UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
|
x
|
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended August 31, 2012
|
|
|
|
|
|
OR
|
|
o
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the transition period from _______________
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commission file number 000-54321
|
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Nevada
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
|
|
68-0678185
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
No. 2 Longbao Street
Xiaodian Zone, Taiyuan City
Shanxi Province, P.R. China
(Address of principal executive offices)
|
|
030031
(Zip Code)
|
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code
86-351-7963988
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Common Stock, Par Value $0.001
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes
o
No
x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes
o
No
x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes
x
No
o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).Yes
x
No
o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K.
o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer
o
|
Accelerated filer
o
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
o
(Do not check if a small reporting company)
|
Smaller reporting company
x
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes
o
No
x
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common stock was last sold as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter was $4,801,205.
As of November 28, 2012, there were 30,069,629 shares of Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE: NONE
CHINA BILINGUAL TECHNOLOGY & EDUCATION GROUP INC.
Table of Contents
PART I
Forward-Looking Statements
Forward-looking statements in this report, including without limitation, statements related to China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc.’s (“China Bilingual”) plans, strategies, objectives, expectations, intentions and adequacy of resources, are made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Investors are cautioned that such forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties including without limitation the following: (i) China Bilingual’s plans, strategies, objectives, expectations and intentions are subject to change at any time at the discretion of China Bilingual.; (ii) China Bilingual’s plans and results of operations will be affected by China Bilingual’s ability to manage growth; and (iii) other risks and uncertainties indicated from time to time in China Bilingual’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “could,” “expects,” “plans,” “intends,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “predicts,” “potential,” or “continue” or the negative of such terms or other comparable terminology. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance or achievements. Moreover, neither we nor any other person assumes responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of such statements. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date hereof. We are under no duty to update any of the forward-looking statements after the date of this report.
Factors that might affect our forward-looking statements include, among other things:
|
|
●
|
overall economic and business conditions;
|
|
|
●
|
the demand for our services;
|
|
|
●
|
competitive factors in the industries in which we compete;
|
|
|
●
|
changes in tax requirements (including tax rate changes, new tax laws and revised tax law interpretations);
|
|
|
●
|
the outcome of litigation and governmental proceedings;
|
|
|
●
|
interest rate fluctuations and other changes in borrowing costs;
|
|
|
●
|
other capital market conditions, including availability of funding sources;
|
|
|
●
|
potential impairment of our indefinite-lived intangible assets and/or our long-lived assets; and
|
|
|
●
|
changes in government regulations related to the education industry.
|
ITEM 1. BUSINESS.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. (the “Company”, “we”, “us” or “our”) is an education company that owns and operates high-quality K-12 private boarding schools in the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”). The Company established school operations in 1998 and currently operates three schools encompassing kindergarten, elementary, middle and high school levels with approximately 14,583 students and 1,876 faculty and staff for the 2012-2013 school year. The Company’s schools are located in Shanxi and Sichuan Provinces and provide students with an innovative and high-quality education with a focus on fluency and cultural skills in both Chinese and English, as well as a strong core curriculum. The schools regularly rank among the top schools in their respective regions for college entrance exam scores and national college entrance rates. The Company’s schools have earned excellent teaching reputations and are recognized for the success of their students and strong faculty. As the PRC experiences rapid industrialization and economic growth, the government is focused on education as a means to increase worker productivity and raise the standard of living. Parents in the PRC’s new middle and upper classes are sending their children to receive private school education to give them an advantage in the PRC’s increasingly competitive workforce. The Company’s sector in education is not subject to corporate income tax in the PRC, and the Company anticipates its growth will come from both organic growth through increased enrollment and expansion of its business model and teaching methods into new schools, which may be acquired by the Company.
The Company was incorporated in the State of Nevada on March 31, 2009 under the name Designer Export, Inc. On June 30, 2010, the Company changed its name to China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc.
On June 30, 2010, the Company entered into a Share Exchange Agreement (“Agreement”) with Kahibah Limited (“KL”), a British Virgin Islands (“BVI”) corporation and its shareholders. According to this Agreement, the Company acquired all the issued and outstanding shares of KL. The Company issued 26,100,076 shares of its common stock, after giving effect to the cancellation of 7,748,343 shares on June 30, 2010, to KL’s shareholders in exchange for 100% of the shares of KL. After the closing of the transaction, the Company had a total of 30,000,005 shares of common stock issued and outstanding, with KL’s shareholders owning 87% of the total issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock, and the balance held by those who held shares of the Company’s common stock prior to the closing of the exchange. This transaction resulted in KL’s shareholders obtaining a majority voting interest in the Company. All shares are shown effective of a 2.582781 forward stock split as of July 14, 2010.
The acquisition of KL and the operations of its subsidiaries were accounted for as a reverse merger (“Merger”), whereby KL is the continuing entity for financial reporting purposes and is deemed, for accounting purposes, to be the acquirer of the Company. In accordance with the applicable accounting guidance for accounting for the business combination as a reverse merger, KL is deemed to have undergone a recapitalization, whereby KL is deemed to have issued common stock to the Company’s common equity holders. Accordingly, although the Company, as KL’s parent company, was deemed to have legally acquired KL, in accordance with the applicable accounting guidance for accounting for the transaction as a reverse merger and re-capitalization, KL is the surviving entity for accounting purposes and its assets and liabilities are recorded at their historical carrying amounts with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded as a result of the accounting merger with the Company.
As part of the acquisition, the Company changed its name to China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. Share and per share amounts stated have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the acquisition. The accompanying financial statements present the historical financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of KL and its operating subsidiaries prior to the recapitalization.
The historical consolidated financial statements of the Company are those of KL, and of the consolidated entities. The consolidated financial statements of the Company presented for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010 included the financial statements of China Bilingual, KL, KL’s subsidiary Taiyuan Taiji Industry Development Co., Ltd. (“Taiyuan Taiji”), a wholly-foreign owned enterprise (“WFOE”) under the laws of the PRC, which owns 95% of the registered capital of Shanxi Taiji Industry Development Co., Ltd. (“Shanxi Taiji”), an equity joint venture company organized under the laws of the PRC. Shanxi Taiji owns all of the registered capital of Shanxi Modern Bilingual School (“Shanxi North Campus”) and Sichuan Guang’an Experimental High School (“Sichuan Guang’an School”), both private non-enterprise entities incorporated under the laws of the PRC, collectively the “Subsidiaries.”
Since the ownership of KL and its Subsidiaries was substantially the same, the merger with each was accounted for as a transfer of equity interests between entities under common control, whereby the acquirer recognized the assets and liabilities of each Subsidiary transferred at their carrying amounts. The reorganization was treated similar to the pooling of interest method with carry over basis. Accordingly, the financial statements for KL and its Subsidiaries have been combined for all periods presented, similar to a pooling of interest. The reorganization of entities under common control was retrospectively applied to the financial statements of all prior periods when the financial statements are issued for a period that includes the date the transaction occurred. Intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated in consolidations.
On August 31, 2011, the Company’s entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement and purchased all of the outstanding equity of Shanxi Rising Education Investment Company Limited (the “Investment Company”) from the equity holders (the “Sellers”) for a total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 (approximately $108,226,806). The net present value of the total fair value consideration transferred equals RMB 650,000,000 (approximately $102,565,721), of which RMB 370,217,933 (approximately $55,444,697) has been paid. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement the balance of the purchase price is to be paid over three years in three scheduled payments as follows: (See Note 20 – Business Combination for additional details on the Equity Transfer Agreement.)
|
|
1)
|
RMB 119,782,067 (approximately $18,900,822) to be paid by August 31, 2012, but was paid on September 3, 2012
|
|
|
2)
|
RMB 100,000,000 (or RMB 87,589,800, approximately $13,821,094, net of discount) by August 31, 2013, and
|
|
|
3)
|
RMB 100,000,000 (or RMB 93,849,000, approximately $14,808,754, net of discount) by August 31, 2014.
|
The net present value of the payments is discounted at the Company’s then current financing interest rate of 6.84%.
The Investment Company, a limited liability company established under the laws of the PRC, is an education company that owns and operates a K-12 private boarding school in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province of the PRC, encompassing kindergarten, primary and secondary education. The Investment Company was established in 2001 and it has share capital of RMB 70,000,000. It is the parent company of Shanxi Rising School (the "Rising School"), founded 2002, which currently serves over 5,400 students from its location in Shanxi Province, the PRC. The Rising School is now known by the Company as the “Shanxi South Campus.”
The acquisition of the Investment Company has been accounted for as a business combination under Accounting Standards Codification Topic 805,
Business Combinations
(“ASC 805”). The total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 has been allocated to the net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values as of August 31, 2011. As of the balance sheet date, August 31, 2011, the exchange rate to the US Dollar was RMB 6.3755.
Prior to closing the Equity Transfer Agreement, the Company became involved in the operations of the Shanxi South Campus in the spring of 2011. With the consent of the Investment Company, the Company assisted in the operations, accounting and promotion of the school to attract more and better students for the 2011-2012 school year. Some of these responsibilities included collecting prepaid tuition, room & board and other school fees (“School Fees”) in advance of the school year, which combined with better operations, higher tuition rates and an increase in enrollment led to an increase in deferred revenue at August 31, 2011. The Company’s involvement at the Shanxi South Campus was under the direction of Investment Company management until it assumed control of the Investment Company on August 31, 2011, in accordance with the Equity Transfer Agreement.
For the purpose of preparing the consolidated financial statement, the total purchase price is allocated to the Company’s net tangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of August 31, 2011.
The adjustments record the purchase price allocation entries as of August 31, 2011, including allocation of fair values of the associated tangible assets, intangible assets and acquired liabilities, to eliminate the Company's historical equity balances and to record the estimated use of cash to fund the cash portion of the acquisition. The adjustments also include certain decreases in intercompany balances eliminated in consolidation.
Accordingly, t
he fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed may be materially impacted by the results of the Company’s on-going operations after the date of the Equity Transfer Agreement.
The Company undertakes to meet the market demands for primary and secondary educational needs through the operations of private boarding schools within the PRC. The following chart shows the Company structure:
Overview
The Company continues to carry on the business of Shanxi Taiji, our PRC operating entity, as our sole line of business.
Shanxi Taiji owns all of the registered capital of Shanxi Modern Bilingual School, a private non-enterprise entity incorporated under the laws of the PRC and Sichuan Guang’an Experimental School, a private non-enterprise entity incorporated under the laws of the PRC. Since its inception, Shanxi Taiji has striven to meet the market demands for kindergarten, primary and secondary educational needs through the establishment of Shanxi Modern Bilingual School and Sichuan Guang’an Experimental School.
After the Transaction, Shanxi Taiji also owns all the registered capital of the Investment Company, a PRC company, which in turn holds 100% of the Shanxi Rising School, a private non-enterprise entity incorporated under the PRC laws, providing kindergarten, primary and secondary school education in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province of the PRC.
Shanxi Modern Bilingual School - North Campus
Shanxi North Campus was established in 1998 by Shanxi Taiji, approved by the Taiyuan Bureau of Education. The school offers upper-middle and high school in one full-time boarding school. It has a good school learning environment with a campus covering 38 acres and 1.4 million square feet of buildings in Taiyuan City, Shanxi. The school has three academic buildings, an administration building, four student apartment buildings, two cafeterias, six teacher residential buildings, a multi-functional arts gymnasium and a high-standard polyurethane plastic 400-meters circular track field, many standard basketball courts and a large children’s playground.
The school is equipped with:
· audio-visual language teaching facilities;
· multimedia amphitheater;
· modern computer classrooms, which allow us to teach remotely;
· physics, chemistry, and biology laboratories;
· library; and
· reading, art and music rooms
Since its inception, the number of students enrolled in our school has increased steadily over the years from nine students at inception in 1998 to approximately 4,893 enrolled students for the 2012 – 2013 school year. Our capacity at the Shanxi North Campus is approximately 6,000 students. The enrollment structure at the Shanxi North Campus changed for this school year so that the campus now accommodates our senior-middle school and high school students. With the addition of our Shanxi South Campus we have transferred our junior-middle school students and primary school students to the new Shanxi South Campus to divide the grade levels between the two campuses. The two campuses are approximately 15 kilometers apart.
The number of staff at the Shanxi North Campus is 785, all of which are full-time, including 40 individuals in the management and administration, 364 teachers and 381 staff members in support. Currently the school has 4,893 students in approximately 132 classes.
The school has received numerous accolades for excellence in teaching. The Taiyuan Bureau of Education awarded our school its “Special Award” for high school education and teaching quality and "Comprehensive Excellence Award", “Junior Secondary Education Teaching Quality Prize" and the "Excellence Award." Other honors the school has earned over the past few years include the "Taiyuan Excellence High School," and "High School Graduation Exam Prize." The school has also been awarded the "Outstanding Private Middle School in Shanxi Province", "Green School in Shanxi Province," "National Children's Computer Examination Training Points" and "Model School in Information Technology in Shanxi Province," and "National Creative Writing Experimental School."
Shanxi Modern Bilingual School - South Campus (formerly known as Shanxi Rising School, acquired August 31, 2011)
Shanxi South Campus was established in 2002 under the name of Shanxi Rising School. The school offers kindergarten, elementary and junior-middle school in one full-time boarding school. The school has a good learning environment with a campus covering 82 acres and 2.2 million square feet of buildings in Jinzhong City, Shanxi (approximately 15 kilometers south of the Company’s Shanxi North Campus). The teaching, administration and residential buildings are all equipped according to the highest national standard.
The school is equipped with:
· lecture classrooms;
· multimedia classrooms;
· special classrooms for art and music;
· metaphase and nature laboratory;
· computer room;
· arts center;
· network center;
· library and reading room; and
· instrument and equipment store house.
The number of the school’s existing staff is 794, all of which are full-time, including 32 individuals in the management and administration, 388 teachers and 374 staff members in support. Currently the school has approximately 6,836 students in 138 classes. The campus has a capacity for 10,000 students.
The school has attained encouraging success in the teaching area. In the entrance examination to senior-middle school in 2011, the school was ranked second in more than 200 middle schools in Taiyuan City. Moreover, the school’s students have won numerous awards for academics and arts achievements.
Sichuan Guang’an School
Sichuan Guang’an School was established in 2002 by Shanxi Taiji, approved by the Guang’an Bureau of Education. The school was originally established by the local government as a high school, but the Company assumed operational control prior to the school opening so that the region would have an established private boarding school operator. The school now offers kindergarten, elementary, middle and high school in one full-time boarding school. It has a good school learning environment with a tree-lined campus covering 23 acres and 750,000 square feet of buildings in Guang’an, Sichuan. We have two academic buildings, an administrative building, four student apartments, four teacher apartment buildings, two cafeterias, an audio-visual technology building (also for the library), a large-scale indoor sports center, a high-standard polyurethane plastic 400-meters circular track field, and many standard basketball courts and a large children’s playground. All school equipment meets provincial-level high school’s standards.
