporting to be designed under supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and
the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
| (c) | Evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented
in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered
by this report based on such evaluation; and |
| (d) | Disclosed in this report any change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting
that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially
affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
| 5. | The Company’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our more recent evaluation
of internal control over financial reporting, to the Company’s auditors and the audit committee of the Company’s board
of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
| (a) | All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control
over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the Company’s ability to record, process, summarize
and report financial information; and |
| (b) | Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant
role in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. |
Date: August 29, 2014
CANALASKA URANIUM LTD
“Harry Chan”
Harry Chan
Chief Financial Officer
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
SECTION 1350 OF CHAPTER 63 OF TITLE 18,
OF THE UNITED STATES CODE (18U.S.C.1350)
ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF
2002
In connection with the Annual Report of CanAlaska
Uranium Ltd. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the year ended April 30, 2014 as filed with the Securities and Exchange
Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Peter Dasler, the Chief Executive Officer of the Company, certify,
pursuant to 18 U.S.C. section 1350, as adopted pursuant to section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to my knowledge:
| (1) | the Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a)
or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and |
| (2) | the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material
respects, the financial condition and result of the operations of the Company. |
Date: August 29, 2014
“Peter Dasler”
Peter Dasler
Chief Executive Officer
CERTIFICATION
PURSUANT TO
SECTION 1350 OF CHAPTER 13 OF TITLE 18
OF THE UNITED STATES CODE (18U.S.C.1350)
ADOPTED
PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF
2002
In connection with the Annual Report of CanAlaska
Uranium Ltd. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the year ended April 30, 2014 as filed with the Securities and Exchange
Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Harry Chan, the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant
to 18 U.S.C. section 1350, as adopted pursuant to section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to my knowledge:
| (1) | the Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a)
or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and |
| (2) | the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material
respects, the financial condition and result of the operations of the Company. |
Date: August 29, 2014
“Harry Chan”
Harry Chan
Chief Financial Officer
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 1 of 24 |
| |
|
|

CanAlaska Uranium Ltd.
CVV - TSX CVVUF - OTCBB DH7N – Frankfurt
Management Discussion and Analysis
For the Fourth Quarter and Year Ended
April 30, 2014
Dated
July 29, 2014
For further information on the Company reference
should be made to the Company’s public filings which are available on SEDAR. Information is also available at the Company’s
website www.canalaska.com. The following information is prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards
as issued by the IASB (IFRS) and denominated in Canadian dollars, unless otherwise noted. This MD&A should be read in conjunction
with the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended April 30, 2014.
Table of Contents:
| 1. |
OVERVIEW OF THE COMPANY AND STRATEGY |
2 |
| 2. |
MILESTONES AND PROJECT UPDATES |
4 |
| 3. |
FINANCIAL POSITION |
14 |
| 4. |
Expenditures Review |
17 |
| 5. |
CASHFLOW REVIEW |
18 |
| 6. |
Other matters |
19 |
| 7. |
Quarterly and annual Financial information |
24 |
This MD&A contains forward-looking information.
Refer to section 6 “Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risks Factors” for a discussion of the risks, uncertainties
and assumptions relating to such information.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 2 of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 1. | | OVERVIEW OF THE COMPANY |
| ü | Exploration expenditures of $0.3 million ($0.5 million net of $0.2
million from reimbursements from partners) for year ended April 30, 2014 in the Athabasca Basin |
| ü | Over 18 projects covering 742,000 hectares focused on Uranium |
| ü | Cash resources of $1.0 million (as at April 30, 2014) |
| ü | 22,068,136 common shares issued and outstanding (July 29, 2014) |
The Company has responded to the drop in market
activity and values since the Fukushima nuclear incident by actively marketing its expertise and uranium exploration projects to
industry and end users for project financings or sales. There has been a slow resurgence in interest, and at the end of the fourth
quarter of our 2014 fiscal year, some renewed interest from North American and Chinese industry groups in response to the Canada-China
nuclear accord. Management has continued with evaluating its priorities, taken steps to streamline non-discretionary expenditures,
continued its efforts to raise funds and continue to explore all opportunities to sell and/or joint venture its properties. The
recoverability of the amounts shown for mineral properties and related deferred costs is dependent upon the existence of economically
recoverable mineral reserves, the ability of the Company to obtain the necessary financing to complete the development, and upon
future profitable production or proceeds from disposition of the mineral properties. Due to the difficult market conditions facing
junior uranium exploration companies there is no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising additional financing.
From time to time, the Company will evaluate new properties and direct activities to these based on the Board of Director’s
evaluation of financial and market considerations at the time.
The Company is an exploration stage company
engaged in the acquisition and exploration of mineral properties, principally in Canada. The Company aims to acquire and advance
its projects to a stage where they can be exploited at a profit or it can arrange joint ventures, whereby other companies provide
funding for development and exploitation. The Company’s principal focus for the past nine years has been the exploration
for high-grade uranium deposits in the Athabasca Basin area of Saskatchewan. There are four projects on which the Company has expended
most of its recent efforts. Three of these projects, West McArthur, Cree East and Fond Du Lac are 50% joint ventures, and the fourth,
NW Manitoba, is 100% owned by the Company. Going forward it is expected that the Company will focus its effort on two of the projects,
West McArthur and Cree East. The Company is actively marketing the remainder of its projects for option, joint venture or sale.
| Table 1: Canadian Strategic Property Summary |
|
|
| Property / Project Name |
Notes |
Hectares |
Life-to Date ("LTD") Expenditures |
| West McArthur |
Ventured with Mitsubishi |
36,000 |
$19,644 |
| Cree East |
Ventured with Korean Consortium |
58,000 |
$19,149 |
| NW Manitoba |
Option with MPVC Inc. |
144,000 |
$7,327 |
| Fond Du Lac |
Option with Fond Du Lac Denesuline |
10,000 |
$4,546 |
| TOTAL |
|
|
$50,667 |
In the Athabasca Basin, the Company’s
most advanced projects are those which the Company has under joint venture with Japanese and Korean entities. The Company has a
strong in-house exploration team along with outside consultants which it can access and has established strategic exploration funding
relationships with MC Resources Canada, a wholly owned subsidiary of Japan’s Mitsubishi Corporation Ltd. (“Mitsubishi”)
on the West McArthur project. On the Cree East project, the Company is the Operator of a 50% joint venture with a Korean Consortium
comprised of Hanwha Corp., Korea Resources Corp. (“KORES”), Korea Electric Power Corporation (“KEPCO”),
and SK Networks Co. Ltd.
Throughout the region, the Company controls
an exploration portfolio of 18 projects totalling over 2,864 square miles (742,000 hectares) and has a land position that rivals
the combined holdings of established uranium producing giants Cameco Corporation and Areva The largest of these projects is the
NW Manitoba Project, located just east of the Saskatchewan-Manitoba provincial border. In 2012, the Company re-started exploration
at the NW Manitoba project, after waiting since 2007 for the Manitoba government approvals related to community consultation. In
early 2012, the Company completed an operating MOU with the local community and geophysics work and target definition started in
March 2012. At the current time, the Company has optioned the project to MPVC Inc. MPVC Inc. may earn an 80% interest in the project
by carrying out a three stage $11.6 million exploration program (see section 2.2.3).
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 3
of 24 |
| |
|
|
In addition, CanAlaska is the operator
of a joint venture with the Fond Du Lac Denesuline community over an area which covers the historic Fond Du Lac uranium deposit,
and where the Company has extended the target area to the east, with a drill intercept of 40.4 metres grading 0.32% uranium.
The Company’s exploration activities
are managed through CanAlaska offices maintained in Vancouver, BC (Head Office) and La
Ronge, Saskatchewan (Field Support and Equipment
Warehouse).
The Company believes that the fundamentals
of the nuclear power industry and the economic superiority of uranium over other energy fuels will ensure the long-term future
of global uranium markets and prices. Since 2004, CanAlaska has expended over $78 million on exploration and research towards the
advancement of uranium discovery on our current project areas. The information gained from this work has provided the Company with
significant evidence regarding the nature and location of mineral rich hydrothermal systems in areas of the Athabasca where previous
information was lacking. The increase in understanding of the geology of the target areas, and the integration of modern geophysical
methods with data processing to get more precise target definition at depth gives management the confidence to continue exploration
for large scale uranium deposits on our projects.
As of July
28, 2014, the Company had 22,068,136 shares outstanding with a total market capitalization of $3.3 million. The Company’s
shares trade on the TSX Venture Exchange (“CVV”) and are quoted on the OTCBB in the United States (“CVVUF”)
and the Frankfurt Stock Exchange (“DH7N”). On December 30, 2013, the Company's shares commenced trading on the TSX
Venture Exchange and ceased trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange.
The financial statements and the Management
Discussion and Analysis have been prepared under IFRS applicable to a going concern, which contemplates the realization of assets
and settlement of liabilities in the normal course of business. For the year ended April 30, 2014, the Company reported a loss
of $0.7 million and as at that date had cash and cash equivalents of $1.0 million, net working capital balance of $1.1 million
and an accumulated deficit of $81.6 million. The Company is pursuing a number of financing alternatives including selling and or
joint venturing some of its properties.
The Company's ability to continue as a going
concern is dependent upon its ability to obtain additional funding from debt, equity or through other arrangements. Management
believes that the cash on hand is sufficient to meet corporate, administrative and selected exploration activities for at least
the next twelve months. Management may either need to dilute its ownership in its properties or secure additional financing to
continue to advance the development of its exploration projects. Management has taken steps to streamline non-discretionary expenditures
and financial overheads and is working to option, joint venture or sell its individual exploration projects. The above factors
cast doubt regarding the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
| 1.2 | | Strategic and Operating Intent |
·
Targeted marketing of uranium projects for financing
·
Restriction of uranium exploration activity until financial markets
recover in this sector
·
Strong commitment to option, joint venture or sale of individual
exploration projects
·
Evaluate alternate commodities and projects suitable for market financing,
or acquisition and sale
·
Company believes that it has the projects, strategic partners, people
and knowledge base, corporate treasury and fund raising ability to maintain a position in the uranium exploration sector, but,
due to increasingly difficult market conditions facing junior mining and junior uranium exploration companies, management has taken
steps to streamline non-discretionary expenditures and financial overheads
·
The Company has tax loss carry-forwards of approximately $9 million
and cumulative Canadian exploration expenses of approximately $18 million
·
Our Korean partners have contributed all of their $19.0 million funding
commitment towards the Cree East project, but have requested a slow-down in expenditures, or the introduction of an incoming partner
·
At the West McArthur project, exploration is being carried out under
a 50/50 joint venture with MC Resources Canada (“MCRC”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Mitsubishi Corporation, and CanAlaska
which has been deferred in 2013/2014 to await better market conditions
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 4 of
24 |
| |
|
|
| 2. | | MILESTONES AND PROJECT UPDATES |
| 2.1 | | Overview– May 1, 2013 to July
29, 2014 |
| · | Kasmere south uranium project sale
completed (June 2014) |
| · | Strongly anomalous radon results
received from MPVC NW Manitoba project (April 2014) |
| · | Kasmere sales agreement (April 2014) |
| · | Reefton purchase agreement (March
2014) |
| · | Listed on the TSX Venture Exchange
(December 2013) |
| · | Application to list on the TSX Venture
Exchange (November 2013) |
| · | NI43-101 report filed for the Cree
East project (November 2013) |
| · | Entered into option agreement with
MPVC Inc. on NW Manitoba project (September 2013) |
| · | Entered into optioned agreement with
Makena on Patterson project (August 2013) |
| · | Reefton option agreement terminated
(August 2013) |
| · | Hanson project - staked twelve claim
blocks (July, August and November 2013) |
| · | BC Copper option agreement terminated
(July 2013) |
| · | Reduced project activities and marketing
non-core assets (June 2013) |
In June 2014, the sale of the Kasmere
South uranium project in Northern Manitoba to East Resource for a total cash payment of $1.8 million and a 2.5% net smelter royalty
was completed.
In April 2014, the Company announced
that MPVC Inc. had received highly anomalous radon results of a recently completed, land-based survey over the Maguire Lake area.
This is located within MPVC's Northwest Manitoba uranium project which was recently optioned from CanAlaska. MPVC reports that
its geologic team is most encouraged by the distribution of radon, resistivity, magnetic and gravity anomalies which are prime
drill targets for uranium mineralization.
In April 2014, the Company announced
that it had entered into a binding agreement to sell its interest in its Kasmere South project in northwestern Manitoba to private
company, East Resources Ltd., for cash payments totalling $1.8 million.
In March 2014, the Company entered
into a purchase agreement for the exploration permit for the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. ("Stevenson") for
aggregate purchase consideration of $20,000. Subsequent to year end, the Company began liquidation proceedings on its New Zealand
subsidiary as there are no significant assets or liabilities remaining in the entity.
On December 30, 2013, the Company's
common shares were listed and commenced trading on the TSX Venture Exchange.
On November 5, 2013, the Company
announced it had made application to list its shares on the TSX Venture Exchange. The application has been made in response to
the Toronto Stock Exchange's (“TSX”) announcement on November 1, 2013 that the Company no longer met the market capital
requirements of the TSX.
In November 2013, the Company filed
a NI43-101 report for the Cree East Project. The report details the programs of work funded by the Korean Consortium partners,
Hanwha, KORES, KEPCO and SK, and the multiple zones of uranium mineralization recognized from the first and second pass drill programs.
In September 2013, the Company entered
into an option agreement with NEX-listed MPVC Inc. ("MPVC") for an interest in the NW Manitoba project. The project covers
143,603 hectares along the Saskatchewan/Manitoba border. In January 2014, the option agreement was revised whereby MPVC may earn
an 80% interest in the project by carrying out a three stage $11.6 million exploration program, make a further cash payment of
$35,000, issue 12 million common shares and issue 6 million common share purchase warrants. In February 2014, the option agreement
with MPVC was amended to extend the date of certain provisions of the agreement from February 28, 2014 to March 14, 2014. In consideration
for amending the agreement, MPVC paid a non-refundable cash deposit in the amount of $50,000 on March 14, 2014.
On August 28, 2013, the Company entered into
an option agreement with Makena Resources Inc. (“Makena”). Makena may earn a 50% interest in the Patterson property
by making cash payments totalling $100,000 by June 1, 2015, issuing 2,500,000 common share by June 1, 2015 and incurring exploration
expenditures totalling $1.4 million by September 30, 2016.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 5
of 24 |
| |
|
|
On August 21, 2013, the option agreement
with Atlantic Industrial Minerals Inc. for the Reefton project was terminated.
In July, August and November 2013, the Company
staked the Hanson project which consists of fourteen blocks of claims in the area of the Pikoo kimberlite discovery, totalling
17.272 hectares located in Saskatchewan for $10,374.
On July 2, 2013, the option agreement with
Tyrone Docherty and Discovery Ventures Ltd. for the BC Copper (Big Creek) project was terminated.
In June 2013, the Company announced that it
had in the past 15 months, reduced project exploration activities to preserve a modest treasury such that there is a minimum of
dilution to existing shareholders during a time of depressed market prices. The Company has been active in the presentation and
marketing of its joint ventures and non-core assets. The marketing of the non-core assets had attracted a number of industry investors
and supporters who have entered into confidentiality agreements to review potential purchase or earn-in joint ventures with the
Company.
Overview
The Company currently has 18 projects within
the Athabasca basin area and has carried out exploration programs on four of these in the past year. In fiscal 2014, the Company
spent $0.3 million ($0.5 million net of $0.2 million from reimbursements from partners) on exploration costs in the Athabasca Basin
area. The two largest exploration projects were at West McArthur and at Cree East.
Exploration spending in the fourth quarter
of 2014 is significantly down from the same comparative quarter of 2013, as the Company has reduced its exploration spend to conserve
cash relative to the prior period. In the fourth quarter, the Company historically spent this time drilling in the winter season
in the Athabasca Basin at our various projects.
The following table summarizes the Company’s
expenditures for twelve months ended April 30, 2014.
|
Table 2: ($000's)
Total Exploration |
Cree East |
West McArthur |
Fond Du Lac |
NW Manitoba |
Other Athabasca Basin Projects |
New Zealand |
Other and Generative Projects |
Total |
| Camp Cost & Operations |
(12) |
- |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(8) |
| Drilling |
27 |
- |
6 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
34 |
| General & Admin |
26 |
36 |
1 |
11 |
14 |
25 |
55 |
168 |
| Geochemistry |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
1 |
| Geology |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
8 |
- |
- |
9 |
| Geophysics |
151 |
- |
- |
- |
32 |
- |
- |
183 |
| Other |
28 |
2 |
- |
76 |
3 |
- |
(12) |
97 |
| Gross Expenditures |
221 |
38 |
11 |
87 |
58 |
25 |
44 |
484 |
| Reimbursements |
(111) |
(19) |
- |
(83) |
- |
- |
- |
(213) |
| Net Expenditures |
110 |
19 |
11 |
4 |
58 |
25 |
44 |
271 |
The following section contains a comparative
breakdown of project expenditures for the Company’s significant projects. Reimbursements represents the amounts received
from our joint venture partners and option partners to be applied against the expenditures for the project.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 6
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 2.2.1 | | West McArthur Project, Saskatchewan – Mitsubishi |
The West McArthur project in the Athabasca
Basin, Saskatchewan, was optioned in April 2007 to Mitsubishi Development Pty Ltd., a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Corporation of Japan.
Under the option agreement, Mitsubishi could exercise an option to earn a 50% interest in the property by investing $11.0 million.
In February 2010, Mitsubishi exercised its option with a payment to the Company and an unincorporated 50/50 joint venture was formed
between the parties to pursue further exploration and development of the property. As at April 30, 2014, the Company holds a 50%
interest in the West McArthur project. Mitsubishi holds the remaining 50% interest in the property. The Company acts as project
operator under the supervision and guidance of Dr. Karl Schimann, P. Geo. and Mr. Peter Dasler, P. Geo. and earns a fee between
5% and 10%, based on expenditures incurred. Included within Other expenses are management fees charged to and reimbursed by Mitsubishi
for CanAlaska acting as the project operator.
| Table 3: ($000's) |
Quarterly |
Year Ended |
|
| West McArthur Project |
Q113 |
Q213 |
Q313 |
Q413 |
Q114 |
Q214 |
Q314 |
Q414 |
Apr-13 |
Apr-14 |
LTD |
| Camp Cost & Operations |
- |
- |
- |
(8) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(8) |
- |
2,976 |
| Drilling |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
6,745 |
| General & Admin |
31 |
26 |
12 |
8 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
11 |
77 |
35 |
2,132 |
| Geochemistry |
15 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
16 |
- |
339 |
| Geology |
48 |
16 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
65 |
- |
1,000 |
| Geophysics |
211 |
12 |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
227 |
- |
5,775 |
| Other |
20 |
3 |
6 |
- |
1 |
2 |
- |
- |
29 |
3 |
677 |
| Gross Expenditures |
325 |
58 |
23 |
- |
7 |
10 |
10 |
11 |
406 |
38 |
19,644 |
| Reimbursement |
(171) |
(30) |
(12) |
- |
(4) |
(5) |
(5) |
(6) |
(213) |
(19) |
(14,227) |
| Net Expenditures |
154 |
28 |
11 |
- |
3 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
193 |
19 |
5,417 |
The West McArthur project is located between
6 and 30 kilometres west of the producing McArthur River uranium mine operated by Cameco Corp, and covers approximately 36,000
hectares. On the property there is evidence of hydrothermal alteration extending well into the sandstone, matching the typical
alteration model of Athabasca unconformity style uranium deposits. There is evidence of uranium mineralization from drill testing
in multiple areas, either as enrichment at the unconformity or in basement stringers. The most compelling features for further
exploration are the uranium values in sandstone higher in the stratigraphy, the hematized and broken rock in the sandstone, and
the pattern of basement offsets and geophysical conductivity.
The project is accessible during the winter
drill season by seasonal winter ice roads and winter trails and during the summer exploration season by air and water. There is
no physical plant or permanent infrastructure on the property and no source of power. There are multiple extensive lakes which
can provide a source of water for the project.
The mineral rights for West McArthur were acquired
between October 2004 and February 2009 from the Ministry of Energy and Resources in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. The claim
numbers are as follows, S-107561, S-107562, S-107563, S-107565, S-107773, S-108010, S-108011, S-108012, S-111412 S-111413, S-111511
and S-111512. The mineral rights to West McArthur are valid and in good standing with the earliest claim requiring renewal in October
2029 with no further exploration expenditures required. An annual assessment report is required to be filed by the Company with
the Ministry of Energy and Resources to disclose the exploration activities on this claim. There is no fee for filing the annual
assessment report.
In April 2012, the Company announced a preliminary
summary of drilling at its West McArthur project. Seven diamond drill holes were completed in February and March 2012, to test
a series of individual zones where the resistivity lows were coincident with the EM conductors within the Grid 5 area. Total meterage
drilled in the season was 6,422 metres, including one abandoned drill hole. The winter 2012 drill programme has demonstrated on
Grid 5 the presence of requisite geological environment for unconformity uranium deposits. Significant faulting and fracturing
are present in a number of drill holes, with individual radioactive spikes or elevated radioactivity in zones of hydrothermal alteration.
In June 2012, the Company reported the results
of drill core geochemistry on the West McArthur property. Drill holes WMA028 and WMA034 produced very positive results for uranium.
Both intersected parts of a highly-altered graphitic pelite unit and are thought to be within 50 metres of the targeted conductor,
which was identified from the down-hole geophysical surveys. The targets generated at the eastern end of Grid 5 matched and extended
a historical conductor, which was drill-tested by Uranerz in 1989. Neither of the two historical drill holes intersected their
targeted basement conductor, but, significantly, contained dravite clay and pyrite along with narrow, steep, clay rich fault gouges/breccia
in the top 350-400 metres of the sandstone column. In one historical hole, the upper 400 metres of sandstone showed anomalous uranium
and trace elements. Drill holes WMA028 and WMA034 are located in this area. Both show deep alteration into the basement rocks,
indicating and confirming a substantial hydrothermal alteration system.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 7
of 24 |
| |
|
|
The potential of this project is for unconformity
style uranium mineralization of both the Simple (Low REE, basement hosted) and the Complex ( High REE, Sandstone hosted) types
of uranium. Previous exploration was hampered by the depths to the basement, however, recent advances with airborne geophysical
survey technology has enabled penetration to those depths. Multiple exploration programs since 2005 have identified targets with
strong geophysical feature, similar to those near existing uranium mines. Limited drill testing in several of these areas have
shown the basement offsets, hydrothermal clay alteration, and elevated uranium geochemistry consistent with the Athabasca unconformity
deposit model. The project, has four target areas which are being evaluated for further drill testing.
The property has undergone a series of exploration
programs, including extensive geophysics and drilling of over 35 drill holes since 2005. Approximately $19.6 million has been spent
by the joint venture.
The next drill programs are dependent on financing.
The project does not have a drill program planned for 2014. Active full season programs of 6-9 drill holes are generally budgeted
at $3 to $4 million, including drill geophysics, camp and logistics. The project currently has a maintenance budget of approximately
$100,000 for 2014 which will be funded 50% by CanAlaska and 50% by Mitsubishi.