The school is equipped with:
· modern art rooms;
· science labs,
· multimedia network classroom
· a language lab;
· a high specification amphitheater;
· music, dance and , piano rooms;
· 400 meters circular track and field; and
· basketball courts, volleyball courts and badminton courts.
The number of the school’s existing staff is 240, all of which are full-time, including 15 individuals in the management and administration, 115 teachers and 110 staff members in support. Currently the school has approximately 2,855 students in 63 classes.
The Sichuan Guang’an School has consistently ranked as the number one school in the region for the rate of college entrance of students. The students of Sichuan Guang’an School have won numerous awards for academics and art achievement at the national, provincial, municipal level, as well as other types of competitions. The school has won awards for college entrance exam scores and education quality from the local and provincial government including “College Entrance Examination Growth Award", awarded by the National Education Ministry; "Key Lessons Experimental School", and named "Huaying Private Education Advanced High School”, first prize in the quality of education. The school is the only local school employing qualified foreign teachers, and it is the region’s first large-scale private education school.
All of our schools feature expert administration, excellent teaching team, small class sizes, bilingual education and a modern learning environment.
Competition
The PRC education industry is highly competitive. Competition among educational institutions is primarily driven by location, courses, research capability and reputation. In all of the geographical areas in which we operate or expect to operate, there are other educational institutions, training centers and other education providers, which provide services comparable to those that we offer or expect to offer. Competition between PRC educational institutions has intensified in recent years due to the increase in private educational institutions and extra-curricular training centers that allow students to choose the educational institutions and courses they would like to attend.
In general, educational institutions compete within the communities they serve based on the teaching quality and specialty of the teachers, enrollment rate, reputation, the physical condition of their facilities and teaching equipment. We strive to distinguish the educational institutions we operate based on the quality provided and our ability to attract and retain teachers with varied specialties. We strive to maintain and improve the level of enrollment and to provide quality facilities and teaching services.
Our schools emphasize the bilingual education model. We integrate English teaching across our entire curriculum and integrate it into the students’ daily lives. We maintain a staff of foreign teachers to teach not only language skills but also cultural skills. Our teachers and staff are well-paid with an average age of 35. Over 80% of our teachers are national, provincial, municipal and district subject leaders, the backbone of teaching in the PRC - considered teaching experts.
We face competition from domestic and international education service providers that are seeking to acquire and operate educational institutions in the PRC. We expect competition for attractive opportunities to intensify because of the continued privatization of the education industry in the PRC and the difficulty in setting up new educational institutions in the PRC, which requires approval from the local Bureau of Education or the Ministry of Education of the PRC. Other competitors, such as high-end standalone, private educational institutions and training centers that cater to high-income consumers and foreign expatriates, have emerged primarily as a result of the increasing affluence of the Chinese population. These standalone private educational institutions and training centers are managed by both foreign and domestic high school, college and university operators.
Government Approvals and Regulations
General Regulatory Environment
The PRC’s education industry is regulated by various government agencies, mainly including the Ministry of Education (the “MOE”). The MOE has branch offices across the PRC to oversee the education industry at the provincial, municipal and county levels, which together with the MOE we refer to as the Education Authorities. These Education Authorities, together with other relevant government agencies, such as the Ministry of Civil Affairs (“MCA”) and Ministry of Labor and Social Security have promulgated rules and regulations relating to the establishment, licensing and operation of educational institutions, the licensing, administration and management of educational staff and the taxation of educational services and incomes.
Operation of Private Schools
Level of Approval
Pursuant to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Education promulgated by the Standing Committee of the Ninth National People’s Congress of the PRC which became effective on September 1, 2003, and the Implementation Rules to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Education issued by the State Council which became effective on April 1, 2004, each private school must obtain a private funded school education permit from the relevant education authority in order to conduct business as an education service provider. Private schools providing certifications, pre-school education, education for self-study aid and other academic education shall be subject to approval by the Education Authorities. The Education Authorities under the local people’s governments at or above the county level shall be responsible for the work relating to private schools of academic education in their own administrative region. The administrative departments for labor and social security and the relevant departments under the local people’s governments at or above the county level shall respectively be responsible for the work relating to private schools of non-academic education which means occupational qualification training and occupational skill training within the scope of their duties. For degree education, (i) establishment of colleges is preliminarily examined by education authorities at the provincial level, and then is examined and approved by the government of the provincial level; (ii) establishment of universities for bachelor or higher degrees is preliminarily examined by education authorities of the provincial level, and then is examined and approved by MOE; (iii) establishment of senior high schools, vocational middle schools and technical secondary schools is preliminarily examined by Education Authorities of the county level, and then is examined and approved by educational authorities of the municipal level and shall be delivered to the government of the municipal level and educational authorities of the provincial level for reference; (iv) establishment of junior middle schools and primary schools is examined and approved by Education Authorities of the county level and shall be delivered to Education Authorities of the municipal level for reference. A duly approved private school will be granted a permit for operating a private school, and shall be registered with the MCA or its local counterparts as a privately run non-enterprise institution. Each of our schools has obtained the permit for operating a private school and has been registered with the relevant local counterpart of the MCA.
Expansion of Business
Pursuant to the Implementation Rules to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Education issued by the State Council in 2004, private schools and government-run schools shall share equal legal status, and the State safeguards the autonomy of the private schools. The State protects the lawful rights and interests of the sponsors, principals, teachers and staff members of private schools. Prospectors and advertisements of private schools shall be approved by relevant examination and approval authorities. Upon the approval of its prospectors and advertisements, the private school enjoys its independent right of recruiting students and enjoys the equal recruiting right as government-run schools of the same kind. The private schools may make plans on the scope, standard and method of recruiting students independently. Private schools shall abide by the relevant regulations with respect to recruiting college-level or above students. In addition, operation of a private school is highly regulated. For example, the types and amounts of fees charged by a private school providing certifications shall be approved by the governmental pricing authority and be publicly disclosed. Thus, for a private school to expand its business, it has some discretionary power, but it must abide by a procedure under which, any increase in recruitment of students or increase in fees must be approved in advance by the relevant authorities.
Levels and Grades of schools
Subject to the Education Law of the People’s Republic of China issued by the eighth National People’s Congress in 1995, schools of the basic education system are divided into four levels including infant school education, primary education, secondary education and higher education. Accordingly, based on the four levels, there are the following kinds of schools: nursery school, primary school, junior middle school, senior high school, and university. Nursery school, primary school and junior middle school represent compulsory education. With respect to universities, there are several kinds of college degrees: bachelor degree, master degree and doctorate degree. And for different levels of private schools, there are different approval authorities. The State Council and all local people’s government at different levels shall supervise and manage the educational work according to the principle of management by different levels and division of labor with individual responsibility. Secondary and lower education shall be managed by the local people’s government under the leadership of the State Council. Higher education shall be managed by the State Council and the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the central government. Besides the basic education system, the state adopts a vocational education system and an adult education system. The people’s government at different levels, relevant administrative departments, enterprises and institutions shall adopt measures to develop and ensure for citizens vocational school education or vocational training in various forms. Meanwhile, no organization or individual may establish or operate a school or any other institution of education for profit-making purposes. However, private schools may be operated for “reasonable returns,” as described in more detail below.
School Privatization
Although no definitive regulation has been promulgated with respect to the privatization of government-run schools, the PRC government has announced a series of regulations and policies to encourage private schools and Sino-foreign-run schools. The Standing Committee of the Ninth National People’s Congress issued Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Schools to encourage social funds to invest in the education industry in 2002. To implement the above law, the State Council issued the Implementation Rules to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Schools in 2004. In order to encourage foreign funds to invest in the PRC education industry and strengthen international exchange and cooperation in the field of education, the State Council also issued Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Chinese-Foreign Schools in 2003. National Development and Reform Commission and Ministry of Commerce jointly modified Catalogue of Foreign Investment Industries in 2007, in which there are encouraged education industry, restricted education industry and prohibited education industry. The encouraged education industry is a higher-degree educational institution (only limited to joint venture or cooperative), the restricted education industry is a common senior high school education mechanism (only limited to joint venture or cooperative) and the prohibited education industry is a compulsory education and military, police, political and other kinds of education that are of a special nature in the PRC.
Special tax rules applicable to preferential tax treatment and non-preferential tax treatment for privately-run schools
Private schools are divided into three categories: private schools established with donated funds; private schools that require reasonable returns and private schools that do not require reasonable returns.
The Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Schools prescribes principally that private schools enjoy the preferential tax treatment polices regulated by the State. And the Implementation Rules to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private Schools prescribes further, that the private schools established by donation and the private schools whose investors do not ask for reasonable rewards of investment may enjoy the same preferential tax and other preferential treatments as the government-run schools. And for private schools whose investors ask for reasonable rewards of investment, its preferential tax treatment policies are jointly formulated by the finance department, tax department and other related administrative departments of the State Council. To date, however, no regulations have been promulgated by the relevant authorities in this regard.
Notwithstanding whether a school is state or privately-owned, the preferential local tax treatments include: business tax, urban maintenance and construction tax, extra charges for education, enterprise income tax, house property tax, deed tax, land-use tax of cities and towns, stamp tax, etc.
1. With respect to the business tax and enterprise income tax: (i) the proceeds from educational services provided by a degree educational school will be exempted from business tax; (ii) the proceeds from students working during school term will be exempted from business tax; (iii) the proceeds from technology development, technology transfer or relevant technological consultant or services provided by school will be exempted from business tax; (iv) the proceeds from caring services provided by a kindergarten or nursing school will be exempted from business tax; (v) the proceeds from further-study classes or training classes held by a government-run preliminary school, secondary school or higher school (not including subordinate enterprises) will be exempted from business tax; (vi) the proceeds from the operation of an enterprise owned wholly by a government-run vocational school will be exempted from business tax, and for the proceeds from the operation of an enterprise owned by a privately-run vocational school, the business tax is not exempted; (vii) donation to education careers from a taxpayer contributed through non-profit social entities or state organs will be exempted from income tax; (viii) the proceeds from an educational institution in accordance with regulations of non-profit income under Enterprise Income Tax Law will be exempted from income tax; and (ix) individual income tax derived from interest of savings deposit of education will be exempted.
2. With respect to the house property tax, land-use tax of cities and towns, stamp tax: (i) house or land of all kinds of schools, kindergartens or nursing schools invested by state or enterprises will be exempted from house property tax or land-use tax; and (ii) the writing papers signed by property owners to denote the property to schools will be exempted from stamp tax.
3. With respect to farm land occupation tax: the farm land approved for schools or nursing schools will be exempted from farm land occupation tax.
Restrictions on Foreign Ownership
The PRC has been gradually relaxing the restrictions on domestic private investment in private schools since 1978. From 1978-1992, the development of private schools was in an early stage; from 1992-1997, the development of private schools was in a fast-development stage; and since 1997, the development of private schools have been in a regulatory development stage. The private school system has become an important and necessary part of the PRC education system. In 2003, the State Council promulgated the Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Operating Chinese-Foreign Schools, and MOE issued the Implementing Rules for the Regulations on Operating Chinese-foreign Schools, or the Implementing Rules, which encourage substantive cooperation between overseas educational organizations with relevant qualifications and experience in providing high-quality education and PRC educational organizations to jointly operate various types of schools in the PRC, with such cooperation in the areas of higher education and occupational education being encouraged. Chinese-foreign cooperative schools are not permitted, however, to engage in compulsory education and military, police, political and other kinds of education that are of a special nature in the PRC.
The establishment of a Chinese-foreign joint venture educational institution in the PRC requires approvals from different levels of government, which are difficult to obtain. An application for establishing a Chinese-foreign cooperatively-run school offering higher education for academic qualifications at or above the regular university education shall be subject to examination and approval of the MOE; an application for establishing a Chinese- foreign cooperatively-run school offering specialized higher education or higher education for non-academic qualifications shall be subject to examination and approval of the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government where the proposed school is to be located. An application for establishing a Chinese-foreign cooperatively-run school offering secondary education for academic qualifications, programs of tutoring self-taught students for examinations, programs offering supplementary teaching of school courses and pre-school education shall be subject to examination and approval of the education administrative department of the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government where the proposed school is to be located. An application for establishing a Chinese-foreign cooperatively-run school offering vocational technical training shall be subject to examination and approval of the labor administrative department of the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government where the proposed school is to be located.
All of the equity interests in Taiyuan Taiji are owned by KL directly. Taiyuan Taiji owns 95% of the equity interests in Shanxi Taiji directly. All of the registered capital of Shanxi North Campus and Sichuan Guang’an School are owned by Shanxi Taiji. All of the registered capital of the Shanxi South Campus are owned by the Investment Company, which is 100% owned by Shanxi Taiji.
Licensing Requirements
Each educational institution in the PRC is required to obtain a private funded school education permit (a “Education Permit”), from the relevant local Education Authority. To obtain an Education Permit, a private school must submit an application to its relevant Education Authority to demonstrate that it (i) has obtained a permit for setting up the educational institution from the relevant Educational Authority; (ii) is in compliance with certain basic operational standards for a legal person pursuant to the PRC Company Law; (iii) is in proper corporate form with proper name, organizational structure and premises; (iv) has adequate funds and meets certain minimum facility and personnel requirements promulgated by MOE; (v) has proper bylaws; and (vi) is capable of bearing civil liabilities independently. In addition, private schools are permitted to conduct only those business activities within the approved business scope established by the relevant Education Authority.
We have regulatory approvals from the education commissions in the Shanxi and Sichuan Provinces (which have the authority to issue and regulate education permits) which constitute the requisite private funded school education permits for the establishment of private schools in price bureau of the provinces, approvals for charging fees from local pricing regulatory authorities and all of the necessary permits, registrations, licenses and/or approvals required by the local government authority to operate.
Organizations and Activities of Private Schools
According to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Private schools, a private school shall set up an executive council, a board of directors or other forms of decision-making bodies of the school.
The executive council or the board of directors of the school shall be composed of the sponsors or their representatives, the principal, and the representatives of the teachers and staff members. More than one-third of the council members or directors shall, at least, have five years’ education or teaching experience each. The executive council or the board of directors of the school shall be composed of not less than five persons, with one of them serving as chairman of the council or board. The list of the names of the chairman and members of the council or the chairman of the board and directors shall be submitted to the examination and approval authority for the record.
The executive council or the board of directors of a school shall exercise the following functions and powers: (i) to appoint and dismiss the principal; (ii) to amend the articles of association of the school and formulate rules and regulations of the school; (iii) to make development plans and approve annual work plans; (iv) to raise funds for running the school, and examine and verify the budgets and final accounts; (v) to decide on the size and the wage standards of the teachers and staff members; (vi) to decide on the division, merging and termination of the school; and (vii) to decide on other important matters.