As at April 30, 2014, the total exploration
costs incurred for the West McArthur project was $19.6 million. Further exploration expenditures for this project have been deferred
in 2013/2014 to await better capital market conditions in order to raise exploration funds. The West McArthur property is without
known reserves and any proposed program is exploratory in nature.

| 2.2.2 | | Cree East Project, Saskatchewan – Korean Consortium |
The Cree East project is located in the south-eastern
portion of the Athabasca Basin, 35 kilometres west of the formerly producing Key Lake mine and 5 to 22 kilometres north of the
south rim of the Athabasca Basin. The project is comprised of 17 contiguous mineral claims totalling approximately 58,000 hectares.
In December 2007 a Korean Consortium (Hanwha Corp., Korea Electric Power Corp., Korea Resources Corp. and SK Networks Co. Ltd.),
agreed to spend $19.0 million on the properties to earn into a 50% interest in the Cree East project.
As
of April 30, 2014, the Korean Consortium has contributed its $19.0 million towards exploration of the project and holds a 50% ownership
interest in both CanAlaska Korea Uranium Ltd. and the Canada-Korea Uranium Limited Partnership. The remaining 50% interest is held
by CanAlaska. The following table summarizes the Korean Consortium
expenditures and advances by quarter and life to date (“LTD”) on the project. The table does not include a $1.0 million
payment made directly to CanAlaska in 2007 ($0.6 million) and 2010 ($0.4 million) for intellectual property associated with the
project. As at April 30, 2014, the Company is holding approximately $176,000 of joint venture funds.
| Table 4: ($000's) |
Quarterly |
Year Ended |
|
| Cree East Project |
Q113 |
Q213 |
Q313 |
Q413 |
Q114 |
Q214 |
Q314 |
Q414 |
Apr-13 |
Apr-14 |
LTD |
| Camp Cost & Operations |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
(13) |
- |
4 |
(12) |
3,332 |
| Drilling |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
27 |
- |
- |
- |
27 |
6,740 |
| General & Admin |
5 |
- |
14 |
18 |
- |
13 |
5 |
9 |
37 |
26 |
502 |
| Geochemistry |
5 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
6 |
- |
537 |
| Geology |
49 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
73 |
1 |
1,583 |
| Geophysics |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
151 |
2 |
151 |
3,410 |
| Management Fees |
10 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
1 |
4 |
- |
17 |
20 |
22 |
1,574 |
| Other |
30 |
4 |
5 |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
7 |
42 |
7 |
1,471 |
| Net Expenditures |
104 |
8 |
25 |
47 |
1 |
46 |
(8) |
184 |
184 |
222 |
19,149 |
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 8
of 24 |
| |
|
|
The project is accessible during the winter
drill season by seasonal winter ice roads and winter trails and during the summer exploration season by air and water. There is
no physical plant or permanent infrastructure on the property and no source of power. There are multiple extensive lakes which
can provide a source of water for the project.
The mineral rights for Cree East were acquired
between November 2004 and June 2010 from the Ministry of Energy and Resources in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. The claim
numbers are as follows, S-107757, S-107774, S-107775, S-107776, S-107777, S-107778, S-107779, S-107780, S-108357, S-108358, S-108382,
S-108383, S-108384, S-108385, S-108386, S-108387 and S-111809. The mineral rights to Cree East are valid and in good standing with
the earliest claim requiring renewal in November 2020 with no further exploration expenditures required. An annual assessment report
is required to be filed by the Company with the Ministry of Energy and Resources to disclose the exploration activities on this
claim. There is no fee for filing the annual assessment report.
The project area covers Athabasca group conglomerates
and sandstones. Sandstone unconformity overlies basement at depths in the order of 200 to 300 metres in the south. Structural breaks
which trend across the across the property further drop the basement to estimated depths of 800 to 900 metres across the northern
edge of the property The basement is composed of the Lower Proterozoic, (Trans Hudson) Mudjatik domain, granitoids and associated
minor supercrustals (psammites, pelites and metavolcanics) A significant portion of the property is considered to be underlain
by rocks of the highly prospective Wollaston Domain.
In May 2012, the Company reported receipt of
uranium assay results and trace element geochemistry for the winter drill program on the Cree East project. The results confirm
the anomalous multi-element enrichments in the large alteration zone identified at Zone B and additional gold and uranium mineralization
in drill hole CRE080, which intersected mineralized iron formation at Zone J.
The property has undergone extensive exploration
since 2005 with $19.1 million expended on surveys, extensive geophysical testing and over 70 drill holes testing targets.
The potential of this project is for unconformity
style uranium mineralization of both the Simple (Low REE, basement hosted) and the Complex (High REE, Sandstone hosted) types of
uranium. The area has numerous conductors and faults which act as both the conduit and the trap for potential uranium mineralization.
A number of structures and conductive targets have been identified from the Company's exploration efforts. The next substantial
work programs on the property will consist mainly of drill testing the current targets. Active full season programs of 15-18 drill
holes are generally budgeted at $3 to $4 million, including drill geophysics, camp and logistics. There is a program of geophysics
to be performed by an external third party for winter field season 2014, budgeted at $350,000 which will be funded by the joint
venture funds held. A $3 million summer drill program has been approved, subject to financing.
Under the Cree East agreement, CanAlaska is
entitled to charge an operator fee of 10% to recoup its indirect costs associated with the project, which the Company recognizes
as management fees. CanAlaska acts as project operator under the supervision and guidance of Dr. Karl Schimann, P. Geo. and Mr.
Peter Dasler, P. Geo.
As at April 30, 2014, the total exploration
costs incurred for the Cree East project was $19.1 million. In March 2014 the Joint Venture carried out geophysical surveys over
the Zone B target area. This surveying was in preparation for a proposed summer drill program. The summer drill program is dependant
upon financing by CanAlaska or others.. The Korean Consortium and CanAlaska are actively marketing the Cree East project for option
or joint venture to allow for the continuation of the drill exploration. Work permits are in place for summer 2014 drilling. The
Cree East property is without known reserves and any proposed program is exploratory in nature.

 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 9
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 2.2.3 | | NW Manitoba, Manitoba |
This property consists of approximately 144,000
hectares and lies between 90 and 170 kilometres northeast along the Wollaston trend of basement formations hosting uranium deposits,
which include Rabbit Lake, Collins Bay and Eagle Point Uranium mines. In May 2012, the Company reported strong geophysical responses
matching geology and uranium mineralized boulders from the recent surveys within the target areas at its NW Manitoba uranium project.
The project was re-started in March 2012 following a four and a half year permitting delay due to consultations between the government
of Manitoba and the local community. The Company has now concluded an operating MOU with the local community and recommenced ground
survey work. The ground resistivity gravity geophysical surveys carried out in March 2012 localized anomalous features typical
of sulphide-bearing mineralization, and zones of clay alteration within areas of shallow overburden. There is a striking correspondence
between the location of gravity anomalies and the low resistivity zones from the survey. These targets are similar in style to
the Andrew Lake uranium project in Nunavut, which has similar resistivity and gravity geophysical responses related to uranium
mineralization hosted in regional fault structures.
In September 2013, the Company entered
into an option agreement with NEX-listed MPVC Inc. ("MPVC") for an interest in the NW Manitoba project. MPVC may earn
an 80% interest in the project by carrying out a three stage $11.6 million exploration program, making a cash payment of $35,000,
issuing 12 million common shares and issuing 6 million common share purchase warrants.
On February 28, 2014, the option
agreement with MPVC for the NW Manitoba project was amended to extend the date of certain provisions of the agreement from February
28, 2014 to March 14, 2014. In consideration for amending the option agreement, MPVC paid a further non-refundable cash deposit
in the amount of $50,000 on March 14, 2014.
In April 2014, the Company announced
that MPVC Inc. had received highly anomalous radon results of a recently completed, land-based survey over the Maguire Lake area.
MPVC reports that its geologic team is most encouraged by the distribution of radon, resistivity, magnetic and gravity anomalies
which are prime drill targets for uranium mineralization.
In Q114 and Q214, the Company recognized
an impairment on certain of its Grease River claims of approximately $57,000 as it did not renew its permits on these claims.
During fiscal 2014, the Company recognized
an impairment on certain of its Poplar claims of approximately $35,000 as it did not renew its permits on these claims.
In Q114 and Q414, the Company recognized an
impairment on certain of its Lake Athabasca claims of approximately $20,000 as it did not renew its permits on these claims.
In Q114, the Company recognized an impairment
on its Hodgson claim of approximately $109,000 as it did not renew its permits on this property. In Q314, the Company re-staked
certain claim blocks for $6,895.
In June 2013, the Collins Bay Extension option
agreement dated July 4, 2009 and amended on March 29, 2011 with Bayswater Uranium Corporation ("Bayswater") was amended
whereby the option period was extended from six years to eight years. In consideration for the extension, the Company accelerated
its staged common share issuances and issued 10,000 common share on July 12, 2013. As a result, in July 2013, the Company issued
an aggregate of 20,000 common shares (post-consolidation) under the amended option agreement for the Collins Bay Extension project.
2.2.9 Carswell
In January 2014, the Company recognized an
impairment on its Carswell claim of approximately $136,000 as it did not renew its permits on this property.
2.2.10 Patterson
In January 2013, the Company acquired three
block of claims, totalling 6,687 hectares located in the Patterson Lake area of the western Athabasca basin. In August 2013, the
Company optioned the claims to Makena Resources Inc. Makena may earn a 50%
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 10
of 24 |
| |
|
|
interest in the property by making cash payments
totalling $100,000 by June 1, 2015, issuing 2,500,000 common share by June 1, 2015 and incurring exploration expenditures totalling
$1.4 million by September 30, 2016.
In September 2012, Atlantic Industrial Minerals
Inc. (“Atlantic”) entered into an option agreement to acquire a 100% interest in the Reefton project, in South Island,
New Zealand by paying $300,000 in staged payments, issuing 300,000 shares of Atlantic to the Company and reimbursing the Company
for the annual permit fees for the property from 2012 to 2015 which are approximately $50,000 per year, and drilling 1,500 metres
by December 31, 2014. In September 2012 and October 2012, the Company received $50,000 from Atlantic for the 2012/2013 annual permit
fee as part of an operating agreement. On August 21, 2013, the option agreement with Atlantic was terminated.
In March 2014, the Company entered
into a purchase agreement to sell the exploration permit for the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. ("Stevenson")
for aggregate purchase consideration of $20,000. In Q414, the Company recognized a loss on disposal of the Reefton project of approximately
$4,000.
The Company has two claim blocks (Big Creek
and Quesnel). Big Creek was under option, but in July 2013, the option agreement with Discovery Ventures Ltd. and Tyrone Docherty
was terminated. The property is currently being marketed.
In July, August and November 2013, the Company
staked the Hanson project which consists of fourteen blocks of claims in the area of the Pikoo kimberlite discovery, totalling
17,272 hectares located in Saskatchewan for $10,374.
In January 2014, the Company entered into a
purchase agreement for two claim blocks in the Hanson project to Copper Reef Mining Corp. ("Copper Reef") for aggregate
purchase consideration of $50,000 in cash and the issuance of 1,000,000 common shares in the capital of Copper Reef and completion
of $50,000 of exploration expenditures. The Company retains a 2% net smelter royalty in the agreement.
In April 2014, the Company announced that it
had entered into a binding agreement to sell its interest in its Kasmere South project in northwestern Manitoba to private company,
East Resources Ltd., for an aggregate cash payment totalling $1.8 million. On March 28, 2014, the Company received a non-refundable
cash payment of $200,000 from East Resources Ltd. Subsequent to year end, the Company also received the remaining cash instalments
of $100,000 and $1.5 million on May 30, 2014 and June 26, 2014 respectively.
The Company uses its technical staff between
field seasons to evaluate other mineral projects for acquisition, either by staking or by option, with the purpose of sale to third
parties. For a full description of the geology and setting of the current projects and of the Company’s other projects, reference
should be made to the “Projects” section, and accompanying news releases of work on the Company’s website at
www.canalaska.com.
|
Table 5:
Other projects update |
Status |
Recent work undertaken |
| BC Copper |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Collins Bay Extension |
Option with Bayswater Uranium |
No significant work undertaken |
| Grease River |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Hanson |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Helmer |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Hodgson |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Kasmere |
Under application |
Exploration permits pending |
| Key |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Lake Athabasca |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| McTavish |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Moon |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Patterson |
Option with Makena Resources Inc. |
Airborne surveys have been contracted |
| Poplar |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Waterbury |
Seeking Venture Partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Rainbow Hill AK |
Seeking Venture partner |
No significant work undertaken |
| Zeballos |
Seeking Venture Partner |
Consolidating ownership |
| Glitter Lake |
Disposed, NSR retained |
|
| Reefton Property, NZ |
Sale to Stevenson Mining Ltd. |
|
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 11
of 24 |
| |
|
|
The Company is restricting its exploration
activities on these Other projects until financial markets recover. The Company intends to continue its efforts to seek a venture
partner either through a joint venture or sales of its other projects.
In fiscal 2014, the Company recognized an impairment
on its Grease River, Poplar, Lake Athabasca, Hodgson and Carswell claims for approximately $357,000 as it did not renew certain
of its claims on these properties.
In May 2014, Golden Fern Resources Limited,
the Company's wholly owned subsidiary in New Zealand, began liquidation proceedings. The New Zealand subsidiary is being liquidated
after the sale of the Reefton project to Stevenson Mining Ltd. and there are no significant assets or liabilities remaining in
the entity.
CanAlaska maintains twelve other
projects in the Athabasca basin; one project in Alaska and four projects in British Columbia. These other projects have value to
the Company but are not being actively explored, other than reviews and reporting. A number of these projects are being marketed
for sale or joint venture, and the company hopes to realize increased value in the future.
All of the samples from the CanAlaska exploration
programs have been submitted to one of two qualified Canadian Laboratories for analysis. Samples submitted to Saskatchewan Research
Laboratories were analyzed for multi-element geochemistry and including uranium by tri-acid digestion and ICP. Samples submitted
for assay for trace element geochemistry to Acme Laboratories in Vancouver BC, were analyzed by aqua regia digestion and ICP analysis.
The samples were collected by CanAlaska field geologists under the supervision of Dr. Karl Schimann, and were shipped in secure
containment to the laboratories noted above.
Our exploration activities requires permitting
in the Province of Saskatchewan. For our projects in Saskatchewan, the Company applies for surface exploration permits from the
Ministry of Environment, a letter of advice from the Heritage Resources Branch of the Ministry of Tourism, Parks, Culture and Sport,
and a Right to Use Water from the Saskatchewan Water Authority. For our exploration projects in the Province of Manitoba, the Company
applies for a Prospecting License, a Work Permit from the Manitoba Department of Conservation, and a notification to the Director
of Mines for airborne surveys. In addition, all exploration activities have to conform to the Fisheries Act in terms of protection
of fish habitat.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 12
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 2.2.16 | | Project Expenditure Summary |
Details of life to date (“LTD”)
exploration and evaluation expenditures:
| Table 6: ($000’s) |
2014 Fiscal Expenditures |
Life to Date - April 30, 2014 |
| Project |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net YTD |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net LTD |
| Athabasca Basin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cree East |
- |
223 |
- |
223 |
- |
19,150 |
- |
19,150 |
| West McArthur |
- |
37 |
(19) |
18 |
65 |
19,578 |
(14,227) |
5,416 |
| Fond Du Lac |
- |
11 |
- |
11 |
120 |
4,427 |
- |
4,547 |
| NW Manitoba |
- |
3 |
- |
3 |
16 |
7,311 |
- |
7,327 |
| Poplar |
- |
- |
(35) |
(35) |
166 |
3,637 |
(3,245) |
558 |
| Grease River |
- |
1 |
(57) |
(56) |
133 |
3,495 |
(2,907) |
721 |
| Key Lake |
- |
- |
- |
- |
24 |
1,027 |
(1,047) |
4 |
| Helmer |
- |
1 |
- |
1 |
107 |
5,047 |
- |
5,154 |
| Lake Athabasca |
- |
- |
(20) |
(20) |
118 |
5,966 |
(20) |
6,064 |
| Hodgson |
7 |
- |
(109) |
(102) |
116 |
1,561 |
(109) |
1,568 |
| Collins Bay |
- |
10 |
- |
10 |
- |
1,319 |
- |
1,319 |
| McTavish |
- |
- |
- |
- |
74 |
687 |
(108) |
653 |
| Ruttan |
- |
33 |
- |
33 |
15 |
67 |
- |
82 |
| Carswell |
- |
1 |
(137) |
(136) |
137 |
754 |
(137) |
754 |
| Other |
0 |
1 |
- |
1 |
57 |
2,568 |
(1,616) |
1,009 |
| New Zealand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Reefton, NZ |
- |
25 |
(24) |
1 |
24 |
811 |
(505) |
330 |
| Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Projects, Various |
12 |
17 |
- |
29 |
86 |
692 |
(425) |
353 |
| Total |
19 |
363 |
(401) |
(19) |
1,258 |
78,097 |
(24,346) |
55,009 |
| Table 7: ($000’s) |
2013 Fiscal Expenditures |
Life to Date - April 30, 2013 |
| Project |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net YTD |
Acquisition Costs |
Exploration Expenditures |
Write-offs/
Reimbursement |
Net LTD |
| Athabasca Basin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cree East |
- |
184 |
- |
184 |
- |
18,927 |
- |
18,927 |
| West McArthur |
- |
406 |
(213) |
193 |
65 |
19,541 |
(14,208) |
5,398 |
| Poplar |
- |
- |
- |
- |
166 |
3,637 |
(3,210) |
593 |
| Fond Du Lac |
- |
17 |
- |
17 |
120 |
4,415 |
- |
4,535 |
| Grease River |
- |
- |
- |
- |
133 |
3,494 |
(2,850) |
777 |
| Cree West |
- |
- |
(48) |
(48) |
- |
1,112 |
(1,112) |
- |
| Key Lake |
- |
- |
- |
- |
24 |
1,027 |
(1,047) |
4 |
| NW Manitoba |
- |
36 |
- |
36 |
16 |
7,308 |
- |
7,324 |
| Helmer |
- |
14 |
- |
14 |
107 |
5,046 |
- |
5,153 |
| Lake Athabasca |
- |
- |
- |
- |
118 |
5,966 |
- |
6,084 |
| Alberta |
- |
2 |
(11) |
(9) |
- |
2,331 |
- |
2,331 |
| Hodgson |
- |
81 |
- |
81 |
109 |
1,561 |
- |
1,670 |
| Arnold |
- |
- |
(35) |
(35) |
- |
1,341 |
- |
1,341 |
| Collins Bay |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1,309 |
- |
1,309 |
| McTavish |
- |
4 |
- |
4 |
74 |
687 |
(108) |
653 |
| Carswell |
- |
23 |
(37) |
(14) |
136 |
753 |
- |
889 |
| Ruttan |
15 |
32 |
- |
47 |
15 |
34 |
- |
49 |
| Other |
4 |
2 |
- |
6 |
57 |
2,870 |
(1,919) |
1,008 |
| New Zealand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Reefton, NZ |
- |
6 |
- |
6 |
24 |
786 |
(481) |
329 |
| Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Projects, Various |
1 |
194 |
(82) |
113 |
74 |
675 |
(425) |
324 |
| Total |
20 |
1,001 |
(426) |
595 |
1,238 |
82,820 |
(25,360) |
58,698 |
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 13
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 3. | | FINANCIAL POSITION
and CAPITAL resources |
| 3.1 | | Cash and Working Capital |
|
Table 8: ($000’s)
Cash and Working Capital |
|
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
1,044 |
1,265 |
| Trade and other receivables |
|
|
|
|
52 |
58 |
| Available-for-sale securities |
|
|
|
|
414 |
86 |
| Trade and other payables |
|
|
|
|
(382) |
(195) |
| Working capital |
|
|
|
|
1,128 |
1,214 |
For analysis and discussion of the movement
in cash and cash equivalents reference should be made to section 5 of this MD&A. Included within cash and cash equivalents
are $0.2 million in funds from the CKU Partnership which are dedicated to the Cree East project. Reference should be made to note
5 of the consolidated financial statements for further details.
As at April 30, 2014, included within trade
and other receivables is approximately $13,000 in Goods and Services Tax ("GST") refunds. The increase in available-for-sale
securities is primarily a result of receiving 1,000,000 shares from Makena Resources Inc. for our Patterson project in Q314, 500,000
shares from Copper Reef for our Hanson project and 2,250,000 shares from MPVC Inc. for our NW Manitoba project in Q414. The decrease
in trade and other receivables for April 30, 2014 is due primarily to a reduction its exploration expenditures in winter 2014 compared
to winter 2013.
The increase in trade and other payables is
due primarily to our exploration activities at our Cree East project compared with the fourth quarter of 2013. The Company operated
an extensive geophysics program at our Cree East project in winter 2014.
| 3.2 | | Other Assets and Liabilities |
|
Table 9: ($000’s)
Other Assets and Liabilities |
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Reclamation bonds |
|
|
|
189 |
203 |
| Property and equipment |
|
|
|
294 |
375 |
| Mineral property interests (section 2.2) |
|
|
|
813 |
1,238 |
During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014,
the Company received approximately $10,000 cash from a refund of a reclamation bond from the Manitoba Mines Branch and also wrote
down approximately $3,000 of reclamation bonds.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 14
of 24 |
| |
|
|
During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014,
exploration and evaluation expenditures were made primarily on the West McArthur, Cree East, Hodgson and BC Copper (section 2).
During fiscal 2014, the Company acquired the
Hanson property by staking 14 blocks of claims totalling 17,272 hectares for approximately $10,000. The Company also re-staked
three blocks of claims totally 11,492 hectares of the Hodgson property for approximately $7,000 to maintain its interest in the
property. The Company also staked two block of claims totalling 723 hectares in south central British Columbia for approximately
$1,000. In addition, the Company recognized an impairment on its Grease River, Poplar, Lake Athabasca, Hodgson and Carswell claims
for approximately $357,000 as it did not renew certain of its permit for these properties.
|
Table 10: ($000’s)
Shareholders’ Equity |
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Common shares |
|
|
|
73,205 |
73,205 |
| Equity reserve |
|
|
|
10,807 |
10,682 |
| Investment revaluation reserve |
|
|
|
(24) |
(1) |
| Deficit |
|
|
|
(81,564) |
(80,856) |
| Total shareholders’ equity |
|
|
|
2,424 |
3,030 |
|
Table 11: (000’s)
Equity Instruments |
|
|
Apr-14 |
Apr-13 |
| Common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
22,068 |
22,058 |
| Options outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
| Number |
|
|
|
3,851 |
3,598 |
| Weighted average price |
|
|
|
$0.20 |
$0.55 |
| Warrants outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
| Number |
|
|
|
- |
72 |
| Weighted average price |
|
|
|
- |
$0.55 |
Equity instruments
As of July 29, 2014, the Company
had the following securities outstanding. Common shares - 22,068,136; Stock options – 4,125,500; and Warrants – nil.
In July 2013, the Company issued
10,000 common shares under the option agreement for the Collins Bay Extension project.