The chairman of the executive council or the board of directors or the principal of a private school shall serve as the legal representative of the school. A private school shall, in reference to the qualifications for the principal of a government-run school of the same grade and category, appoint its principal, and the age limit may appropriately be extended both ways, and the appointment shall be reported to the examination and approval authority for verification and approval.
The principal of a private school shall be in charge of education, teaching and administration of the school, and exercise the following functions and powers: (i) to carry out the decisions made by the executive council, board of directors or any other form of decision-making body; (ii) to put into execution the development plans, draw up the annual work plans and financial budgets, and formulate the rules and regulations of the school; (iii) to appoint and dismiss staff members of the school, and give rewards and impose punishments; (iv) to make arrangements for education, teaching and scientific research and ensure the quality of education and teaching; (v) to be responsible for the daily work of school administration; and (vi) other powers delegated by the executive council, the board of directors or any other form of decision-making body of the school.
A private school may, on the basis of relevant classifications, the length of schooling and academic performance and in accordance with the relevant regulations of the State, issue academic credentials, certificates for completing a course or qualification certificates of training to the students it enrolls. Students who receive training in vocational skills may be awarded vocational qualification certificates of the State when they are considered qualified by the vocational skills appraisal authority approved by the State. A private school shall, in accordance with law, ensure that the teachers and staff members participate in democratic management and supervision through the representative assembly of the teachers and staff members with the teachers as the main body, or through other forms. Teachers and staff members of a private school shall, in accordance with the Trade Union Law, have the right to form trade union organizations to protect their lawful rights and interests.
We believe that Shanxi North Campus, Shanxi South Campus and Sichuan Guang’an School currently operate in compliance with the relevant regulations.
Ownership of Foreign Entities by PRC Residents
The PRC State Administration of Foreign Exchange, or SAFE, issued a public notice, or the SAFE Notice, in October 2005 regarding the use of special purpose vehicles, or SPVs, by PRC residents seeking offshore financing to fund investments in the PRC. The SAFE Notice requires PRC residents to register with and receive approvals from SAFE in connection with offshore investment activities. The SAFE Notice provides that each PRC resident who is an ultimate controller of the offshore company must complete the prescribed registration procedure with the relevant local branch of SAFE prior to establishing or assuming control of an offshore company for the purpose of transferring to that offshore company assets of or equity interest in a PRC enterprise.
The notice applies retroactively. As a result, PRC residents who have established or acquired control of these SPVs that have made onshore investments in the PRC were required to complete the relevant overseas investment foreign exchange registration procedures by March 31, 2006. These PRC residents must also amend the registration with the relevant SAFE branch in the following circumstances: (i) the PRC residents have completed the injection of equity investment or assets of a domestic company into the SPV; (ii) the overseas funding of the SPV has been completed; or (iii) there is a material change in the capital of the SPV. If we are deemed an SPV under the SAFE Notice, we would be required to comply with the approval and registration requirements under the SAFE Notice. As of date of this report, our PRC shareholders have not registered their ownership interests in us with SAFE because our PRC shareholders believe that the SAFE Notice is not applicable to them. In the event SAFE holds a different view from that of our shareholders, failure of our PRC shareholders to comply with these registration requirements may subject them to fines or legal sanctions or limit the ability of Shanxi Taiji to obtain or update its foreign exchange registration certificate with SAFE, which may in turn subject us to fines or legal sanctions, restrict our cross-border investment activities or limit Shanxi Taiji ability to distribute dividends to us.
Regulations on Foreign Currency Exchange
Under the Foreign Currency Administration Rules promulgated by the State Council in 1996 and last revised on August 5, 2008 and various other regulations issued by SAFE, and other relevant PRC government authorities, Renminbi is convertible into other currencies for the purpose of current account items, such as trade related receipts and payments, interest and dividends. The conversion of Renminbi into other currencies and remittance of the converted foreign currency outside the PRC for the purpose of capital account items, such as direct equity investments, loans and repatriation of investment, requires the prior approval from SAFE or its local office. Payments for transactions that take place within the PRC must be made in Renminbi. PRC companies may repatriate foreign currency payments received from abroad subject to SAFE’s requirements. Foreign-invested enterprises may retain foreign currency in accounts with designated foreign exchange banks. Domestic enterprises may convert all of their foreign currency current account proceeds into Renminbi. Capital investments by the Company into Taiyuan Taiji will be considered capital account items, which are subject to rigorous regulations and controls in the PRC. Payments for international equipment will be considered current account items, which only need to satisfy certain documentary and procedural requirements of the foreign exchange regulations.
Regulations on Dividend Distribution
The principal regulations governing dividend distributions by wholly foreign owned enterprises and Sino-foreign equity joint ventures include:
|
|
•
|
|
The Wholly Foreign Owned Enterprise Law (1986), as amended;
|
|
|
•
|
|
The Wholly Foreign Owned Enterprise Law Implementing Rules (1990), as amended;
|
|
|
•
|
|
The Sino-foreign Equity Joint Venture Enterprise Law (1979), as amended; and
|
|
|
•
|
|
The Sino-foreign Equity Joint Venture Enterprise Law Implementing Rules (1983), as amended.
|
Under these regulations, wholly foreign owned enterprises and Sino-foreign equity joint ventures in the PRC may pay dividends only out of their accumulated profits, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. Additionally, before paying dividends to their shareholders, these foreign-invested enterprises are required to set aside at least 10% of their profits each year, if any, to fund certain reserve funds until the amount of the cumulative total reserve funds reaches 50% of the relevant company’s registered capital. Accordingly, our wholly-owned subsidiary, Taiyuan Taiji is allowed to distribute dividends to us only after having set aside the required amount of its profits into the reserve funds as required under applicable PRC laws and regulations.
Employees
We have approximately 1,876 employees, all of which are full-time consisting of approximately 57 in corporate management and staff positions, 87 individuals in school management and administration, 867 teachers and 865 support staff members. None of our employees are represented by a labor union. We intend to hire additional employees on an as-needed basis during the next 12 months.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
There are numerous and varied risks, known and unknown, that may prevent us from achieving our goals. If any of these risks actually occur, our business, financial condition or results of operation may be materially adversely affected. In such case, the trading price of our common stock could decline and investors could lose all or part of their investment.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
If we are unable to continue to attract course participants to enroll in our courses, our revenues may decline and we may not be able to maintain profitability.
The success of our business depends primarily on the number of enrollments in our schools and the amount of tuition that we can charge. Therefore, our ability to continue to attract course students to enroll in our courses and maintain revenue growth is critical to the continued success and growth of our business. This in turn will depend on several factors, including our ability to develop new courses and enhance existing courses to respond to changes in market trends and demands of students, to effectively market our schools to a broader base of prospective course participants, to train and retain qualified lecturers and tutors, to develop additional high-quality educational content and to respond to competitive pressures. If we are unable to increase our enrollments in some of our relatively new courses and generate sufficient tuition to exceed the incremental costs associated with developing and delivering such new courses, we may be unable to maintain substantial revenue growth.
Failure to attract and retain qualified personnel and experienced senior management could disrupt our operations and adversely affect our business and competitiveness.
Our continuing success is dependent, to a large extent, on our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel and experienced senior management. If one or more of our senior management team members are unable or unwilling to continue to work for us, we may not be able to replace them within a reasonable period of time or at all, and our business may be severely disrupted, our financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected and we may incur additional expenses in recruiting and training additional personnel. If any of our senior management joins a competitor or forms a competing business, our business may be severely disrupted.
We have been operating under our current ownership structure for a limited time which may make it difficult for you to evaluate our business and prospects.
We acquired all of the issued and outstanding capital of Kahibah Limited in June 2010. Shanxi North Campus and Sichuan Guang'an School commenced operations in 1998 and 2002, respectively. We acquired the Shanxi South Campus on August 31, 2011 and the school commenced operations in 2002. Accordingly, we have a limited history for our operation upon which you can evaluate the viability and sustainability of our business and its acceptance by students. Our present and future competitors may have longer operating histories, larger student enrollments, larger teams of professional staff and greater financial, technical, marketing and other resources.
We are dependent on the Shanxi North Campus, Shanxi South Campus and Sichuan Guang’an School for all of our revenues. Any adverse development relating to any of these schools could materially and adversely affect our future results of operations.
Shanxi North Campus, Shanxi South Campus and Sichuan Guang’an School account for all of our revenue. Unless we are successful in acquiring control of and operating other educational institutions, all of our revenue will continue to be derived from these three schools. As a result, any development that has a material adverse effect on one or more of these schools may have a material adverse effect upon our business and financial performance, including developments such as the following:
|
|
·
|
any reduction in student enrollment at any of these educational institutions;
|
|
|
·
|
any increase in competition from other schools; and
|
|
|
·
|
the failure to attract and retain high quality teaching staff in our schools.
|
We may lose market share and our profitability may be materially and adversely affected, if we fail to compete effectively with our present and future competitors or to adjust effectively to changing market conditions and trends.
We face competition from providers of online vocational/career education, training, and expect to face increasing competition from existing competitors and new market entrants in the traditional education. The provision of professional education and test preparation courses over the Internet is a relatively recent concept. Although traditional classroom instruction is generally viewed as a more accepted method, online education is increasingly apparent as an acceptable means of receiving training and instruction. We therefore compete with providers of online education institutions and training centers in the various subject areas for which we offer courses. In addition, due to low barriers to entry for Internet-based businesses, we expect to face increasing competition from both existing domestic competitors and new entrants on the online education side. We may face increased competition from international competitors that cooperate with local businesses to provide services based on the foreign partners’ technology and experience developed in their home markets.
If we fail to develop and introduce new courses, services and products that meet our target customers’ expectations, or adopt new technologies important to our business, our competitive position and ability to generate revenues may be materially and adversely affected.
Our core business is centered on acquiring control of schools that provide kindergarten, primary school, secondary school and high school educations in urban communities. As the growing trend toward urbanization is expected to result in more people seeking job and career advancement opportunities in urban areas, the development of new courses, services and products is subject to risks and uncertainties. Unexpected technical, operational, logistical, regulatory or other problems could delay or prevent the introduction of one or more of new courses, service or products. Moreover, we cannot assure you that any of these courses, products and services will match the quality or popularity of those developed by our competitors, achieve widespread market acceptance or generate the desired level of income. The technology used in internet and value-added telecommunications services and products in general, and in online education services in particular, has evolved a lot in recent years. The online course providers seek to satisfy the demand of self-taught learners for high-level education and part-time workers seeking time flexibility. Providers of traditional education may lose part of the target course participants, if they fail to anticipate and adapt to such technological changes.
Risks Relating to Regulation of Our Business and to Our Structure
The education sector, in which all of our business is conducted, is subject to extensive regulation in the PRC, and our ability to conduct business is highly dependent on our compliance with these regulatory frameworks.
The PRC government regulates all aspects of the education sector, including licensing of parties to perform various services, pricing of tuition and other fees, curriculum content, standards for the operations of schools and learning centers associated with foreign participation. The laws and regulations applicable to the education sector are in some aspects vague and uncertain, and often lack detailed implementing regulations. These laws and regulations are subject to change, and new laws and regulations may be adopted, some of which may have retroactive application or have a negative effect on our business. For example, in 2003, the PRC government adopted a new regulatory framework for Chinese-foreign cooperation in education. This new framework may encourage institutions with more experience, better reputations, greater technological know-how and larger financial resources than we have to compete against us and limit our growth. In addition, because the PRC government and the public view the conduct of educational institutions as a vital social service, there is considerable ongoing scrutiny of the education sector and its participants.
We must comply with PRC’s extensive regulations on private and foreign participation in the education sector, which has caused us to adopt complex structural arrangements with our PRC subsidiary and PRC affiliated entity. If the relevant PRC authorities decide our structural arrangements do not comply with these restrictions, we would be precluded from conducting some or all of our current business.
Although our corporate structure and business are designed to comply with the limitations on foreign investment and participation in the education sector, we cannot assure you that we will not be found to be in violation of any current or future PRC laws and regulations. There are substantial uncertainties regarding the interpretation and application of PRC laws and regulations. If we or our PRC subsidiary or PRC affiliated entity are found to be or to have been in violation of PRC laws or regulations limiting foreign ownership or participation in the education sector, the relevant regulatory authorities have broad discretion in dealing with such violation, including but not limited to:
|
|
•
|
|
levying fines and confiscating illegal income;
|
|
|
•
|
|
requiring us to discontinue all or a portion of our business; and/or
|
|
|
•
|
|
revoking business licenses.
|
Any of these or similar actions could cause significant disruption to our business operations or render us unable to conduct all or a substantial portion of our business operations.
The preferential tax treatment status of the educational institutions we operate places limitations on our ability to freely operate our business, including limitations on pricing and our ability to withdraw profits from the educational institutions we operate for distribution to shareholders or for use in other parts of our business. The educational institutions we operate may incur additional costs if they seek to convert to non-preferential tax treatment status and we cannot assure you that the educational institutions we operate will be able to retain their preferential tax treatment status.