In March 2012, the Company issued
283,000 common shares for gross proceeds of $121,690. A finder’s fee of $4,867 in cash and 11,320 warrants were issued in
connection with the financing. Each finder’s warrant entitles the holder to purchase on additional common share for a period
of 18 months from the closing date, at a price of $0.55 per warrant share. The share purchase warrants issued as part of this placement
have been recorded at a fair value of $1,825 using the Black Scholes model.
In March 2012, the Company issued
1,522,000 flow-through common shares for gross proceeds of $776,220. A finder’s fee of $31,049 in cash and 60,880 warrants
were issued in connection with the financing. $68,490 was allocated to premium as the market value on the date of close was less
than the offering price associated with this offering. Each finder’s warrant entitles the holder to purchase one additional
common share for a period of 18 months from the closing date at a price of $0.55 per warrant share. The share purchase warrants
issued as part of this placement have been recorded at a fair value of $9,816 using the Black Scholes model.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 15
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| Table 12: Proceeds from Financings |
|
|
| Date |
Type |
Intended Use |
Actual Use |
| March 2012 |
$0.1 million – 283,000 common shares |
Uranium exploration in Saskatchewan |
As Intended |
| March 2012 |
$0.8 million – 1,522,000 flow-through common shares |
Uranium exploration in Saskatchewan |
As Intended |
| Table 13: ($000’s) |
Quarterly |
Year End |
|
| Quarterly Net Loss & Comprehensive Loss Summary |
Q113 |
Q213 |
Q313 |
Q413 |
Q114 |
Q214 |
Q314 |
Q414 |
2013 |
2014 |
|
| Exploration Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Mineral property expenditures net of
reimbursements |
324 |
186 |
92 |
30 |
29 |
87 |
15 |
140 |
632 |
271 |
|
| |
Write-down on reclamation bonds |
110 |
- |
- |
- |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
110 |
3 |
|
| |
Mineral property write-offs |
35 |
48 |
- |
54 |
143 |
33 |
141 |
40 |
137 |
357 |
|
| |
Recoveries on option payments received |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(240) |
(25) |
(481) |
- |
(746) |
|
| |
Equipment rental income |
(4) |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(11) |
(1) |
(3) |
(12) |
|
| |
|
465 |
235 |
92 |
84 |
175 |
(120) |
120 |
(302) |
876 |
(127) |
|
| Other Expenses (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Consulting, labour and
professional fees |
321 |
248 |
144 |
121 |
100 |
87 |
110 |
105 |
834 |
402 |
|
| |
Depreciation |
27 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
108 |
80 |
|
| |
Gain on disposal of properties and equipments |
- |
(2) |
(8) |
14 |
1 |
- |
- |
4 |
4 |
5 |
|
| |
Foreign exchange (gain) loss |
- |
- |
(1) |
- |
- |
- |
(1) |
2 |
(1) |
1 |
|
| |
Insurance, licenses and filing fees |
20 |
31 |
10 |
24 |
19 |
29 |
37 |
13 |
85 |
98 |
|
| |
Interest income |
(9) |
(7) |
(4) |
(4) |
(4) |
(2) |
(2) |
(2) |
(24) |
(10) |
|
| |
Other corporate costs |
20 |
15 |
13 |
19 |
9 |
9 |
10 |
5 |
67 |
33 |
|
| |
Investor relations and presentations |
28 |
2 |
7 |
15 |
1 |
2 |
9 |
10 |
52 |
22 |
|
| |
Rent |
34 |
36 |
37 |
20 |
4 |
7 |
7 |
8 |
127 |
26 |
|
| |
Stock-based payments |
16 |
23 |
- |
137 |
- |
20 |
105 |
- |
176 |
125 |
|
| |
Travel and accommodation |
11 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
19 |
9 |
|
| |
Impairment and loss (gain) on
disposal of available-for-sale
securities |
- |
- |
- |
83 |
8 |
16 |
12 |
38 |
83 |
74 |
|
| |
Management fees |
(27) |
(9) |
(4) |
(6) |
(1) |
(5) |
- |
(24) |
(46) |
(30) |
|
| |
|
441 |
367 |
223 |
453 |
159 |
185 |
308 |
183 |
1,484 |
835 |
|
| Net (loss) earnings for the period |
(906) |
(602) |
(315) |
(537) |
(334) |
(65) |
(428) |
119 |
(2,360) |
(708) |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Items that may be subsequently reclassified
to
profit or loss: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Unrealized loss (gain) on available-
for-sale securities |
76 |
8 |
15 |
(45) |
23 |
(40) |
86 |
(46) |
54 |
23 |
|
| Total comprehensive (loss) earnings |
(982) |
(610) |
(330) |
(492) |
(357) |
(25) |
(514) |
165 |
(2,414) |
(731) |
|
| Basic and diluted (loss) earnings per share |
(0.04) |
(0.03) |
(0.01) |
(0.02) |
(0.02) |
(0.00) |
(0.02) |
0.01 |
(0.11) |
(0.03) |
|
In the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014, the
Company spent $0.5 million on exploration costs and recovered $0.2 million from our exploration partners for a net
mineral property expenditure of $0.3 million.
For the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014, the
Company recognized mineral property impairments on the Grease River, Poplar, Lake Athabasca, Hodgson and Carswell projects for
approximately $357,000 as the Company did not renew certain of its permits for these projects.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 16
of 24 |
| |
|
|
Camp and other miscellaneous exploration equipment
owned by the Company is maintained at our La Ronge warehouse. Equipment rental income is comprised of income (cost recapture) from
charging exploration projects for the rental of this equipment. In Q412, the equipment rental income is related to the winter drill
programs for the Cree East and West McArthur projects. In Q1 and Q2, 2013, the rental income is related to the summer work program
on the BC Copper project. In Q3 and Q4 2014, the rental income is related to the rental of tents and camp supplies to a 3rd party.
Consulting,
labour, and professional fees are
lower than the same comparative prior period. The decrease is primarily attributed to a decrease in the salaries expense from the
re-negotiated employment agreements for senior staff and management which began effective August 2012. The Company has terminated
some staff and re-negotiated employment agreements with senior staff and management in efforts to minimize the Company’s
operating costs. The Company also reduced it usage of professionals and consultants in Q414 compared to Q413. As of January 1,
2013, the independent directors of the Company have not received directors’ fees in the form of cash, in order to assist
the Company in its plans to control its operation costs.
Insurance, licenses and filing fees are higher
for fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013. The increase is primarily due to the TSX Venture listing fees incurred in Q314 as the
Company’s shares began trading on the TSX Venture Exchange on December 30, 2013. In Q1, Q2 and Q4 2014, insurance, license
and filing fees were consistent relative to the same comparative prior periods.
Interest income was lower in 2014 compared
to 2013. The decrease was attributed to the decreased cash balances held during the year.
Investor relations expenses were lower in 2014
compared to 2013. The decrease is primarily attributed to the decrease in services provided by a Canadian investor relations firm.
The Company received contract services from the Canadian investor relations firm which started in June of 2011 and terminated in
July 2012.
Rent expense was lower in Q414 compared to
Q314 as a Company sublet its office space in its effort to reduce it cash burn and operating costs going forward. The Company is
however committed to the full lease amount, not the net for the head lease on the Vancouver office space.
The share-based payments amount for the year
is lower than the amount for the previous year. The decrease was primarily due to the decrease in the fair value calculation on
the options granted in fiscal 2014 relative to fiscal 2013. During fiscal 2014, there were 1,591,750 options granted with an average
fair value of $0.07 per option compared to 1,357,500 option granted with an average fair value of $0.13 per option in fiscal 2013.
A write-down on available-for-sale securities
of approximately $74,000 was recorded in fiscal 2014. This was attributed to a significant or prolonged impairment on a number
of investments. The Company wrote the balances down to their market values due to the significant decline in market value that
was viewed as other than a temporary impairment.
Management fees were lower in fiscal 2014 compared
to fiscal 2013. This was primarily due to the decrease in our exploration activities relative to last year. During fiscal 2014,
the Company spent $0.5 million on exploration, of which $0.3 million were related to our joint venture projects where management
fees were generated. During fiscal 2013, the Company spent $1.0 million on exploration, of which $0.6 million were related to joint
venture projects.
| 5. | | CASHFLOW and liquidity
REVIEW |
As of April 30, 2014, the Company had $1.0
million in cash and cash equivalents and working capital of $1.1 million and as of April 30, 2013, the Company had $1.3 million
in cash and cash equivalents and working capital of $1.2 million.
The Company’s operating activities resulted
in net cash outflows of $0.6 million and $3.2 million for the fiscal years ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 respectively. Operating
activities and costs for fiscal 2014 are lower than fiscal 2013 as the Company reduced its exploration activities and option or
sold several of its projects during the year, as well as continued its efforts to minimize it operating costs to conserve its cash
reserves.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 17
of 24 |
| |
|
|
Financing activities resulted in net cash outflows
of approximately $1,000 and $5,000 for the fiscal years ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 respectively. During the fiscal year ended
April 30, 2014, the Company paid finders fees related to a prior financing in March 2012. In fiscal 2013, the Company incurred
TSX listing fees related to the Company’s share compensation plan. Currently, junior uranium exploration companies are finding
it difficult to seek financing. The Company is working to sell option or joint venture non core assets.
Investing activities resulted in net cash inflow
of approximately $396,000 and $72,000 for fiscal year ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 respectively. During the year ended April 30,
2014, the Company received cash option payments of approximately $385,000. The Company also staked the Hansen project for approximately
$10,000, the Hodgson project for approximately $7,000 and the Big Creek project for approximately $1,000. The Company also recovered
approximately $10,000 of reclamation bonds deposited with the Manitoba Mines Branch and the Company also sold the Reefton project
for $20,000 to Stevenson Mining during the year. During the year ended April 30, 2013, the Company acquired the Ruttan property
and the Patterson Lake property by staking five blocks of claims totalling 7,742 hectares for approximately $20,000 and received
$75,000 in option payments from Discovery Ventures Ltd. The Company also received approximately $19,000 from the sale of certain
property and equipment.
For a full version of the risks and critical
accounting estimates and policies reference should be made to the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements for
the year ended April 30, 2014, which are available on the Company’s website at www.canalaska.com and the risk factor section
of the most recently filed Form 20-F on EDGAR.
| 6.1 | | Related Party Transactions |
Related parties include the Board of Directors and Officers of the
Company and enterprises which are controlled by these individuals.
The remuneration of directors and key management
of the Company for the year ended April 30, 2014 and 2013 were as follows. Certain compensation is paid to Schimann Consultants,
a company controlled by the VP of Exploration.
|
Table 14: ($000’s)
Compensations to Related Parties |
|
|
| ($000’s) |
|
|
2014 |
2013 |
| Employment benefits |
|
|
220 |
272 |
| Schimann Consultants |
|
|
82 |
131 |
| Directors fees |
|
|
- |
80 |
| Share-based compensation |
|
|
118 |
129 |
The directors and key management were awarded
the following share options under the employee share option plan during the fiscal year ended April 30, 2014:
| Table 15: Share Option Issuance |
| Date of grant |
Number of options |
Exercise price |
Expiry |
| November 5, 2013 |
1,103,750 |
$0.12 |
November 5, 2018 |
| January 7, 2014 |
400,000 |
$0.12 |
January 7, 2019 |
Due to increasingly difficult market conditions
facing junior uranium exploration companies, management is currently in the process of evaluating its priorities and taking steps
to streamline non discretionary expenditures. Should management be unsuccessful in its coming exploration programs it may either
need to dilute its ownership in its properties and/or secure additional financing to continue to advance the development of its
projects.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 18
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 6.3 | | Critical Accounting Estimates and Judgments |
| 6.3.1 | | Share-Based Payment Plan |
The Company operates an equity-settled, share-based
compensation plan, under which the entity receives services from employees and non-employees as consideration for equity instruments
(options) of the Company. The total amount to be expensed is determined by reference to the fair value of the options granted.
The fair value of share-based compensation
is determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and management’s assumptions as disclosed in note 10 of the audited
consolidated financial statements for the year ended April 30, 2014. When a stock option is exercised, the Company recognizes an
increase in its share capital equivalent to the consideration paid by the option holder and the fair value amount previously recognized
in equity reserve. The fair value of any stock options granted to directors, officers and employees of the Company is recorded
as an expense over the vesting period of the options with a corresponding increase in equity reserve.
| 6.3.2 | | Mineral Property Interest |
The recoverability of the amounts shown for
mineral properties and related deferred costs is dependent upon the existence of economically recoverable mineral reserves, the
ability of the Company to obtain the necessary financing to complete the development, and upon future profitable production or
proceeds from disposition of the mineral properties. Due to increasingly difficult market conditions facing junior uranium exploration
companies there is no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising additional financing. The amounts shown as mineral
property costs represent net acquisition costs incurred to date and do not necessarily represent current or future values of the
mineral properties.
The consolidated financial statements have
been prepared on a going concern basis. The going concern basis of presentation assumes that the Company will continue in operation
for the foreseeable future and be able to realize its assets and discharge its liabilities and commitments in the normal course
of business. The financial statements do not include any adjustments to the carrying values of assets and liabilities and the reported
expenses and statement of financial position classification that would be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as
a going concern. These adjustments could be material. Refer to section 1.2.
| 6.4 | | Disclosure Controls and Internal Control over Financial
Reporting |
Disclosure controls and procedures ("DC&P")
are designed to provide reasonable assurance that all relevant information is gathered and reported to senior management, including
the Company's Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, on a timely basis so that appropriate decisions can be made
regarding public disclosure. Internal control over financial reporting ("ICFR") is designed to provide reasonable assurance
that such financial information is reliable and complete. As at the end of the period covered by this management's discussion and
analysis, management of the Company, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer, evaluated
the effectiveness of the Company's DC&P and ICFR as required by Canadian securities laws. Based on that evaluation, the Chief
Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this management's
discussion and analysis, the DC&P were effective to provide reasonable assurance that material information relating to the
Company was made known to senior management by others and information required to be disclosed by the Company in its annual filings,
interim filings (as such terms are defined under National Instrument 52-109 – Certification of Disclosure in Issuers' Annual
and Interim Filings) or other reports filed or submitted by it under securities legislation were recorded, processed, summarized
and reported within the time periods specified in securities legislation. The Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer
have also concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this management's discussion and analysis, the Company's ICFR
is effective and the ICFR provides reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of
financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS. To design its
ICFR, the Company used the Internal Control –Integrated
Framework (1992) (COSO Framework) published by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. There are
no material weaknesses in the Company's ICFR. During the year ended April 30, 2014 there were no changes to the Company's ICFR
that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company's
ICFR.
| 6.5 | | Forward Looking Statements |
Certain statements included in this “MD&A”
constitute forward-looking statements, including those identified by the expressions “anticipate”, “believe”,
“plan”, “estimate”, “expect”, “intend”, “may”, “should”
and similar expressions to the extent they relate to the Company or its management. The forward-looking statements are not historical
facts but reflect current expectations regarding future results or events. This MD&A contains forward-looking
statements. These forward-looking statements are based on current expectations and various estimates, factors and assumptions and
involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 19
of 24 |
| |
|
|
Information concerning the interpretation of
drill results also may be considered forward-looking statements; as such information constitutes a prediction of what mineralization
might be found to be present if and when a project is actually developed. The estimates, risks and uncertainties described in this
MD&A are not necessarily all of the important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed
in the Company’s forward-looking statements. In addition, any forward-looking statements represent the Company’s estimates
only as of the date of this MD&A and should not be relied upon as representing the Company’s estimates as of any subsequent
date. The material factors and assumptions that were applied in making the forward-looking statements in this MD&A include:
(a) execution of the Company’s existing plans or exploration programs for each of its properties, either of which may change
due to changes in the views of the Company, or if new information arises which makes it prudent to change such plans or programs;
and (b) the accuracy of current interpretation of drill and other exploration results, since new information or new interpretation
of existing information may result in changes in the Company’s expectations. Readers should not place undue reliance on the
Company’s forward-looking statements, as the Company’s actual results, performance or achievements may differ materially
from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements if known or unknown
risks, uncertainties or other factors affect the Company’s business, or if the Company’s estimates or assumptions prove
inaccurate. Therefore, the Company cannot provide any assurance that forward-looking statements will materialize.
| 6.6 | | New Accounting Standards Adopted |
The following standards were adopted effective
May 1, 2013.
(i) IFRS 10, Consolidated Financial Statements,
requires an entity to consolidate an investee when it has power over the investee, is exposed, or has rights, to variable returns
from its involvement with the investee and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the investee. Under existing
IFRS, consolidation was required when an entity has the power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as
to obtain benefits from its activities. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
(ii) IFRS 11, Joint Arrangements, requires
a venturer to classify its interest in a joint arrangement as a joint venture or joint operation. Joint ventures will be accounted
for using the equity method of accounting whereas for a joint operation the venturer will recognize its share of the assets, liabilities,
revenue and expenses of the joint operation. Under previous IFRS, entities had the choice to proportionately consolidate or equity
account for interests in jointly controlled entities. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated
financial statements.
(iii) IFRS 12, Disclosure of Interests in
Other Entities, outlines the disclosure requirements for interests in subsidiaries and other entities to enable users to evaluate
the risks associated with interests in other entities and the effects of those interests on an entity's financial position, financial
performance and cash flow. The adoption of this standard had no effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
(iv) IFRS 13, Fair Value Measurement,
provides a single framework for measuring fair value. The measurement of the fair value of an asset or liability is based on assumptions
that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability under current market conditions, including assumptions about
risk. The Company adopted IFRS 13 on May 1, 2013 on a prospective basis. The adoption of IFRS 13 did not require any adjustments
to the valuation techniques used by the Company to measure fair value and did not result in any measurement adjustments as at May
1, 2013.
(v) The Company has adopted the amendments
to IAS 1 effective May 1, 2013. These amendments required the Company to group other comprehensive income by those that will be
reclassified subsequently to profit or loss and those that will not be reclassified. The adoption of this standard had no effect
on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
| 6.7 | | Future Accounting Pronouncements |
Unless otherwise noted, the following new or
revised standards will be effective for the Company in future periods.
(i) IFRS 9 Financial Instruments, was
issued in November 2009 and addresses classification and measurement of financial assets. It replaces the multiple category and
measurement models in IAS 39 for debt instruments with a new mixed measurement model having only two categories: amortized cost and fair
value through profit or loss. IFRS 9 also replaces the models for measuring equity instruments. Such instruments are either recognized
at fair value through profit or loss or at fair value through other comprehensive income. Where equity instruments are measured
at fair value through other comprehensive income, dividends are recognized in profit or loss to the extent that they do not clearly
represent a return of investment; however, other gains and losses (including impairments) associated with such instruments remain
in accumulated comprehensive income indefinitely.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 20
of 24 |
| |
|
|
Requirements for financial liabilities were
added to IFRS 9 in October 2010 and they largely carried forward existing requirements in IAS 39, Financial Instruments - Recognition
and Measurement, except that fair value changes due to credit risk for liabilities designated at fair value through profit
and loss are generally recorded in other comprehensive income. In February 2014, the IASB tentatively determined that the revised
effective date for IFRS 9 would be January 1, 2018. The Company has not yet completed an assessment of the impact of adopting IFRS
9.
(ii) IFRIC 21, Accounting for Levies imposed
by Governments, clarifies that the obligating event giving rise to a liability to pay a levy is the activity described in the relevant
legislation that triggers payment of the levy. IFRIC 21 is effective for the Company beginning on May 1, 2014. The Company is currently
assessing the impact of this guidance.
The Company is engaged in the exploration of
mineral properties, an inherently risky business. There is no assurance that funds spent on the exploration and development of
a mineral deposit will result in the discovery of an economic ore body. Most exploration projects do not result in the discovery
of commercially mineable ore deposits.
| 6.8.1 | | Cash Flows and Additional Funding Requirements |
The Company has limited financial resources,
no sources of operating cash flows and no assurances that sufficient funding, including adequate financing, will be available.
If the Company’s exploration programs are successful, additional funds will be required in order to complete the development
of its projects. The sources of funds currently available to the Company are the sale of marketable securities, the raising of
equity capital or the offering of an ownership interest in its projects to a third party. There is no assurance that the Company
will be successful in raising sufficient funds to conduct further exploration and development of its projects or to fulfill its
obligations under the terms of any option or joint venture agreements, in which case the Company may have to delay or indefinitely
postpone further exploration and development, or forfeit its interest in its projects or prospects. Without further financing and
exploration work on its properties the Company expects its current 741,794 ha of property to reduce to 695,283 ha by December 31
2014, and 655,495 ha by December 31 2015. The Company’s Fond Du Lac property reached its last anniversary on February 25
2014, after February 2015 a new lease or a special lease extension will be required by the Fond Du Lac community from Aboriginal
and Northern Affairs Canada. The Cree East and West McArthur projects, with current work filings are in good standing for a minimum
15 years from the current date. Refer to section 1.1.
The profitability of the Company’s operations
will be dependent upon the market price of mineral commodities. Mineral prices fluctuate widely and are affected by numerous factors
beyond the control of the Company. The prices of mineral commodities have fluctuated widely in recent years. Current and future
price declines could cause commercial production to be impracticable. The Company’s future revenues and earnings also could
be affected by the prices of other commodities such as fuel and other consumable items, although to a lesser extent than by the
price of mineral commodities.
The mining industry is intensely competitive
in all of its phases, and the Company competes with many companies possessing greater financial resources and technical facilities
than itself with respect to the discovery and acquisition of interests in mineral properties, the recruitment and retention of
qualified employees and other persons to carry out its mineral exploration activities. The Company has a large land position in
the Athabasca Basin, and has carried out extensive exploration, but has not defined an economic deposit. Other exploration companies
have been successful with the discovery of deposits in the Athabasca, and these companies tend to attract investors away from
CanAlaska.
CanAlaska relies on the ongoing support of its JV partners to fund their portion of exploration, however additional funding from
the current partners is uncertain. Competition in the mining industry could adversely affect the Company’s prospects for
mineral exploration in the future.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 21
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 6.8.4 | | Foreign Political Risk |
The Company’s material property interests
are currently located in Canada. Some of the Company’s interests are exposed to various degrees of political, economic and
other risks and uncertainties. The Company’s operations and investments may be affected by local political and economic developments,
including expropriation, nationalization, invalidation of government orders, permits or agreements pertaining to property rights,
political unrest, labour disputes, limitations on repatriation of earnings, limitations on mineral exports, limitations on foreign
ownership, inability to obtain or delays in obtaining necessary mining permits, opposition to mining from local, environmental
or other non-governmental organizations, government participation, royalties, duties, rates of exchange, high rates of inflation,
price controls, exchange controls, currency fluctuations, taxation and changes in laws, regulations or policies as well as by laws
and policies of Canada affecting foreign trade, investment and taxation.
| 6.8.5 | | Government Laws, Regulation and Permitting |
Mining and exploration activities of the Company
are subject to both domestic and foreign laws and regulations governing prospecting, development, production, taxes, labour standards,
occupational health, mine safety, waste disposal, toxic substances, the environment and other matters. Although the Company believes
that all exploration activities are currently carried out in accordance with all applicable rules and regulations, no assurance
can be given that new rules and regulations will not be enacted or that existing rules and regulations will not be applied in a
manner which could limit or curtail production or development. Amendments to current laws and regulations governing the operations
and activities of the Company or more stringent implementation thereof could have a substantial adverse impact on the Company.