The educational institutions we operate are classified as educational institutions with preferential tax treatment, entitling them to certain tax benefits including exemption from income, turnover and property taxes. However, as a result of their preferential tax treatment status, the educational institutions we operate are prohibited from setting prices for educational services and accommodations above certain price thresholds set by the PRC government and are required to reinvest distributable profits into operations rather than being allowed to distribute profits as investment returns to the educational institutions’ owners. As a result, the educational institutions we operate are limited in the prices they may charge for educational services and accommodations and may not distribute their profits to Shanxi Taiji. These restrictions limit the financial returns the educational institutions we operate may achieve and prevent Shanxi Taiji from receiving profits from the educational institutions for investment in other high schools, acquisitions of other high schools and universities or use in other parts of its business. The only fees we anticipate that Shanxi Taiji will be able to receive from the educational institutions we operate are service fees to be paid by the educational institutions for technical services, investment and management consulting services provided by Shanxi Taiji to the educational institutions we operate. As a result, for as long as the educational institutions we operate retain their preferential tax treatment status, Shanxi Taiji will be unable to use the profits from the operations of the educational institutions it owns for reinvestment in or expansion of its business (other than reinvestment of the funds in the educational institutions from which the profits were derived) or for distribution to its shareholders. Accordingly, we anticipate that at some point in the future Shanxi Taiji will convert the educational institutions we operate to non-preferential tax treatment entities to enable it to distribute their profits to Shanxi Taiji for use in other parts of its business. We are not able to predict the time of such conversion at this time. Factors to be considered in determining whether to undertake this conversion include, our ability to acquire control of additional educational institutions, the pace at which we are able to acquire control of additional educational institutions, our competitive position in the education industry in the PRC and any negative impact the increase in tax expense will have on the network of educational institutions’ operating margins. Potential problems related to the conversion decision include, but are not limited to, Shanxi Taiji’s ability to obtain the necessary regulatory approvals for such a conversion. The conversion of the educational institutions we operate from entities that receive preferential tax treatment to entities that do not receive preferential tax treatment may result in an increase in the price of educational services provided by the network educational institutions in order to mitigate the effect of increased taxes and maintain the same profit margin. Any increase in prices for our services may result in the loss of price sensitive students. If the educational institutions we operate are converted into entities that do not receive preferential tax treatment entities, they will only be able to pay to Shanxi Taiji profits that have been generated from and after the date of conversion. An educational institution that does not receive preferential tax treatment is permitted to set its own pricing schemes and may distribute profits to its investors, but is required to pay corporate income taxes in the PRC. As a result, if Shanxi Taiji converts the educational institutions we operate to entities that do not receive preferential tax treatment, the educational institutions we operate will be less competitive against the state-sponsored high schools, colleges and universities which receive preferential tax treatment, as they will be required to pay income taxes on the their profits from and after the date of conversion. At the time of conversion, those educational institutions will become subject to corporate income tax in the PRC and we will be required to make payments to the local governments. A change in laws or a failure by one of the educational institutions we operate to satisfy the requirements of maintaining preferential tax treatment status may cause one or more of the educational institutions we operate to lose preferential tax treatment status. As a result, we cannot assure you that the educational institutions we operate or expect to operate will continue to qualify as preferential tax treatment entities and enjoy this preferential tax treatment in the future. We also cannot assure you that the laws will remain the same and that Shanxi Taiji will be able to convert the educational institutions we operate to non-preferential tax treatment entities at times that are desirable for our business. A loss of preferential tax treatment status by any of the educational institutions we operate before the desired time, or an inability to convert any of the educational institutions we operate to non-preferential tax treatment status at the desired time, may have a material adverse effect on our business, competitive position, cash flows, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The PRC’s economic, political and social conditions, as well as governmental policies, could affect the financial markets in the PRC and our liquidity and access to capital and our ability to operate our business.
The PRC economy differs from the economies of most developed countries in many respects, including the amount of government involvement, level of development, growth rate, control of foreign exchange and allocation of resources. While the PRC economy has experienced significant growth over the past, growth has been uneven, both geographically and among various sectors of the economy. The PRC government has implemented various measures to encourage economic growth and guide the allocation of resources. Some of these measures benefit the overall PRC economy, but may also have a negative effect on us.
The PRC economy has been transitioning from a planned economy to a more market-oriented economy. Although the PRC government has implemented measures since the late 1970s emphasizing the utilization of market forces for economic reform, the reduction of state ownership of productive assets and the establishment of improved corporate governance in business enterprises, a substantial portion of productive assets in the PRC are still owned by the PRC government. In addition, the PRC government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. The PRC government also exercises significant control over the PRC economic growth through the allocation of resources, controlling payment of foreign currency- denominated obligations, setting monetary policy and providing preferential treatment to particular industries or companies. Since late 2003, the PRC government implemented a number of measures, such as raising bank reserves against deposit rates to place additional limitations on the ability of commercial banks to make loans and raise interest rates, in order to slow down specific segments of the PRC economy which it believed to be overheating. These actions, as well as future actions and policies of the PRC government, could materially affect our liquidity and access to capital and our ability to operate our business.
The PRC legal system is a civil law system based on written statutes. Unlike common law systems, it is a system in which decided legal cases have little precedential value. In 1979, the PRC government began to promulgate a comprehensive system of laws and regulations governing economic matters in general. The overall effect of legislation over the past 33 years has significantly enhanced the protections afforded to various forms of foreign investment in the PRC. Our PRC subsidiary, Taiyuan Taiji, is a wholly foreign-owned enterprise which is an enterprise incorporated in the PRC and wholly-owned by foreign investors. Taiyuan Taiji is subject to laws and regulations applicable to foreign investment in the PRC in general and laws and regulations applicable to wholly foreign-owned enterprises in particular. However, these laws, regulations and legal requirements change frequently, and their interpretation and enforcement involve uncertainties. For example, we may have to resort to administrative and court proceedings to enforce the legal protection that we enjoy either by law or contract. However, since PRC administrative and court authorities have significant discretion in interpreting and implementing statutory and contractual terms, it may be more difficult to evaluate the outcome of administrative and court proceedings and the level of legal protection we enjoy than in more developed legal systems.
Recent regulations relating to offshore investment activities by PRC residents may increase the administrative burden we face and create regulatory uncertainties that could restrict our overseas and cross-border investment activity, and a failure by our shareholders who are PRC residents to make any required applications and filings pursuant to such regulations may prevent us from being able to distribute profits and could expose us and our PRC resident shareholders to liability under PRC law.
The PRC National Development and Reform Commission, or NDRC, and SAFE recently promulgated regulations that require PRC residents and PRC corporate entities to register with and obtain approvals from relevant PRC government authorities in connection with their direct or indirect offshore investment activities. These regulations apply to our shareholders who are PRC residents and may apply to any offshore acquisitions that we make in the future.
Under the SAFE regulations, PRC residents who make, or have previously made, direct or indirect investments in offshore companies will be required to register those investments. In addition, any PRC resident who is a direct or indirect shareholder of an offshore company is required to file with the local branch of SAFE, with respect to that offshore company, any material change involving capital variation, such as an increase or decrease in capital, transfer or swap of shares, merger, division, long term equity or debt investment or creation of any security interest over the assets located in the PRC. If any PRC shareholder fails to make the required SAFE registration, the PRC subsidiaries of that offshore parent company may be prohibited from distributing their profits and the proceeds from any reduction in capital, share transfer or liquidation, to their offshore parent company, and the offshore parent company may also be prohibited from injecting additional capital into their PRC subsidiaries. Moreover, failure to comply with the various SAFE registration requirements described above could result in liability under PRC laws for evasion of applicable foreign exchange restrictions.
The tuition charged by the educational institutions are all subject to price controls administered by the PRC government, and our revenue is highly dependent on the level of these tuition charges.
Our revenue comes primarily from the tuition revenue from our schools, and the tuition charges are subject to price controls administered by various price control offices. In light of the substantial increase in tuitions and other education-related fees in the PRC in recent years, the PRC’s price control authorities may impose stricter price control on tuition charges in the future. If the tuition charges, upon which our revenue depends, were to be decreased or if they were not to be increased in line with increases in our costs because of the actions of PRC’s administrative price controls, our revenue and profitability would be adversely affected. We cannot assure you that all of the educational institutions will not be found to be in violation of any requirement regarding the tuition charges. The failure by the educational institutions to comply with applicable laws and regulations could subject them to administrative penalties such as fines, which will adversely affect our business and operation.
The PRC tax authorities may require us to pay additional taxes in connection with our acquisitions of offshore entities that conducted their PRC operations through their affiliates in the PRC.
Our operations and transactions are subject to review by the PRC tax authorities pursuant to relevant PRC laws and regulations. However, these laws, regulations and legal requirements change frequently, and their interpretation and enforcement involve uncertainties. For example, in the case of some of our acquisitions of offshore entities that conducted their PRC operations through their affiliates in the PRC, we cannot assure you that the PRC tax authorities will not require us to pay additional taxes in relation to such acquisitions. In the event that the sellers failed to pay any taxes required under PRC law in connection with these transactions, the PRC tax authorities might require us to pay the tax, together with late-payment interest and penalties.
Restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to utilize our revenues effectively.
Substantially all of our revenues and operating expenses are denominated in Renminbi. The Renminbi is currently convertible under the “current account”, which includes dividends, trade and service-related foreign exchange transactions, but not under the “capital account”, which includes foreign direct investment and loans. Currently, Taiyuan Taiji may purchase foreign exchange for settlement of “current account transactions”, including payment of dividends to us, without the approval of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange. However, we cannot assure you that the relevant PRC governmental authorities will not limit or eliminate our ability to purchase foreign currencies in the future. Since a significant amount of our future revenues will be denominated in Renminbi, any existing and future restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to utilize revenues generated in Renminbi to fund our business activities outside the PRC, if any, or expenditures denominated in foreign currencies. Foreign exchange transactions under the capital account are still subject to limitations and require approvals from, or registration with, the State Administration of Foreign Exchange and other relevant PRC governmental authorities. This could affect Taiyuan Taiji’s ability to obtain foreign exchange through debt or equity financing, including by means of loans or capital contributions from us.
Appreciation or depreciation in the value of the Renminbi relative to the U.S. dollar would affect our financial results reported in U.S. dollar terms without giving effect to any underlying change in our business or results of operations. Since July 2005, the Renminbi is no longer pegged solely to the U.S. dollar. Instead, it is reported to be pegged against a basket of currencies, determined by the PRC, against which it can rise or fall by as much as 0.3% each day. This change in policy has resulted in the gradual increase in the value of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar over time. As of August 31, 2012, US$1.00 = Renminbi 6.3374. The Renminbi may appreciate or depreciate significantly in value against the U.S. dollar in the long term, depending on the fluctuation of the basket of currencies against which it is currently valued or it may be permitted to enter into a full float, which may also result in a significant appreciation or depreciation of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar. Fluctuations in the exchange rate will also affect the relative value of any dividend we issue in the future which will be exchanged into U.S. dollars and earnings from and the value of any U.S. dollar-denominated investments we make in the future.
Very limited hedging transactions are available in the PRC to reduce our exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. To date, we have not entered into any hedging transactions in an effort to reduce our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. We do not intend to enter into any hedging transactions. Even if we may decide to enter into hedging transactions in the future, the availability and effectiveness of these hedges may be limited and we may not be able to successfully hedge our exposure at all. In addition, our currency exchange losses may be magnified by PRC exchange control regulations that restrict our ability to convert Renminbi into foreign currency.
We may be negatively affected by the recent global financial market and economic crisis.
The recent global financial crisis has adversely affected the United States and other world economies. Although the PRC Government has adopted increasingly flexible macroeconomic policies, including an announced fiscal stimulus package, aimed at offsetting the slowdown brought about by the global financial crisis, as the financial crisis has broadened and intensified, the growth of the PRC’s overall economy has been negatively impacted. In addition, the ongoing global financial crisis affecting the banking system and financial markets has resulted in a severe tightening in credit markets, a low level of liquidity in many financial markets and increased volatility in credit and equity markets. If these conditions continue or worsen, our cost of borrowing may increase and it may become more difficult to obtain financing for our operations or investments, which may adversely affect our business operations and implementation of our growth strategy.
If the educational institutions we operate are unable to obtain necessary governmental approvals for their expansion plans, our business and our prospects for growing our business may be adversely affected.
In the PRC, high schools, colleges or universities expansion plans may require governmental approval in advance. For example, the educational institutions we operate may need to obtain governmental approval to add additional educational facilities and to purchase and spread educational product, such as reference books and multi-media study materials. If the educational institutions we operate are unable to obtain the necessary governmental approvals to expand the operations of the educational institutions we operate, our ability to generate additional revenue through the expansion of educational services and facilities will be limited.
Delay or failure in obtaining necessary approvals and building ownership certificates for the buildings of the educational institutions we operate may have an adverse impact on our business and operations.
Our future success substantially depends on our ability to significantly expand the facilities of the educational institutions we operate necessary to accommodate increasing student enrollments. However, the expansion of the facilities of educational institutions we operate may be constrained by the lack of land to develop new buildings or the lack of funds to construct or acquire new buildings, although all required building permits were obtained in connection with construction of the buildings. Building ownership certificates for the newly constructed buildings may not yet have been obtained. Although there is no legal requirement that educational institutions obtain these ownership certificates by a specific date, the failure to obtain these certificates will preclude educational institutions from mortgaging these properties until such certificates are obtained. Future buildings to be constructed may require a certain time period after their completion to obtain the building ownership certificate. Although educational institutions have secured the land use rights over the land occupied by these buildings and have invested in the construction of these buildings, we cannot assure you that educational institutions will obtain these certificates in a timely manner, or at all. Any delay or failure in obtaining necessary approvals to maintain the legitimate use of educational institutions buildings may have an adverse impact on our business and operations.
Compliance with rules and requirements applicable to public companies may cause us to incur increased costs, which may negatively affect our results of operations.
As a U.S. public company, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the SEC, has required changes in corporate governance practices of U.S. public companies. We expect these rules and regulations to increase our legal, accounting and financial compliance costs.
In addition, our administrative staff has been required to perform additional tasks. We have adopted additional internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures, adopted an insider trading policy and bear all of the internal and external costs of preparing and distributing periodic public reports in compliance with our obligations under the securities laws.
Furthermore, changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and related regulations implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission, are creating uncertainty for public companies, increasing legal and financial compliance costs and making some activities more time consuming. We are currently evaluating and monitoring developments with respect to new and proposed rules and cannot predict or estimate the amount of additional costs we may incur or the timing of such costs. These laws, regulations and standards are subject to varying interpretations, in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. This could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices. We intend to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards, and this investment may result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management’s time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. If our efforts to comply with new laws, regulations and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies due to ambiguities related to practice, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us and our business may be harmed. We also expect that being a public company and these new rules and regulations will make it more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain coverage. These factors could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified members of our board of directors, particularly to serve on our audit committee and compensation committee, and qualified executive officers.
We will also incur additional costs associated with our public company reporting requirements. We are currently evaluating and monitoring developments with respect to these new rules, and we cannot predict or estimate the amount of additional costs we may incur or the timing of such costs.
Changes in U.S. generally accepted accounting principles may impact our reported financial results of operations.
Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). A change in accounting standards or practices can have a significant effect on our reported results and may even affect our reporting of transactions completed before the change is effective. New accounting pronouncements and varying interpretations of accounting pronouncements have occurred and are likely to occur in the future. Changes to existing rules or the questioning of current practices may adversely affect our reported financial results or the way we conduct our business.
In June 2009, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Codification 810-10, “Consolidation—Overall” (“ASC 810-10”, previously SFAS 167, “Amendments to FASB Interpretation No. 46(R)”). This accounting standard is effective for our fiscal year beginning January 1, 2010. This accounting standard eliminates exceptions of the previously issued pronouncement related to consolidation of qualifying special purpose entities, contains new criteria for determining the primary beneficiary, and increases the frequency of required reassessments to determine whether a company is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity.
You may face difficulties in protecting your interests because we conduct all of our operations in the PRC and most of our officers reside in the PRC.
We conduct all of our operations in the PRC. All of our officers, except our Chief Financial Officer, reside in and most of the assets of those persons are located in the PRC. As a result, it may be difficult or impossible for you to bring an action against us in the PRC. Even if you are successful in bringing an action of this kind, you still may not be able to enforce a judgment against our assets or the assets of our directors and officers.
Risks Related to our Securities
As a result of the Merger, KL became a subsidiary of ours and since we are subject to the reporting requirements of federal securities laws, this can be expensive and may divert resources from other projects, thus impairing its ability to grow.
As a result of the Merger, KL became a subsidiary of ours and, accordingly, is subject to the information and reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), and other federal securities laws, including compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act”). The costs of preparing and filing annual and quarterly reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC (including reporting of the Merger) and furnishing audited reports to stockholders will cause our expenses to be higher than they would have been if KL had remained privately held and did not consummate the Merger.
It may be time consuming, difficult and costly for us to develop and implement the internal controls and reporting procedures required by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. We will need to hire additional financial reporting, internal controls and other finance personnel in order to develop and implement appropriate internal controls and reporting procedures. If we are unable to comply with the internal controls requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, then we may not be able to obtain the independent accountant certifications required by such act, which may preclude us from keeping our filings with the SEC current and interfere with the ability of investors to trade our securities and for our shares to continue to be quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board or to list on any national securities exchange.
If we fail to establish and maintain an effective system of internal control, we may not be able to report our financial results accurately or to prevent fraud. Any inability to report and file our financial results accurately and timely could harm our reputation and adversely impact the trading price of our common stock.
Effective internal control is necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and prevent fraud. If we cannot provide reliable financial reports or prevent fraud, we may not be able to manage our business as effectively as we would if an effective control environment existed, and our business and reputation with investors may be harmed. As a result, our small size and any current internal control deficiencies may adversely affect our financial condition, results of operation and access to capital. We have not performed an in-depth analysis to determine if historical un-discovered failures of internal controls exist, and may in the future discover areas of our internal control that need improvement.
Public company compliance may make it more difficult to attract and retain officers and directors.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act and rules implemented by the SEC have required changes in corporate governance practices of public companies. As a public company, we expect these rules and regulations to increase our compliance costs in 2012 and beyond and to make certain activities more time consuming and costly. As a public company, we also expect that these rules and regulations may make it more difficult and expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. As a result, it may be more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors or as executive officers, and to maintain insurance at reasonable rates, or at all.
Because we became public by means of a reverse merger, we may not be able to attract the attention of major brokerage firms.
There may be risks associated with us becoming public through a “reverse merger.” Securities analysts of major brokerage firms may not provide coverage of us since there is no incentive to brokerage firms to recommend the purchase of our common stock. No assurance can be given that brokerage firms will, in the future, want to conduct any offerings on behalf of our post-Merger company.
Our stock price may be volatile.
The market price of our common stock is likely to be highly volatile and could fluctuate widely in response to various factors, many of which are beyond our control, including the following:
|
·
|
changes in our industry;
|
|
·
|
competitive pricing pressures;
|
|
·
|
our ability to obtain working capital financing;
|
|
·
|
additions or departures of key personnel;
|
|
·
|
limited “public float” following the Merger, in the hands of a small number of persons whose sales or lack of sales could result in positive or negative pricing pressure on the market price for our common stock;
|
|
·
|
sales of our common stock;
|
|
·
|
our ability to execute our business plan;
|
|
·
|
operating results that fall below expectations;
|
|
·
|
loss of any strategic relationship;
|
|
·
|
regulatory developments;
|
|
·
|
economic and other external factors;
|
|
·
|
period-to-period fluctuations in our financial results; and
|
|
·
|
inability to develop or acquire new or needed technology.
|
In addition, the securities markets have from time to time experienced significant price and volume fluctuations that are unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. These market fluctuations may also materially and adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
We have not paid dividends in the past and do not expect to pay dividends in the future. Any return on investment may be limited to the value of our common stock.
We have never paid cash dividends on our common stock and do not anticipate doing so in the foreseeable future. The payment of dividends on our common stock will depend on earnings, financial condition and other business and economic factors affecting us at such time as our board of directors may consider relevant. If we do not pay dividends, our common stock may be less valuable because a return on your investment will only occur if our stock price appreciates.
Our shares of common stock are very thinly traded, and the price may not reflect our value and there can be no assurance that there will be an active market for our shares of common stock either now or in the future.
Our shares of common stock are very thinly traded, only a small percentage of our common stock is available to be traded and is held by a small number of holders and the price, if traded, may not reflect our actual or perceived value. There can be no assurance that there will be an active market for our shares of common stock either now or in the future. The market liquidity will be dependent on the perception of our operating business, among other things. We will take certain steps including utilizing investor awareness campaigns, press releases, road shows and conferences to increase awareness of our business and any steps that we might take to bring us to the awareness of investors may require we compensate consultants with cash and/or stock. There can be no assurance that there will be any awareness generated or the results of any efforts will result in any impact on our trading volume. Consequently, investors may not be able to liquidate their investment or liquidate it at a price that reflects the value of the business and trading may be at an inflated price relative to the performance of our company due to, among other things, availability of sellers of our shares. If a market should develop, the price may be highly volatile. Because there may be a low price for our shares of common stock, many brokerage firms or clearing firms may not be willing to effect transactions in the securities or accept our shares for deposit in an account. Even if an investor finds a broker willing to effect a transaction in the shares of our common stock, the combination of brokerage commissions, transfer fees, taxes, if any, and any other selling costs may exceed the selling price. Further, many lending institutions will not permit the use of low priced shares of common stock as collateral for any loans.
There is currently a limited liquid trading market for our common stock and we cannot ensure that one will ever develop or be sustained.
To date there has been a limited trading market for our common stock. We cannot predict how liquid the market for our common stock might become. We anticipate having our common stock continue to be quoted for trading on the OTC Bulletin Board, however, we cannot be sure that such quotations will continue. As soon as is practicable, we anticipate applying for listing of our common stock on either the NYSE Amex, The NASDAQ Capital Market or other national securities exchange, assuming that we can satisfy the initial listing standards for such exchange. We currently do not satisfy the initial listing standards, and cannot ensure that we will be able to satisfy such listing standards or that our common stock will be accepted for listing on any such exchange. Should we fail to satisfy the initial listing standards of such exchanges, or our common stock is otherwise rejected for listing and remain listed on the OTC Bulletin Board or suspended from the OTC Bulletin Board, the trading price of our common stock could suffer and the trading market for our common stock may be less liquid and our common stock price may be subject to increased volatility.
Furthermore, for companies whose securities are traded in the OTC Bulletin Board, it is more difficult (1) to obtain accurate quotations, (2) to obtain coverage for significant news events because major wire services generally do not publish press releases about such companies, and (3) to obtain needed capital.
Our common stock may be deemed a “penny stock,” which would make it more difficult for our investors to sell their shares.
Our common stock may be subject to the “penny stock” rules adopted under Section 15(g) of the Exchange Act. The penny stock rules generally apply to companies whose common stock is not listed on The NASDAQ Stock Market or other national securities exchange and trades at less than $5.00 per share, other than companies that have had average revenue of at least $6,000,000 for the last three years or that have tangible net worth of at least $5,000,000 ($2,000,000 if the company has been operating for three or more years). These rules require, among other things, that brokers who trade penny stock to persons other than “established customers” complete certain documentation, make suitability inquiries of investors and provide investors with certain information concerning trading in the security, including a risk disclosure document and quote information under certain circumstances. Many brokers have decided not to trade penny stocks because of the requirements of the penny stock rules and, as a result, the number of broker-dealers willing to act as market makers in such securities is limited. If we remain subject to the penny stock rules for any significant period, it could have an adverse effect on the market, if any, for our securities. If our securities are subject to the penny stock rules, investors will find it more difficult to dispose of our securities.
Offers or availability for sale of a substantial number of shares of our common stock may cause the price of our common stock to decline.
If our stockholders sell substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market, the expiration of any statutory holding period, under Rule 144, it could create a circumstance commonly referred to as an “overhang” and in anticipation of which the market price of our common stock could fall. The existence of an overhang, whether or not sales have occurred or are occurring, also could make more difficult our ability to raise additional financing through the sale of equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and price that we deem reasonable or appropriate.
Because our directors and executive officers are among our largest stockholders, they can exert significant control over our business and affairs and have actual or potential interests that may depart from those of our other stockholders.
Our directors and executive officers will own or control a significant percentage of the common stock following the Merger. Additionally, the holdings of our directors and executive officers may increase in the future upon vesting or other maturation of exercise rights under any of the options or warrants they may hold or in the future be granted or if they otherwise acquire additional shares of our common stock. Following the Merger, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Ren Zhiqing, beneficially owns 20,400,000 shares of our common stock, or a total of approximately 68% of the voting power of all our outstanding shares of stock. The interests of such persons may differ from the interests of our other stockholders. As a result, in addition to their board seats and offices, such persons will have significant influence over and control all corporate actions requiring stockholder approval, irrespective of how the Company’s other stockholders may vote, including the following actions:
|
|
·
|
to elect or defeat the election of our directors;
|
|
|
·
|
to amend or prevent amendment of our Certificate of Incorporation or By-laws;
|
|
|
·
|
to effect or prevent a merger, sale of assets or other corporate transaction; and
|
|
|
·
|
to control the outcome of any other matter submitted to our stockholders for vote.
|
In addition, such persons’ stock ownership may discourage a potential acquirer from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of the Company, which in turn could reduce our stock price or prevent our stockholders from realizing a premium over our stock price.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
All land in the PRC is owned by the government and cannot be sold to any individual or entity. Instead, the government grants or allocates landholders a "land use right," which we sometimes refer to informally as land ownership. There are four methods to acquire land use rights in the PRC: (1) grant of the right to use land; (2) assignment of the right to use land; (3) lease of the right to use land; and (4) allocated land use rights. In comparison with Western common law concepts, granted land use rights are similar to life estates and allocated land use rights are in some ways similar to leaseholds. Granted land use rights are provided by the government in exchange for a grant fee, and carry the rights to pledge, mortgage, lease, and transfer within the term of the grant. Land is granted for a fixed term, generally 70 years for residential use, 50 years for industrial use, and 40 years for commercial and other use. The term is renewable in theory. Unlike the typical case in Western nations, granted land must be used for the specific purpose for which it was granted. Allocated land use rights are generally provided by the government for an indefinite period (usually to state-owned entities) and cannot be pledged, mortgaged, leased, or transferred by the user. Allocated land can be reclaimed by the government at any time. Allocated land use rights may be converted into granted land use rights upon the payment of a grant fee to the government.
Shanxi Taiji holds the certificate of ownership of property of the PRC, which indicates:
|
Certificate No.
|
|
How Held
|
|
Location
|
|
Purpose
|
|
Area (sq. m.)
|
|
Reg. Date
|
|
Shanxi North Campus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bing Govt. Land (2000)
No. 00048
|
|
|
|
18 Longbao Street
Taiyuan, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bing Govt. Land (2000)
No. 00047
|
|
|
|
18 Longbao Street
Taiyuan, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bing Govt. Land (2006)
No. 20196
|
|
|
|
18 Longbao Street
Taiyuan, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bing Govt. Land (2000)
No. 20087
|
|
|
|
40 Double Tower South Road Taiyuan, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jing Kai Govt. Land (2007)
No. 0206005
|
|
|
|
108 State Road south, Yu tai Road, Jinzhong, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jing Kai Govt. Land (2007)
No. 0206004
|
|
|
|
108 State Road south, Yu tai Road, Jinzhong, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jing Kai Govt. Land (2008)
No. 0206010
|
|
|
|
108 State Road south, Yu tai Road, Jinzhong, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jing Kai Govt. Land (2009)
No. 0206002
|
|
|
|
108 State Road south, Yu tai Road, Jinzhong, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jing Kai Govt. Land (2008)
No. 0206011
|
|
|
|
108 State Road south, Yu tai Road, Jinzhong, Shanxi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
China registered (2002)
No. 1437
|
|
|
|
Shanhe Duan, Guanghua St.
Huaying City, Sichuan
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
China registered (2004)
No. 1505
|
|
|
|
Shanhe Duan, Guanghua St.
Huaying City, Sichuan
|
|
For Education & Dormitory
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
From time to time, we may become involved in various lawsuits and legal proceedings which arise in the ordinary course of business. We are currently not a party to any legal proceeding and are not aware of any legal claims that we believe will have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Our common stock has been quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board under the symbol CBLY.OB since July 29, 2010. Prior to July 29, 2010, there was no active market for our common stock. Trading of our common stock commenced on September 28, 2010. As of November 28, 2012, there were 56 holders of record of our common stock according to our transfer agent records.
The following table sets forth the high and low bid prices for our common stock for the periods indicated, as reported by the OTC Bulletin Board. The quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commission, and may not represent actual transactions.
|
Year Ended August 31, 2012
|
|
High Price
|
|
|
Low Price
|
|
1
st
Quarter Ended November 30, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
nd
Quarter Ended February 28, 2012
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
rd
Quarter Ended May 31, 2012
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
th
Quarter Ended August 31, 2012
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended August 31, 2011
|
|
High Price
|
|
|
Low Price
|
|
1
st
Quarter Ended November 30, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
nd
Quarter Ended February 28, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
rd
Quarter Ended May 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
th
Quarter Ended August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The last reported sales price of our common stock on the OTC Bulletin Board on November 28, 2012 was $0.45 per share.
The Securities and Exchange Commission has adopted Rule 15g-9 which establishes the definition of a “penny stock,” for purposes relevant to us, as any equity security that has a market price of less than $5.00 per share or with an exercise price of less than $5.00 per share, subject to certain exceptions. For any transaction involving a penny stock, unless exempt, the rules require: (i) that a broker or dealer approve a person’s account for transactions in penny stocks and (ii) the broker or dealer receive from the investor a written agreement to the transaction, setting forth the identity and quantity of the penny stock to be purchased. In order to approve a person’s account for transactions in penny stocks, the broker or dealer must (i) obtain financial information and investment experience and objectives of the person; and (ii) make a reasonable determination that the transactions in penny stocks are suitable for that person and that person has sufficient knowledge and experience in financial matters to be capable of evaluating the risks of transactions in penny stocks. The broker or dealer must also deliver, prior to any transaction in a penny stock, a disclosure schedule prepared by the Commission relating to the penny stock market, which, in highlight form, (i) sets forth the basis on which the broker or dealer made the suitability determination and (ii) that the broker or dealer received a signed, written agreement from the investor prior to the transaction. Disclosure also has to be made about the risks of investing in penny stocks in both public offerings and in secondary trading, and about commissions payable to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative, current quotations for the securities and the rights and remedies available to an investor in cases of fraud in penny stock transactions. Finally, monthly statements have to be sent disclosing recent price information for the penny stock held in the account and information on the limited market in penny stocks.
Description of Securities
Common Stock
We are authorized to issue 75,000,000 shares of common stock, $0.001 par value per share. As of November 28, 2012 there were 30,069,629 common shares issued and outstanding.
The holders of our common stock have equal ratable rights to dividends from funds legally available if and when declared by the Company’s board of directors and are entitled to share ratably in all of our assets available for distribution to holders of common stock upon liquidation, dissolution or winding up of our affairs. Our common stock does not provide the right to a preemptive, subscription or conversion rights and there are no redemption or sinking fund provisions or rights. Our common stock holders are entitled to one non-cumulative vote per share on all matters on which shareholders may vote.