The operations of the Company will require
licenses and permits from various governmental authorities to carry out exploration and development at its projects. In Canada,
the issuance of governmental licenses and permits are increasingly being influenced by land use consultations between the government
and local First Nations communities. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to obtain the necessary licences and
permits on acceptable terms, in a timely manner or at all. Any failure to comply with permits and applicable laws and regulations,
even if inadvertent, could result in the interruption or closure of operations or material fines, penalties or other liabilities.
Acquisition of rights to the mineral properties
is a very detailed and time-consuming process. Title to, and the area of, mineral properties may be disputed. Although the Company
has investigated the title to all of the properties for which it holds concessions or other mineral leases or licenses or in respect
of which it has a right to earn an interest, the Company cannot give an assurance that title to such properties will not be challenged
or impugned.
The Company has the right to earn an increased
economic interest in certain of its properties. To earn this increased interest, the Company is required to make certain exploration
expenditures and payments of cash and/or Company shares. If the Company fails to make these expenditures and payments, the Company
may lose its right to such properties and forfeit any funds expended up to such time.
| 6.8.7 | | Estimates of Mineral Resources |
The mineral resource estimates used by the
Company are estimates only and no assurance can be given that any particular level of recovery of minerals will in fact be realized
or that an identified resource will ever qualify as a commercially mineable (or viable) deposit which can be legally or commercially
exploited. In addition, the grade of mineralization ultimately mined may differ from that indicated by drilling results and such
differences could be material.
The success of the Company will be largely
dependent upon the performance of its key officers, consultants and employees. Locating mineral deposits depends on a number of
factors, not the least of which is the technical skill of the exploration personnel involved. The success of the Company is largely
dependent on the performance of its key individuals. Failure to retain key individuals or to attract or retain additional key individuals
with necessary skills could have a materially adverse impact upon the Company’s success. The Company on July 31, 2012, has
terminated all long term employment contracts with senior management and has completed the negotiation of reduced contracts with
the CEO, former CFO and VP Exploration. The VP Corporate Development position was terminated and the responsibilities have been
assumed by the CEO. Remaining technical staff are working on part time contracts. In January 2013, Mr. Chan, the Corporate Controller
took over the position of CFO replacing Mr. Ramachandran. In June 2013, the Company received the resignation of board member, Hubert
Marleau. On September 26, 2014 the Company accepted the resignation of board member, Michael Riley. Dr, Karl Schimann, VP Exploration,
was appointed to the board of directors on September 26, 2014 in Mr. Riley’s place. On January 7, 2014, Kathleen Kennedy
Townsend was appointed to the Company's board of directors.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 22
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 6.8.9 | | Volatility of Share Price |
Market prices for shares of early stage companies
are often volatile. Factors such as announcements of mineral discoveries, financial results, and other factors could have a significant
effect on the price of the Company’s shares and the amount of financing that can be raised by the Company.
| 6.8.10 | | Foreign Currency Exchange |
A small portion of the Company’s expenses
are now, and are expected to continue to be incurred in foreign currencies. The Company’s business will be subject to risks
typical of an international business including, but not limited to, differing tax structures, regulations and restrictions and
general foreign exchange rate volatility. Fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Canadian dollar and such other currencies
may have a material effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations and could result in downward
price pressure for the Company’s products or losses from currency exchange rate fluctuations. The Company does not actively
hedge against foreign currency fluctuations.
| 6.8.11 | | Conflict of Interest |
Some of the Company’s directors and officers
are directors and officers of other natural resource or mining-related companies. These associations may give rise from time to
time to conflicts of interest. As a result of such conflict, the Company may miss the opportunity to participate in certain transactions.
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 23
of 24 |
| |
|
|
| 7. | | QUARTERLY and annual
FINANCIAL INFORMATION |
The following tables sets out a summary
of the Company’s results:
| Table 16: ($000’s) |
Quarterly |
Year End |
|
| Quarterly Net Loss & Comprehensive Loss Summary |
Q113 |
Q213 |
Q313 |
Q413 |
Q114 |
Q214 |
Q314 |
Q414 |
2013 |
2014 |
|
| Exploration Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Mineral property expenditures net of
reimbursements |
324 |
186 |
92 |
30 |
29 |
87 |
15 |
140 |
632 |
271 |
|
| |
Write-down on reclamation bonds |
110 |
- |
- |
- |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
110 |
3 |
|
| |
Mineral property write-offs |
35 |
48 |
- |
54 |
143 |
33 |
141 |
40 |
137 |
357 |
|
| |
Recoveries on option payments received |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(240) |
(25) |
(481) |
- |
(746) |
|
| |
Equipment rental income |
(4) |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
(11) |
(1) |
(3) |
(12) |
|
| |
|
465 |
235 |
92 |
84 |
175 |
(120) |
120 |
(302) |
876 |
(127) |
|
| Other Expenses (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Consulting, labour and
professional fees |
321 |
248 |
144 |
121 |
100 |
87 |
110 |
105 |
834 |
402 |
|
| |
Depreciation |
27 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
108 |
80 |
|
| |
Gain on disposal of properties and equipments |
- |
(2) |
(8) |
14 |
1 |
- |
- |
4 |
4 |
5 |
|
| |
Foreign exchange (gain) loss |
- |
- |
(1) |
- |
- |
- |
(1) |
2 |
(1) |
1 |
|
| |
Insurance, licenses and filing fees |
20 |
31 |
10 |
24 |
19 |
29 |
37 |
13 |
85 |
98 |
|
| |
Interest income |
(9) |
(7) |
(4) |
(4) |
(4) |
(2) |
(2) |
(2) |
(24) |
(10) |
|
| |
Other corporate costs |
20 |
15 |
13 |
19 |
9 |
9 |
10 |
5 |
67 |
33 |
|
| |
Investor relations and presentations |
28 |
2 |
7 |
15 |
1 |
2 |
9 |
10 |
52 |
22 |
|
| |
Rent |
34 |
36 |
37 |
20 |
4 |
7 |
7 |
8 |
127 |
26 |
|
| |
Stock-based payments |
16 |
23 |
- |
137 |
- |
20 |
105 |
- |
176 |
125 |
|
| |
Travel and accommodation |
11 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
19 |
9 |
|
| |
Impairment and loss (gain) on
disposal of available-for-sale
securities |
- |
- |
- |
83 |
8 |
16 |
12 |
38 |
83 |
74 |
|
| |
Management fees |
(27) |
(9) |
(4) |
(6) |
(1) |
(5) |
- |
(24) |
(46) |
(30) |
|
| |
|
441 |
367 |
223 |
453 |
159 |
185 |
308 |
183 |
1,484 |
835 |
|
| Net (loss) earnings for the period |
(906) |
(602) |
(315) |
(537) |
(334) |
(65) |
(428) |
119 |
(2,360) |
(708) |
|
| Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Items that may be subsequently reclassified
to
Profit or loss: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Unrealized loss (gain) on available-
for-sale securities |
76 |
8 |
15 |
(45) |
23 |
(40) |
86 |
(46) |
54 |
23 |
|
| Total comprehensive (loss) earnings |
(982) |
(610) |
(330) |
(492) |
(357) |
(25) |
(514) |
165 |
(2,414) |
(731) |
|
| (Loss) earnings per share |
(0.04) |
(0.03) |
(0.01) |
(0.02) |
(0.02) |
(0.00) |
(0.02) |
0.01 |
(0.11) |
(0.03) |
|
 |
CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. – MD&A April 30, 2014 |
Page 24 of
24 |
| |
|
|
| Table 17: ($000’s) Financial Position Summary |
As at |
| Apr 30, 2012 |
Jul 31, 2012 |
Oct 31, 2012 |
Jan 31, 2013 |
Apr 30, 2013 |
Jul 31, 2013 |
Oct 31, 2013 |
Jan 31, 2014 |
Apr 30, 2014 |
| Financial Position |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Cash and cash equivalents |
4,394 |
2,425 |
1,741 |
1,464 |
1,265 |
1,105 |
909 |
755 |
1,044 |
| |
Trade and other receivables |
243 |
96 |
98 |
72 |
58 |
42 |
66 |
59 |
52 |
| |
Available-for-sale securities |
223 |
146 |
138 |
123 |
86 |
79 |
259 |
160 |
414 |
| Total Current Assets |
4,860 |
2,667 |
1,977 |
1,659 |
1,409 |
1,226 |
1,234 |
974 |
1,510 |
| |
Reclamation bond |
345 |
203 |
203 |
203 |
203 |
200 |
189 |
190 |
189 |
| |
Property and equipment |
504 |
477 |
447 |
417 |
375 |
354 |
334 |
314 |
294 |
| |
Mineral property interests |
1,356 |
1,327 |
1,288 |
1,292 |
1,238 |
1,098 |
1,069 |
938 |
813 |
| Total Assets |
7,065 |
4,674 |
3,915 |
3,571 |
3,225 |
2,878 |
2,826 |
2,416 |
2,806 |
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Trade and other payables |
1,792 |
367 |
200 |
186 |
195 |
204 |
158 |
157 |
382 |
| Total Liabilities |
1,792 |
367 |
200 |
186 |
195 |
204 |
158 |
157 |
382 |
| Shareholders’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Common shares |
73,210 |
73,210 |
73,205 |
73,205 |
73,205 |
73,206 |
73,205 |
73,205 |
73,205 |
| |
Equity reserve |
10,506 |
10,522 |
10,545 |
10,545 |
10,682 |
10,682 |
10,702 |
10,807 |
10,807 |
| |
Investment revaluation reserve |
53 |
(23) |
(31) |
(46) |
(1) |
(24) |
16 |
(70) |
(24) |
| |
Deficit |
(78,496) |
(79,402) |
(80,004) |
(80,319) |
(80,856) |
(81,190) |
(81,255) |
(81,683) |
(81,564) |
| Total Shareholders’ Equity |
5,273 |
4,307 |
3,715 |
3,385 |
3,030 |
2,674 |
2,668 |
2,259 |
2,424 |
| |
7,065 |
4,674 |
3,915 |
3,571 |
3,225 |
2,878 |
2,826 |
2,416 |
2,806 |
|
Weighted average common shares
outstanding (000’s) |
20,425 |
22,058 |
22,058 |
22,058 |
22,058 |
22,060 |
22,068 |
22,068 |
22,068 |
| Working Capital |
3,068 |
2,300 |
1,777 |
1,473 |
1,214 |
1,022 |
1,076 |
817 |
1,128 |
| Table 18: ($000's) Selected Annual Information |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
| Loss before discontinued operations |
(6,869) |
(2,360) |
(708) |
| Loss before discontinued operations per-share |
(0.34) |
(0.11) |
(0.03) |
| Loss before discontinued operations diluted per-share |
(0.34) |
(0.11) |
(0.03) |
| Net loss |
(6,869) |
(2,360) |
(708) |
| Net loss per-share |
(0.34) |
(0.11) |
(0.03) |
| Net loss diluted per-share |
(0.34) |
(0.11) |
(0.03) |
| Total assets |
7,065 |
3,225 |
2,806 |
| Cash dividends declared |
- |
- |
- |

CANALASKA URANIUM LTD.
AUDIT COMMITTEE CHARTER
The audit committee is elected annually by
the board of directors to assist the board in fulfilling its oversight responsibilities. The committee is primarily responsible
to the board for the overseeing of managements process of reporting of the financial statements, management discussion and analysis
(“MD&A”) and other financial reports provided by the Canalaska Uranium Ltd., (the “Company”) to any
regulatory authority or to the public. Secondly, the committee is required to review the system of internal controls for finance,
accounting, and legal compliance. Performance of other duties as may be required from time to time by the board of directors or
as required by the amendment of this charter.