All shares of common stock now outstanding are fully paid for and non-assessable. Our Articles of Incorporation, Bylaws and the applicable statutes of the State of Nevada for a more complete description of the rights and liabilities of holders of the Company’s securities. All material terms of our common stock have been addressed in this section.
Holders of shares of our common stock do not have cumulative voting rights, which means that the holders of more than 50% of the outstanding shares, voting for the election of directors, can elect all of the directors to be elected, if they so choose, and, in that event, the holders of the remaining shares will not be able to elect any of the Company’s directors.
Preferred Stock
As of November 28, 2012, we are not authorized to issue shares of preferred stock.
Dividends
The Company has not paid any cash dividends to common stock shareholders. The declaration of any future cash dividends is at the discretion of the Company’s board of directors and depends upon the Company’s earnings, if any, the Company’s capital requirements and financial position, the Company’s general economic conditions, and other pertinent conditions. It is the Company’s present intention not to pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future, but rather to reinvest earnings, if any, in the Company’s business operations.
Warrants
As of November 28, 2012, we have no outstanding warrants to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock.
Options
As of November 28, 2012, we have no outstanding options to purchase shares the Company’s common stock.
Transfer Agent
Our transfer agent is Island Stock Transfer, 15500 Roosevelt Boulevard, Suite 301, Clearwater, FL 33760.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
On June 16, 2012, the Company issued 55,101 shares of previously accrued restricted common stock accounted for as stock based compensation including 29,191 shares to its Chief Financial Officer, 2,955 shares each to two of its independent directors, Dora Dong and Jun Zhang, and 20,000 shares to its financial controller.
The above-mentioned securities were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933. The issuance of these shares was exempt from registration, in part pursuant to Regulation S and Regulation D under the Securities Act of 1933 and in part pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
Not applicable.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this document. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements. The words or phrases “would be,” “will allow,” “expect to”, “intends to,” “will likely result,” “are expected to,” “will continue,” “is anticipated,” “estimate,” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Such statements include, among others, those statements concerning our expected financial performance, our corporate strategy and operational plans. Actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements as a result of a number of risks and uncertainties, including, among others: (a) those risks and uncertainties related to general economic conditions in the PRC, including regulatory factors that may affect such economic conditions; (b) whether we are able to manage our planned growth efficiently and operate profitable operations, including whether our management will be able to identify, hire, train, retain, motivate and manage required personnel or that management will be able to successfully manage and exploit existing and potential market opportunities; (c) whether we are able to generate sufficient revenues or obtain financing to sustain and grow our operations; and (d) whether we are able to successfully fulfill our primary requirements for cash which are explained below under “Liquidity and Capital Resources”. Unless otherwise required by applicable law, we do not undertake, and we specifically disclaim any obligation, to update any forward-looking statements to reflect occurrences, developments, unanticipated events or any other circumstances after the date of such statement unless required by law. For additional information regarding these risks and uncertainties, see “Risk Factors”. Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. In addition, our consolidated financial statements and the financial data included in this document reflect the Merger and have been prepared as if our current corporate structure had been in place throughout the relevant periods.
Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations ("MD&A") is designed to provide information that is supplemental to, and should be read together with, the Company’s consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Information in this Item 7 is intended to assist the reader in obtaining an understanding of the consolidated financial statements, the changes in certain key items in those financial statements from year to year, the primary factors that accounted for those changes, and any known trends or uncertainties that the Company is aware of that may have a material effect on the Company’s future performance, as well as how certain accounting principles affect the consolidated financial statements. MD&A includes the following sections:
|
·
|
Highlights and Executive Summary
|
|
·
|
Results of Operations—an analysis of the Company’s consolidated results of operations, for the period presented in the consolidated financial statements
|
|
·
|
Liquidity and Capital Resources—an analysis of the effect of the Company’s operating, financing and investing activities on the Company’s liquidity and capital resources
|
|
·
|
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements—a discussion of such commitments and arrangements
|
|
·
|
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates—a discussion of accounting policies that require significant judgments and estimates
|
Highlights and Executive Summary
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. (the “Company”, “we”, “us” or “our”) is an education company that owns and operates high-quality K-12 private boarding schools in the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”). The Company established school operations in 1998 and currently operates three schools encompassing kindergarten, elementary, middle and high school levels with approximately 14,583 students and 1,876 faculty and staff for the 2012-2011 school year. The Company’s schools are located in Shanxi and Sichuan Provinces and provide students with an innovative and high-quality education with a focus on fluency and cultural skills in both Chinese and English, as well as a strong core curriculum. The schools regularly rank among the top schools in their respective regions for college entrance exam scores and national college entrance rates. The Company’s schools have earned excellent teaching reputations and are recognized for the success of their students and strong faculty. As the PRC experiences rapid industrialization and economic growth, the government is focused on education as a means to increase worker productivity and raise the standard of living. Parents in the PRC’s new middle and upper classes are sending their children to receive private school education to give them an advantage in the PRC’s increasingly competitive workforce. The Company’s sector in education is not subject to corporate income tax, and the Company anticipates its growth will come from both organic growth through increased enrollment and expansion of its business model and teaching methods into new schools, which may be acquired by the Company.
The Company was incorporated in the State of Nevada on March 31, 2009 under the name Designer Export, Inc. On June 30, 2010, the Company changed its name to China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc.
Results of Operations
Operation Results for the Years Ended August 31, 2012 and 2011
Revenues
During the year ended August 31, 2012, we had total revenues of $42,200,354, an increase of $16,780,838 or 66.0% as compared to total revenues of $25,419,516 during the year ended August 31, 2011. The revenue growth was primarily attributable to the acquisition of our third school campus – the Shanxi South School, which led to an increase in enrollment of 4,718 students for the 2011- 2012 school year from approximately 9,200 students to 13,918 students. We also increased our average full-fare tuition by $226 or 7.2% to $3,352 per student for the 2011 – 2012 school year from $3,126 per student for the 2010 – 2011 school year. The school year typically runs from September 1 through August 31 and corresponds to the fiscal year end on August 31. The Company recognizes prepaid school fees (including tuition, room & board and other school fees, herein after "School Fees") evenly over the twelve month period.
Cost of Revenue
During the year ended August 31, 2012, our cost of revenue was $23,839,738 (56.5% of revenues), an increase of $13,667,132 or 134.4% as compared to cost of revenue of $10,172,606 (40.0% of revenues) during the year ended August 31, 2011. The increase in cost of revenue was primarily the result of an increase in costs in connection with the acquisition of our third campus and the increase in enrollment of approximately 4,681 students. The third campus acquired on August 31, 2011 was previously underutilized and our overall capacity utilization rate decreased from over 90% for our two schools during the year ended August 31, 2011 to approximately 66% for the three schools during the year ended August 31, 2012. The Company continues to work toward increasing the capacity utilization of all three schools, which lowers the fixed costs per student based on higher enrollment. The increased costs for the year ended August 31, 2012 was from increased teacher and staff salaries to support the increased enrollment, as well as $3.6 million in depreciation and amortization expense allocated to cost of revenue primarily associated with the approximately $108.2 million acquisition of the third campus.
General and Administrative Expenses
During the year ended August 31, 2012, general and administrative expenses was $3,140,188, an increase of $1,394,999 or 79.9% as compared to $1,745,189 for the year ended August 31, 2011. General and administrative expense increased due to the increase in administrative overhead expenses, costs of operating as a public company and $1.0 million in depreciation and amortization expense allocated to general and administrative expenses, all primarily associated with the newly acquired third campus.
Interest Expense
Interest expense was $5,631,405 for the year ended August 31, 2012, an increase of $5,535,834 or 5,792.4% as compared to $95,571 for the year ended August 31, 2011. The increase in interest expense was a result of the financing for the acquisition of our third school, comprising $2,246,955 in interest on a bank loan of RMB 100,000,000 (approximately $15.9 million) obtained by the Company in August 2011 and $3,384,450 on the accretion of the implied interest in the long-term and short-term portion of the payable - acquisition resulting from the fair value discount recorded as interest expense based on the payment plan to the seller.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (“EBITDA”)
EBITDA was $19,707,649 for the year ended August 31, 2012, an increase of $5,146,908 or 35.3% compared to $14,560,741 for the year ended August 31, 2011. The increase was primarily attributable to the increase in revenues as a result of the increase in total enrollment of 4,681 students for the year ended August 31, 2012.
Net Income
As a result of the factors described above, net income attributable to shareholders was $9,645,628 for the year ended August 31, 2012, a decrease of $3,787,126 or 28.2% as compared to $13,432,754 for the year ended August 31, 2011. The decrease between the periods resulted primarily from the increase in interest expense, depreciation and amortization associated with the acquisition of our third school. Total interest, depreciation and amortization, primarily associated with the acqusition of the third school, was $10,062,021.
Basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”) decreased $0.13 to $0.32 per share for the year ended August 31, 2012 from $0.45 per share for the year ended August 31, 2011 due to the decrease in net income.
Comprehensive Income
The functional currency of the Company is Chinese Renminbi (“RMB”), but we report our results in U.S. Dollars. The conversion of our accounts from RMB to U.S. Dollars results in translation adjustments. As a result, we achieved a currency translation adjustment gain of $252,324 during the year ended August 31, 2012, a decrease of $1,447,493 or 85.2% as compared to a gain of $1,699,817 during the year ended August 31, 2011. Our comprehensive income was $9,897,952 for the year ended August 31, 2012, a decrease of $5,234,619 or 34.6% as compared to $15,132,571 for the year ended August 31, 2011.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of August 31, 2012, our cash and cash equivalents were $30,410,983. Our principle source of liquidity comes from deferred School Fees from students who attend our schools. The Company collects tuition in advance of the school year and therefore has no accounts receivable. We also use our other current assets balance of $4,078,038 to finance school related activities as advances or prepayment for the purchase of school and boarding related materials for the day-to-day operations of the school. Based on our current operating plan, we believe that our existing resources, including cash flow generated from operations as well as available bank loans, will be sufficient to meet our working capital requirement for our current operations and any prepaid tuition obligations. In August 2012 we repaid our one-year bank loan and replaced it with an $11,045,539 three-year bank loan at a 7.38% interest rate. The Company also has $4,550,762 in related party debt from its Chairman, which is non-interest bearing and may be renewed at the Company’s option. The Company’s installment payment of $18,900,822 for the acquisition of the Shanxi South Campus (Short-term payable acqusition) was due on August 31, 2012, but was paid from our cash balance on September 3, 2012. The Company has collected substantially all of its prepaid tuition for the 2012 – 2013 school year and recorded it as a liability under deferred school fees of $45,902,425. Based on our profit margin and available debt sources, we believe we have sufficient cash to operate our business. We are also considering alternatives for longer-term outside financing of debt or equity based on the asset strength of our balance sheet. In order to fully implement our business plan and continue our growth, however, we will require additional capital either from our shareholders or from outside sources, although there is no assurance that we will be able to obtain additional capital at suitable terms if and when it is needed.
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Cash provided by operating activities increased $10,557,558 or 67.5% to $26,205,622 for the year ended August 31, 2012 compared to $15,648,064 provided by operating activities for the year ended August 31, 2011. The increase was primarily attributable to the increase of $3,441,955 in deferred school fees and the decrease of $5,805,743 in operating advances accounted for under other current assets, as well as the addition of non-cash items of $4,487,221 in depreciation and amortization.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Cash used in investing activities decreased $18,511,437 or 95.1% to $963,997 for the year ended August 31, 2012 as compared to $19,475,434 used in the year ended August 31, 2011. The decrease in cash used in investing activities resulted from the decrease from the business combination associated with the acquisition of the Shanxi South Campus.
Cash Flow from Financing Activities
Cash used in financing activities increased $18,425,840 or 218.9% to $10,004,901 for the years ended August 31, 2012 as compared to $8,420,939 provided by the year ended August 31, 2011. The increase in cash used in financing activities resulted from paying off the short-term bank loan, paying down related party payables and the seller loan for the acquisition of the Shanxi South School.
The following is a summary of our cash flows provided by (used in) operating, investing, and financing activities during the periods indicated:
|
|
|
Years Ended
August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited)
|
|
Cash at beginning of period
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by operating activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plan of Operations
As described herein, the Company completed the Equity Transfer Agreement dated August 31, 2011 for the acquisition of the Shanxi South Campus, formerly known as the Shanxi Rising School. We expect to continue to expand our enrollment base utilizing the excess capacity at our existing schools in addition to marketing and expanding enrollment at the Shanxi South Campus. Our strategy is to leverage our strong academic reputation to develop additional business. We are also actively seeking opportunities to expand our business that we consider accretive to earnings. We intend to grow our business model through the acquisition of existing schools to increase our total enrollment. In order to fully implement our business plan and continue our growth, however, we will require additional capital either from our shareholders or from outside sources, although there is no assurance that we will be able to obtain additional capital at suitable terms if and when it is needed.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements, financings, or other relationships that are currently material or reasonably likely to be material to our financial position or results of operations.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The discussion and analysis of the Company’s results of operations and liquidity and capital resources are based on the Company’s consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. In connection with the preparation of consolidated financial statements, the Company is required to make assumptions and estimates about future events, and apply judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses, and the related disclosures. The assumptions, estimates and judgments included within these estimates are based on historical experience, current trends and other factors the Company believes to be relevant at the time the consolidated financial statements were prepared. On a regular basis, the accounting policies, assumptions, estimates and judgments are reviewed to ensure that the consolidated financial statements are presented fairly and in accordance with GAAP. However, because future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty, actual results could differ from the assumptions and estimates, and such differences could be material.
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Significant estimates and assumptions are used for, but are not limited to: (1) asset impairments (2) revenue recognition. Future events and their effects cannot be predicted with certainty, and accordingly, accounting estimates require the exercise of judgment. The accounting estimates used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements will change as new events occur, as more experience is acquired, as additional information is obtained and as the Company’s operating environment changes. The Company evaluates and updates these assumptions and estimates on an ongoing basis and may employ outside experts to assist with these evaluations. Actual results could differ from the estimates that have been used.
Significant accounting policies are discussed in Note 3,
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,
to the accompanying consolidated financial statements. The Company believes the following accounting policies are the most critical to aid in fully understanding and evaluating the Company’s reported financial results, as they require management to make difficult, subjective or complex judgments, and to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain.