COMPOSITION OF AUDIT COMMITTEE
The audit committee is composed of three independent
directors. A quorum shall be a majority of members. The chair of the audit committee will be elected by the board of directors.
The term for the members will be for one year at which time they may be re-nominated.
RELEVANT EDUCATION AND EXPERIENCE
All of the members of the audit committee shall
be financially literate. Financially literate is the ability to read and understand a set of financial statements that present
a level of complexity of the issues that can presumably be expected to be raised by the Company’s financial statements. Members
will have relevant education or experience to sufficiently execute their duties and responsibilities.
The audit committee is required to name the
financial expert who should have a strong financial ability to understand and assess accounting principles relating to estimates,
accruals and reserves and financial statements, an understanding of internal controls and the financial reporting process, and
experience in the preparation and auditing or evaluating issuers of a similar level of accounting complexity.
ROLE OF THE AUDIT COMMITTEE
The primary purpose of the audit committee
is to:
- Oversee the selection and appointment of an auditor
- Oversee the conducting of the audit
- Review and appraise the performance of the auditors, and recommend
replacement if warranted
- Set the remuneration to be paid to the auditors for the audit
- Pre-approve all non-audit services to be provided to the Company or
its subsidiary entities by the issuer’s external auditor
- Oversee the process by which management identifies and manages principle
risks that could impact the financial reporting process
- Monitor the integrity of the financial reporting process and system
of internal controls regarding the reporting process and ensure implementation of such controls and procedures
- Oversee the Company’s compliance with legal and regulatory reporting
- Where appropriate, engage independent counsel and or other advisors
as may be necessary to carry out its duties
- Review and update this Audit Committee Charter on an annual basis or
as required
- Assist the CEO in reviewing the performance of the Chief Financial
Officer (“CFO”)
- On an annual basis the Committee shall report to the Board that they
are compliant with the duties and responsibilities of this Charter
RELATIONSHIP WITH AUDITORS
The audit committee members shall:
- Review and discuss any disclosed relationships or services that may
impact the objectivity and independence of the auditors
- Consult with auditors independent of management
- Review any significant judgements made by management in the preparation
of the financial statements
- Review any significant disagreements or difficulties during the audit
- Review and approve any non-audit services to be provided to the Company
INTERNAL CONTROL OVERSIGHT
The Audit Committee provides oversight of the
internal control and disclosure procedures and systems that are designed by management to effectively control the financial, monetary,
operational, technical and administrative processes undertaken by the Company which may include:
| · | information technology systems |
| · | document and records handling |
| · | disclosure and reporting |
| · | authorization and management systems |
Disclosure controls and procedures ("DC&P")
are designed to provide reasonable assurance that all relevant information is gathered and reported to senior management, including
the Company's Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, on a timely basis so that appropriate decisions can be made
regarding public disclosure. Internal control over financial reporting ("ICFR") is designed to provide reasonable assurance
that such financial information is reliable and complete.
The Chief Financial Officer is responsible
for the preparation, presentation and integrity of the financial statements and any financial information filed with securities
regulatory authorities or stock exchanges or otherwise publicly disseminated and for maintaining appropriate accounting and financial
reporting principles and policies and internal controls and procedures that provide for compliance with accounting standards and
applicable laws and regulations.
Due to its inherent limitations, no system
of internal control over financial reporting, including those determined to be effective, may prevent or detect all misstatements.
Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate
because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
MEETINGS OF THE AUDIT COMMITTEE
The committee will meet at least four times
per year and to discuss specific issues when necessary. These meetings will be either of in person or via teleconferencing. A quorum
will be a minimum of two members, or the committee may delegate some of its duties to one or more members.
The minutes of the meetings should be recorded
and approved as a true record of the decisions taken. A secretary should be appointed to set up the meetings, prepare the agendas,
take minutes and prepare any necessary information for the members.
The committee is authorized to invite management
or other specialists to meetings in order to provide expert opinion or information in respect of issues being discussed.
PUBLIC DISCLOSURE OF FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The audit committee must review and approve
the Company’s interim and annual financials statements and the associated MD&A before they are presented to the Board
for full Board approval, prior to the information being disclosed to the regulatory authorities and for public distribution.
AUTHORITIES
In order to undertake its activities, the committee
is authorized to study and investigate any activity within the organization or its subsidiaries, and shall require all employees
to co-operate fully with such investigations. The committee is also authorized to appoint any additional experts that it considers
necessary in the completion of its duties.
ANNUAL REVIEW OF CHARTER AND REPORT TO THE
BOARD
The Audit committee members will review this
Charter on an annually basis, or as needed and will report to the Board on an annual basis that the Committee has executed its
duties in compliance with this Charter.

CANALASKA URANIUM LTD.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE POLICY
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE OBJECTIVES
The objective of this corporate governance
policy is to set out an effective, transparent system of guidelines establishing the accountability for the supervising and managing
of the affairs of CanAlaska Uranium Ltd. (the “Company”). These guidelines have been implemented to insure that adequate
information is made available so that management decisions can be independently monitored and reviewed.
It is management’s belief that through
the implementation of these practices, the overall stewardship of the Company will be affected in a positive way, by strengthening
the effectiveness of its Board of Directors and by empowering the independent action of its special committees.
Within the framework of ongoing development
and implementation of these policy’s and procedures, the Company will realize a more comprehensive system of communicating
and reporting which in turn will insure a high level of confidence from all of its shareholders and business partners.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE PRACTICES
Corporate Governance Committee
A Corporate Governance Committee (CGC) has
been established for the Company. The Committee is to consist of three independent directors. The Chairperson will be elected by
the Board of Directors on an annual basis. The term for the members of the CGC will be for one year at which time they may be re-nominated.
The duties of the committee are to oversee
and recommend to the board appropriate governance processes including:
- suitable corporate governance policies
- board organization and other committee structures
- potential candidates for nomination to the board
- evaluation of the performance of the board
- selection and appointment of the CEO
- Evaluation of the CEO’s management succession plans
- board composition and qualifications
Code of Ethics
The CGC shall have the responsibility to develop
and maintain a Code of Ethics (“COE”) for the Company to be used as principle guidelines of conduct for
all of its directors, officers, contractors, consultants, advisors and employees. The COE will be included in the orientation of
all new employees, directors, officers, contractors, consultants, advisors and committee members.
These guidelines shall include accountability
to adherence to the COE and a system for the reporting of unethical conduct. This COE will be reviewed and amended by the
CGC at a minimum of an annual basis. All directors will be required to acknowledge in writing on an annual basis that they have
read and understood the COE and that they are compliant with the requirements.
Board Mandate
The CGC will have the responsibility to see
that the board adopts a written mandate which outlines and acknowledges the responsibility of the members. This mandate will include,
among other things, establishing a culture of integrity throughout the organization, strategic planning, succession planning, the
handling of any conflicts of interest and disclosure policies. This mandate must include a process where any breach of the directives
of this mandate can effectively be reported and dealt with.
Board Composition
The Board is currently comprised of six members.
The Board will reconsider its actual size from time to time.
The Board believes that the majority of its
members should be independent. On an annual basis the Board will determine which of its directors is independent based on the rules
of applicable securities regulators and will publish its determination in the management proxy circular for the Company’s
annual meeting of shareholders.
Director Expectations
The CGC shall be responsible to develop a comprehensive
list of expectations of its directors. The CGC members have the responsibility to ensure that the existing directors have an orientation
including an overview of the roll of the board of directors. Any new incoming directors shall be made familiar with these expectations
and understand that they must be willing to comply with the duties and responsibilities of the directorship. The directors will
receive a copy, read, and be familiar with the Company’s Code of Ethics, and Disclosure Policy.
The CGC will review these guidelines at least on an annual basis for any changing requirements of its board.
Advisory Board Guidelines
The CGC has developed set of guidelines for
the members of its advisory board. Each of the Company’s advisors will receive a copy of the guidelines along with a copy
of the COE and Disclosure Policy. The guidelines will be reviewed and amended as required on an annual
basis.
Nomination Committee
The CGC will also act as the Company’s
Nominating Committee and as such will have the responsibility of identifying individuals qualified to become members of the board,
or to sit on any of its committees. The CGC will recommend composition of, and changes in, the composition of the board or any
of its committees when deficiencies have been identified, and will carry out a complete assessment of the performance of the board
on an annual basis.
Compensation Committee
The Company’s compensation committee
is comprised of three independent directors. This committee must review the compensation of senior management on an annual basis
and assist in the administration of the Company’s share option plan.
The Compensation Committee is responsible for
ensuring that the remuneration and incentive packages of Executive Management are fair and suitable to attract, motivate and retain
personnel of the right calibre to meet the organizations needs. The Compensation Committee should establish a framework for all
remuneration packages within the Company.
Compensation policies established by the committee
should be in line with the Company’s overall strategic goals and objectives and should be linked to the achievement of these
goals. The policies should be constructed to avoid creating conflict of interest
situations thereby ensuring that the executive management and other employees are encouraged to always act in the best interest
of the Company.
The committee should consider the issues of
compensation differentials within the organization to ensure that there is parity between the compensation of executives and the
value of their contribution to the organization. There should be particular consideration given to CEO remuneration levels to ensure
that performance and reward are linked in accordance with usual practice within that industry, relative values at other similar
organizations and previous awards given in prior years.
The CGC will review and approve the Compensation
Committee Charter on an annual basis.
Audit Committee
The CGC has the responsibility to see that
the Company is in compliance with the requirement to appoint the audit committee at the first board meeting held after each annual
shareholders meeting. The audit committee is to be comprised of 3 independent directors. A Chairperson will be elected on an annual
basis by the Board of Directors. The term will be for one year at which time they may be re-nominated.
The audit committee is among other things charged
with the responsibility of establishing auditor independence, to access the effectiveness of internal control system and for reviewing
and approving the annual and interim financial statements of the Company before they are forwarded for full board approval and
then distributed to the public.
The CGC will review and approve the Audit
Committee Charter on an annual basis.
Disclosure Policy
The Company has developed a Disclosure Policy
to ensure that the communication of material information to the investing public is reported on a timely basis and that the information
reported is balanced, accurate, and broadly disseminated in accordance with all applicable legal, regulatory and stock exchange
requirements.
This policy provides guidelines for the handling
of material information, maintaining confidentiality, designated spokespersons, media releases, dealing with media, rumours and
forward looking information. The policy sets out requirements for blackout periods, electronic communications, communicating and
enforcing this policy.
The CGC will review and approve the Disclosure
Policy on an annual basis.
Advance Notice Policy
The Company has adopted an Advance
Notice Policy for the purpose of providing shareholders,
directors and management of the Company with a clear framework for nominating directors of
the Company at a shareholders’ meeting. The Policy is designed to further CanAlaska’s commitment to:
(i) facilitating
an orderly and efficient annual general or, where the need arises, special meeting,
process; (ii) ensuring that all shareholders receive adequate notice of the director nominations and sufficient information
regarding all director nominees; and (iii) allowing shareholders to register an informed vote
after having been afforded reasonable time for appropriate deliberation.
The Board of Directors will review
the Advance Notice Policy on an annual basis.
Public Disclosure of Corporate Governance
The Company will disclose on its website, SEDAR
and EDGAR the current version of these guidelines, the Code of Ethics, Audit Committee Charter, Disclosure
Policy, Advance Notice Policy and other policies that are developed in the future that may require public disclosure.
CanAlaska Uranium (QX) (USOTC:CVVUF)
Historical Stock Chart
From Oct 2024 to Nov 2024
CanAlaska Uranium (QX) (USOTC:CVVUF)
Historical Stock Chart
From Nov 2023 to Nov 2024