Impairment analysis for long-lived assets and intangible assets
The Company’s long-lived assets and other assets (consisting of property and equipment and purchased intangible assets) are reviewed for impairment in accordance with the guidance of the FASB Topic ASC 360, “
Property, Plant, and Equipment”,
and FASB ASC Topic 205 “
Presentation of Financial Statements
”. The Company tests for impairment losses on long-lived assets used in operations whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of an asset to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such asset is considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its fair value. Impairment evaluations involve management’s estimates on asset useful lives and future cash flows. Actual useful lives and cash flows could be different from those estimated by management which could have a material effect on our reporting results and financial positions. Fair value is determined through various valuation techniques including discounted cash flow models, quoted market values and third-party independent appraisals, as considered necessary. Through August 31, 2012, the Company had not experienced impairment losses on its long-lived assets.
Revenue Recognition
In accordance with the Securities and Exchange Commission’s (“SEC”) Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) Topic 13,
Revenue Recognition
, the Company recognizes revenues when it is realized or realizable and earned. The Company records revenues when the following four fundamental criteria under SAB 104 are met: (i) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, (ii) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered, (iii) the price to the customer is fixed or determinable, and (iv) collection of the resulting receivable is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are satisfied are recorded as prepaid tuition.
Revenues consist primarily of tuition and fees derived from providing meals and housing for students living on campus. Revenues from tuition and fees are recognized pro-rata (on a straight-line basis) over the relevant period attended by the student of the applicable grade or program. The school year runs September 1 through August 31 and prepaid tuition is recognized over the twelve-month period. If a student withdraws from a course or program within three months after the school year starts, the paid but unearned portion of the student’s tuition is 67% refunded. If a student withdraws after the first three months in a school year, no tuition will be refunded. As a result, the Company has recorded prepaid tuition as a current liability on the consolidated balance sheet in the event a student withdraws from school and the Company has to return a portion of the prepaid tuition. In past years there were minimal students who withdrew from a course or program before the end of a school year.
The Company normally receives prepaid tuition and fees from students at their initial admission or before the start of the school year on September 1. Some students will benefit from a discount of fees if they prepay tuition for two to three years of school term. Prepaid tuition is the portion of payments received but not earned and is reflected as a current liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as such amounts are expected to be earned, but may be refundable within the next year.
Management has discussed the development and selection of these critical accounting policies with the Board of Directors and the Board has reviewed the disclosures presented above relating to them.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Not applicable.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
Russell E. Anderson, CPA
Russ Bradshaw, CPA
William R. Denney, CPA
Sandra Chen, CPA
5296 S. Commerce Dr
Suite 300
Salt Lake City, Utah 84107
USA
(T) 801.281.4700
(F) 801.281.4701
Suite A, 5/F
Max Share Center
373 Kings Road
North Point
Hong Kong
(T) 852.21.555.333
(F) 852.21.165.222
abcpas.net
|
|
|
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To The Board of Directors and Stockholders of
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group, Inc.
Taiyuan Shanxi, China
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of China Bilingual Technology & Education Group, Inc. (the Company) as of August 31, 2012 and 2011, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, cash flows, and changes in stockholders’ equity for the year ended August 31, 2012, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States of America). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. The company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of China Bilingual Technology & Education Group, Inc. as of August 31, 2012 and 2011, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended August 31, 2012, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
s/Anderson Bradshaw PLLC
Salt Lake City, Utah
November 29, 2012
|
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 31,
2012
|
|
|
August 31,
2011
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deposit paid for long-term assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term payable-acquisition
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Home purchase down payment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term payable-acquisition
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock, $0.001par value; 75,000,000 shares authorized; 30,069,629, 30,014,528 issued and outstanding as of August 31, 2012 and 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional paid in capital
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes to these consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these balance sheets.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
|
For the Years Ended
August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited )
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42,200,354
|
|
|
|
25,419,516
|
|
|
|
|
|
23,839,738
|
|
|
|
10,172,606
|
|
|
|
|
|
18,360,616
|
|
|
|
15,246,910
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and Administrative Expenses
|
|
|
3,140,188
|
|
|
|
1,745,189
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,140,188
|
|
|
|
1,745,189
|
|
|
|
|
|
15,220,428
|
|
|
|
13,501,721
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56,605
|
|
|
|
26,604
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5,631,405
|
)
|
|
|
(95,571
|
)
|
NET INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES
|
|
$
|
9,645,628
|
|
|
$
|
13,432,754
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
9,645,628
|
|
|
$
|
13,432,754
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings per Common Share:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.32
|
|
|
$
|
0.45
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
0.32
|
|
|
$
|
0.45
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30,094,205
|
|
|
|
30,010,932
|
|
|
|
|
|
30,094,205
|
|
|
|
30,010,932
|
|
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these statements.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
|
For the Eight Months Ended August 31,2011
|
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REVENUES
|
|
$
|
17,297,051
|
|
|
$
|
24,367,395
|
|
|
COST OF REVENUES
|
|
|
6,558,876
|
|
|
|
10,841,190
|
|
|
GROSS PROFIT
|
|
|
10,738,175
|
|
|
|
13,526,205
|
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and Administrative Expenses
|
|
|
1,214,060
|
|
|
|
1,593,386
|
|
|
TOTAL OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
1,214,060
|
|
|
|
1,593,386
|
|
|
INCOME FROM OPERATIONS
|
|
|
9,524,115
|
|
|
|
11,932,819
|
|
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Income
|
|
|
15,516
|
|
|
|
33,262
|
|
|
Interest Expense
|
|
|
(95,571
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
NET INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES
|
|
|
9,444,060
|
|
|
|
11,966,081
|
|
|
INCOME TAX EXPENSE
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
NET INCOME
|
|
$
|
9,444,060
|
|
|
$
|
11,966,081
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings per Common Share:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic
|
|
$
|
0.31
|
|
|
$
|
0.43
|
|
|
Diluted
|
|
$
|
0.31
|
|
|
$
|
0.43
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic
|
|
|
30,008,014
|
|
|
|
28,044,698
|
|
|
Diluted
|
|
|
30,008,014
|
|
|
|
28,044,698
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these statements.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
|
|
|
|
For the Years Ended
August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited )
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation, net of tax
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these statements.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
|
|
|
For the Eight Months Ended August 31,2011
|
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCOME
|
|
$
|
9,444,060
|
|
|
$
|
11,966,081
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation, net of tax
|
|
|
1,432,623
|
|
|
|
801,583
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
|
$
|
10,876,683
|
|
|
$
|
12,767,664
|
|
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these statements.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Stockholders' Equity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
Paid-In
|
|
|
Comprehensive
|
|
|
Retained
|
|
|
Stockholders'
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
|
Income
|
|
|
Earnings
|
|
|
Equity (Deficit)
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes to these consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these balance sheets.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In US Dollars)
|
|
|
For The Years
Ended August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unaudited
|
|
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation of property and equipment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of land use rights
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjustments in net cash (used in) provided by operating activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deposits - long term assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advances to related parties receivables
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payments on acquisition payables
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Repayments) of related party loans payables
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Repayments) short term debt
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non cash investing and financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term payable – acquisition
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term payable – acquisition
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deposit-long-term asset transfer to fixed asset
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these statements.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In US Dollars)
|
|
|
For the
Eight
Months Ended
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
For the
Year Ended
December 31, 2010
|
|
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
9,444,060
|
|
|
$
|
11,966,081
|
|
Depreciation of property and equipment
|
|
|
651,674
|
|
|
|
965,795
|
|
Amortization of land use rights
|
|
|
102,434
|
|
|
|
148,637
|
|
|
|
|
|
105,449
|
|
|
|
18,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjustments in net cash (used in) provided by operating activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2,515,705
|
)
|
|
|
(845,830
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
108,421
|
|
|
|
(19,948
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
(90,525
|
)
|
|
|
(94,450
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
(16,873
|
)
|
|
|
126,057
|
|
|
|
|
|
(64,765
|
)
|
|
|
(234,874
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
(347,269
|
)
|
|
|
(1,076,964
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
9,139,176
|
|
|
|
(1,712,385
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
23,168
|
|
|
|
146,457
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
|
|
|
16,539,245
|
|
|
|
9,386,576
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deposits - long term assets
|
|
|
(18,389
|
)
|
|
|
(8,618,441
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
(225,055
|
)
|
|
|
(191,953
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
(16,021,106
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
Proceeds from related parties receivables
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
3,062,969
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
|
|
(16,264,550
|
)
|
|
|
(5,747,425
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repayments from related party loans
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(1,215,691
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
8,420,939
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities
|
|
|
8,420,939
|
|
|
|
(1,215,691
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
|
|
|
1,081,677
|
|
|
|
122,666
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
9,777,311
|
|
|
|
2,546,126
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year
|
|
|
5,313,210
|
|
|
|
2,767,084
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of year
|
|
$
|
15,090,521
|
|
|
$
|
5,313,210
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
95,571
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
Non cash investing and financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
7,842,522
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
15,685,044
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
Short-term payable – acquisition
|
|
$
|
22,560,426
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
Long-term payable – acquisition
|
|
$
|
26,602,306
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
Deposit paid for long-term assets
|
|
$
|
(8,782,894
|
)
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these statements.
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the Years Ended August 31, 2012 and 2011
NOTE 1 -NATURE OF BUSINESS
Description of Business
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. (the “Company”), is an education company that owns and operates high-quality K-12 private boarding schools in China. The Company established school operations in 1998 and currently operates three schools encompassing kindergarten, elementary, middle and high school levels. The Company’s schools are located in Shanxi and Sichuan Provinces and focus on fluency and cultural skills in both Chinese and English, as well as the PRC core curriculum. The Company’s sector in education is not subject to corporate income tax in the PRC.
Control by Principal Shareholders
The Company’s directors, executive officers and their affiliates or related parties, own beneficially and in the aggregate, the majority of the voting power of the outstanding shares of the common stock of the Company. Accordingly, the directors, executive officers and their affiliates, if they voted their shares uniformly, would have the ability to control the approval of most corporate actions, including increasing the authorized capital stock of the Company and the dissolution, merger or sale of the Company's assets or business.
Financial Statements Presented
The consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with the accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”).
The Company was incorporated in the State of Nevada on March 31, 2009 under the name Designer Export, Inc. On June 30, 2010, the Company changed its name to China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc.
On June 30, 2010, the Company entered into a Share Exchange Agreement (the “Agreement”) with Kahibah Limited (“KL”), a British Virgin Islands (“BVI”) corporation and its shareholders. According to this Agreement, the Company acquired all the issued and outstanding shares of KL. The Company issued 26,100,076 shares of its common stock, after giving effect to the cancellation of 7,748,343 shares on June 30, 2010, to KL’s shareholders in exchange for 100% of the shares of KL. After the closing of the transaction, the Company had a total of 30,000,005 shares of common stock issued and outstanding, with KL’s shareholders owning 87% of the total issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock, and the balance held by those who held shares of the Company’s common stock prior to the closing of the exchange. This transaction resulted in KL’s shareholders obtaining a majority voting interest in the Company. All shares are shown effective of a 2.582781 forward stock split as of July 14, 2010.
The acquisition of KL and the operations of its subsidiaries were accounted for as a reverse merger, whereby KL is the continuing entity for financial reporting purposes and is deemed, for accounting purposes, to be the acquirer of the Company. In accordance with the applicable accounting guidance for accounting for the business combination as a reverse merger, KL is deemed to have undergone a recapitalization, whereby KL is deemed to have issued common stock to the Company’s common equity holders. Accordingly, although the Company, as KL’s parent company, was deemed to have legally acquired KL, in accordance with the applicable accounting guidance for accounting for the transaction as a reverse merger and re-capitalization, KL is the surviving entity for accounting purposes and its assets and liabilities are recorded at their historical carrying amounts with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded as a result of the accounting merger with the Company.
As part of the acquisition, the Company changed its name to China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. Share and per share amounts stated have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the acquisition. The accompanying financial statements present the historical financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of KL and its operating subsidiaries prior to the recapitalization.
The historical consolidated financial statements of the Company are those of KL, and of the consolidated entities. The consolidated financial statements of the Company presented for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010 include the financial statements of China Bilingual, KL, KL’s subsidiary Taiyuan Taiji Industry Development co., Ltd. (“Taiyuan Taiji”), a wholly-foreign owned enterprise (“WFOE”) under the laws of the Peoples Republic of China (“PRC”), which owns 95% of the registered capital of Shanxi Taiji Industry Development Co., Ltd. (“Shanxi Taiji”), an equity joint venture company organized under the laws of the PRC. The remaining 5% ownership of Shanxi Taiji is owned by Ms. Ren Baiv, the sister of the Company's Chairman, Mr. Ren Ziging. The 5% ownership is held by Ms. Ren Baiv on behalf of Taiynan Taiji in accordance with local Chinese regulations, therefor no non-controlling interest is recognized. Shanxi Taiji owns all of the registered capital of Shanxi Modern Bilingual School (“Shanxi North Campus”) and Sichuan Guang’an Experimental High School (“Sichuan Guang’an School”), both private non-enterprise entities incorporated under the laws of the PRC, collectively the “Subsidiaries.”
Since the ownership of KL and its Subsidiaries was substantially the same, the merger with each was accounted for as a transfer of equity interests between entities under common control, whereby the acquirer recognized the assets and liabilities of each Subsidiary transferred at their carrying amounts. The reorganization was treated similar to the pooling of interest method with carry over basis. Accordingly, the financial statements for KL and its Subsidiaries have been combined for all periods presented, similar to a pooling of interest. The reorganization of entities under common control was retrospectively applied to the financial statements of all prior periods when the financial statements are issued for a period that includes the date the transaction occurred. Intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated in consolidations.
On August 31, 2011, the Company’s entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement and purchased all of the outstanding equity of Shanxi Rising Education Investment Company Limited (the “Investment Company”) from the equity holders (the “Sellers”) for a total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 (approximately $108,226,806). The net present value of the total fair value consideration transferred equals RMB 650,000,000 (approximately $102,565,721), of which RMB 370,217,933 (approximately $55,444,697) has been paid. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement the balance of the purchase price is to be paid over three years in three scheduled payments as follows: (See Note 20 – Business Combination for additional details on the Equity Transfer Agreement.)
|
|
1)
|
RMB 119,782,067 (approximately $18,900,822) to be paid by August 31, 2012, but was paid on September 3, 2012
|
|
|
2)
|
RMB 100,000,000 (or RMB 87,589,800, approximately $13,821,094, net of discount) by August 31, 2013, and
|
|
|
3)
|
RMB 100,000,000 (or RMB 93,849,000, approximately $14,808,754, net of discount) by August 31, 2014.
|
The net present value of the payments is discounted at the Company’s then current financing interest rate of 6.84%.
The Investment Company, a limited liability company established under the laws of the PRC, is an education company that owns and operates a K-12 private boarding school in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province of the PRC, encompassing kindergarten, primary and secondary education. The Investment Company was established in 2001 and it has share capital of RMB 70,000,000. It is the parent company of Shanxi Rising School (the "Rising School"), founded 2002, which currently serves over 5,400 students from its location in Shanxi Province, PRC. The Rising School is now known by the Company as the “Shanxi South Campus.”
The acquisition of the Investment Company has been accounted for as a business combination under Accounting Standards Codification Topic 805,
Business Combinations
(“ASC 805”). The total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 has been allocated to the net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values as of August 31, 2011. As of the balance sheet date, August 31, 2011, the exchange rate to the US Dollar was RMB 6.3755.
Prior to closing the Equity Transfer Agreement, the Company became involved in the operations of the Shanxi South Campus in the spring of 2011. With the consent of the Investment Company, the Company assisted in the operations, accounting and promotion of the school to attract more and better students for the 2011-2012 school year. Some of these responsibilities included collecting prepaid tuition, room & board and other school fees (“School Fees”) in advance of the school year, which combined with better operations, higher tuition rates and an increase in enrollment led to an increase in deferred revenue at August 31, 2011. The Company’s involvement at the Shanxi South Campus was under the direction of Investment Company management until it assumed control of the Investment Company on August 31, 2011, in accordance with the Equity Transfer Agreement.
For the purpose of preparing the consolidated financial statement, the total purchase price is allocated to the Company’s net tangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of August 31, 2011.
The adjustments record the purchase price allocation entries as of August 31, 2011, including allocation of fair values of the associated tangible assets, intangible assets and acquired liabilities, to eliminate the Company's historical equity balances and to record the estimated use of cash to fund the cash portion of the acquisition. The adjustments also include certain decreases in intercompany balances eliminated in consolidation.
Accordingly, t
he fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed may be materially impacted by the results of the Company’s on-going operations after the date of the Equity Transfer Agreement.
Principles of Consolidation
The condensed consolidated financial statements include the accounts of China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and the following subsidiaries:
|
Subsidiaries
|
State and Countries Registered In
|
|
% Ownership
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
Taiyuan Taiji Industry Development Co., Ltd.
|
People’s Republic of China
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
Shanxi Taiji Industrial Development Co., Ltd.(i)
|
People’s Republic of China
|
|
|
95
|
%
|
Shanxi Modern Bilingual School (ii)
|
People’s Republic of China
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
Sichuan Guang’an Experimental High School (iii)
|
People’s Republic of China
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
Shanxi Rising Education Investment Company Ltd. (iv)
|
People’s Republic of China
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
|
People’s Republic of China
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
(i) Shanxi Taiji Industrial Development Co., Ltd. was incorporated as a limited liability company on July 25, 1997 under PRC law. It is currently 95% owned by Taiyuan Taiji and 5% owned by Ms. Ren Baiv. On November 25, 2009, KL entered into a share exchange agreement to sell the remaining 5% ownership to Ms. Ren Baiv. Ms. Ren Baiv is the sister of Mr. Ren Zhiqing, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. At December 31, 2010 Ms. Ren Baiv paid 1 million Renminbi (“RMB”) as part of the capital contribution. The 5% ownership is held by Ms. Ren Baiv on behalf of the Taiyuan Taiji in accordance with local Chinese regulations, therefore no non-controlling interest is recognized. Shanxi Taiji is an equity joint venture under the laws of the PRC. The Shanxi North Campus, Modern Bilingual School and Sichuan Guang’an Experimental High School (the “Schools”) hold the requisite governmental licenses to provide private educational services within their province in China. Each province sets its own licensing criteria and duration following the general guidelines established by the national government for education standards.
(ii) Shanxi Modern Bilingual School (the “Shanxi North School”) was established in 1998 by Shanxi Taiji. It operates as a private K-12 boarding school on a 38 acre campus in Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province. The Shanxi School holds a three year provincial license to be renewed May, 2013.
(iii) Sichuan Guang’an Experimental High School (the “Sichuan Guang’an School”) was established in 2002 by Shanxi Taiji. It operates as a private K-12 boarding school on a 23 acre campus in Guang’an, Sichuan Province. The Sichuan Guang'an School holds a four year provincial license currently submitted for renewal.
(iv) Shanxi Rising Education Investment Company Ltd. (the “Investment Company”) was established in 2001 to own and operate private boarding schools in the PRC. The Investment Company has share capital of RMB 70,000,000. It is the parent company of one school, the Shanxi Rising School, which was acquired by the Company on August 31, 2011. The Investment Company has no operations other than its ownership of the Shanxi Rising School.
(v) Shanxi Rising School (the “Shanxi South School”) was established in 2002 by the Investment Company as a private boarding school encompassing kindergarten, primary and secondary education located in the Shanxi Province of the PRC. The school has been assimilated in the operation of the Company and re-branded as the Shanxi South School operating as a private K-12 boarding school on an 82 acre campus comprised of over 2.3 million square feet of facilities, including 18 dormitories with capacity for 10,000 students, academic classrooms, gymnasium, theatre, natatorium, cafeteria and other administrative and academic buildings. The Shanxi South School holds a four year provincial license to be renewed April 2015.
All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
NOTE 2 –
USE OF ESTIMATES
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting periods. Measurement, estimates and assumptions are used for, but not limited to, the selection of the useful lives of property and equipment, impairment of long-lived assets, fair values and revenue recognition. Management makes these estimates using the best information available at the time the estimates are made; however, actual results, when ultimately realized, could differ from those estimates. The current economic environment has increased the degree of uncertainty inherent in these estimates and assumptions.
NOTE 3 –
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
This summary of significant accounting policies of the Company is presented to assist in understanding the Company’s consolidated financial statements. The consolidated financial statements and notes are representations of the Company’s management, which is responsible for their integrity and objectivity. These accounting policies conform to US GAAP and have been consistently applied in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) established the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 105-10 (formerly Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 168,
The FASB Accounting Standards Codification and Hierarchy of Generally Accepted
Accounting Principles, a replacement of ASB
ASC 105-10 establishes the FASB ASC as the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied in preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”). The adoption of this standard had no impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
(a) Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company applies the provisions of accounting guidance, FASB ASC Topic 820 that requires all entities to disclose the fair value of financial instruments, both assets and liabilities recognized and not recognized on the balance sheet, for which it is practicable to estimate fair value, and defines fair value of a financial instrument as the amount at which the instrument could be exchanged in a current transaction between willing parties. As of August 31, 2012 and 2011, the fair value of cash and cash equivalents, other receivables, accounts payable, short term bank loans, and other payables approximated carrying value due to the short maturity of the instruments, quoted market prices or interest rates which fluctuate with market rates except for related party debt or receivables for which it is not practicable to estimate fair value.
Fair Value Measurements
Effective April 1, 2009, the FASB ASC Topic 820,
Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure
, requires disclosures about fair value of financial instruments in quarterly reports as well as in annual reports.
The FASB ASC Topic 820 clarifies the definition of fair value for financial reporting, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and requires additional disclosures about the use of fair value measurements.
Various inputs are considered when determining the fair value of the Company’s financial instruments. The inputs or methodologies used for valuing securities are not necessarily an indication of the risk associated with investing in these securities. These inputs are summarized in the three broad levels listed below:
Level 1 – observable market inputs that are unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2 – other significant observable inputs (including quoted prices for similar securities, interest rates, credit risks, etc.).
Level 3 – significant unobservable inputs (including the Company’s own assumptions in determining the fair market value of financial instruments).
The Company’s adoption of FASB ASC Topic 820 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
The carrying value of financial assets and liabilities recorded at fair value is measured on a recurring or nonrecurring basis. Financial assets and liabilities measured on a nonrecurring basis are those that are adjusted to fair value when a significant event occurs. The Company had no financial assets or liabilities carried and measured on a nonrecurring basis during the reporting periods. Financial assets and liabilities measured on a recurring basis are those that are adjusted to fair value each time a financial statement is prepared. The Company had no financial assets and/or liabilities carried at fair value on a recurring basis at August 31, 2012 and 2011.
The availability of inputs observable in the market varies from instrument to instrument and depends on a variety of factors including the type of instrument, whether the instrument is actively traded, and other characteristics particular to the transaction. For many financial instruments, pricing inputs are readily observable in the market, the valuation methodology used is widely accepted by market participants, and the valuation does not require significant management discretion. For other financial instruments, pricing inputs are less observable in the market and may require management judgment.
(b) Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the consolidated statements of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. There are no restrictions to cash at August 31, 2012. A substantial amount of the Company’s cash is held in bank accounts in the PRC and is not protected by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) insurance or any other similar insurance. Given the current economic environment and the financial conditions of the banking industry there is a risk that deposits may not be readily available. Cash held in the PRC amounted to $30,408,830 and $15,088,156 at August 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The PRC places limitations on expatriating cash out of the country, which may limit the Company’s ability to pay dividends.
(c) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company’s long-lived assets and other assets (consisting of property and equipment and purchased land use rights) are reviewed for impairment in accordance with the guidance of the FASB ASC Topic 360-10,
Property, Plant, and Equipment
, and FASB ASC Topic 205,
Presentation of Financial Statements
. The Company tests for impairment losses on long-lived assets used in operations whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of an asset to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such asset is considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its fair value. Impairment evaluations involve management’s estimates on asset useful lives and future cash flows. Actual useful lives and cash flows could be different from those estimated by management which could have a material effect on our reporting results and financial position. Fair value is determined through various valuation techniques including discounted cash flow models, quoted market values and third-party independent appraisals, as considered necessary. Through August 31, 2012, the Company had not experienced impairment losses on its long-lived assets. However, there can be no assurances that demand for the Company’s services will continue, which could result in an impairment of long-lived assets in the future.
(d) Income taxes
On March 16, 2007, the PRC National People’s Congress passed the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law (“New EIT Law”) which became effective on January 1, 2008. Pursuant to the New EIT Law, a unified enterprise income tax rate of 25% and unified tax deduction standards will be applied consistently to both domestic-invested enterprises and foreign-invested enterprises.
Shanxi Taiji, Taiyuan Taiji and the Investment Company are taxed pursuant to the New EIT Law with a unified enterprise income tax rate of 25%. Shanxi Taiji, Taiyuan Taiji and the Investment Company did not pay any income taxes during the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and for the year ended December 31, 2010 due to net losses experienced in the past reporting periods. The three entities may apply the past periods’ net operating losses to futures years’ profits in order to reduce tax liability. Since Shanxi Taiji, Taiyuan Taiji and Investment Company have minimal business operations, the three entities are unlikely to have profits in future periods. As a result, all deferred tax assets and liabilities are deminimus, and management would have a 100% valuation allowance for all deferred tax assets.
The Company has three subsidiaries registered as private schools (the “school-subsidiaries”), which are not subject to income taxes determined in accordance with the Law for Promoting Private Education (2003) and school-subsidiaries registered as private schools not requiring reasonable returns (similar to a not-for-profit entity) are treated as public schools and are generally not subject to enterprise income taxes. Therefore, the school-subsidiaries are tax exempt, including Shanxi North Campus, Shanxi South Campus and Sichuan Guangan School.
Kahibah Limited is exempt from income tax on all sources of income pursuant to the tax law in the British Virgin Islands. However, pursuant and subsequent to the reverse merger, the parent company in the U.S. may pay tax in future years.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred taxes of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. Deferred income tax expense represents the change during the period in the deferred tax assets and liabilities. The components of the deferred tax assets and liabilities are individually classified as current or non-current based on their characteristics. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. A provision has not been made at August 31, 2012 and 2011 and December 31, 2010 for U.S. or additional foreign withholding taxes of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries because it is the present intention of management to reinvest the undistributed earnings indefinitely in foreign operations. Generally, such earnings become subject to U.S. tax upon the remittance of dividends and under certain other circumstances. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of deferred tax liability on such undistributed earnings.
The Company recognizes that virtually all tax positions in the PRC are not free of some degree of uncertainty due to tax law and policy changes by the government. However, the Company cannot reasonably quantify political risk factors and thus must depend on guidance issued by current government officials.
Based on all known facts and circumstances and current tax law, the Company believes that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits as of August 31, 2012 and 2011 and December 31, 2010, are not material to its results of operations, financial condition or cash flows. The Company also believes that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits as of August 31, 2012 and 2011 and December 31, 2010, if recognized, would not have a material effect on its effective tax rate. The Company further believes that there are no tax positions for which it is reasonably possible, based on the current PRC tax law and policy, that the unrecognized tax benefits will significantly increase or decrease over the next twelve months producing, individually or in the aggregate, a material effect on the Company’s results of operations, financial condition or cash flows as of August 31, 2012 and 2011 and December 31, 2010, but the tax years are still open for examination.
(e) Revenue Recognition and Deferred School Fees
Revenues consist primarily of tuition, room & board and other fees (the "School Fees") derived from providing meals and housing for students living on campus. Revenues from School Fees are recognized pro-rata (on a straight-line basis) over the relevant period attended by the student of the applicable grade or program. The school year typically runs September 1 through August 31 and deferred School Fees are recognized over the twelve-month period. If a student withdraws from a course or program within three months after the school year starts, the paid but unearned portion of the student’s School Fees is 67% refunded. If a student withdraws after the first three months in a school year, no School Fees will be refunded. As a result, the Company has recorded deferred School Fees as a current liability on the consolidated balance sheet in the event a student withdraws from school and the Company has to return a portion of the deferred School Fees. In past years there were minimal students who withdrew from a course or program before the end of a school year.
The Company normally receives deferred School Fees from students at their initial admission or before the start of the school year on September 1. As of August 31, 2012, all students at the North and South Campuses are required to fully prepay school fees at the beginning of the school year by September 1, 2012 for the 2012-2013 school year. At the Sichuan Campus students are required to fully prepay school fees for the first semester at the beginning of the school year by September 1, and the second semester must be fully prepaid before the beginning of the second semester by March 1. In prior periods this policy was not fully enforced. Some students will benefit from a discount of fees if they prepay School Fees for two to three years of school term. Deferred School Fees is the portion of payments received but not earned and is reflected as a current liability under deferred School Fees in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as such amounts are expected to be earned, but may be refundable within the next year.
Below is a schedule of deferred School Fees as of August 31, 2012 expected to be recognized into revenue over twelve months for the next year ended August 31 (corresponds to school year – September 1 through August 31) and thereafter as follows:
|
Twelve Month Period Ended August 31
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(f) Foreign Currency Translation
The Company’s principal country of operations is The PRC. The financial position and results of operations of the Company are determined using the local currency (“Renminbi or RMB”) as the functional currency. The results of operations denominated in foreign currency are translated at the average rate of exchange during the reporting period.
Assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at the balance sheet date are translated at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date. The results of operations are translated from Renminbi to US Dollar at the weighted average rate of exchange during the reporting period. The registered equity capital denominated in the functional currency is translated at the historical rate of exchange at the time of capital contribution. All translation adjustments resulting from the translation of the financial statements into the reporting currency (“US Dollars”) are dealt with as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
Translation adjustments net of tax totaled $252,324 and $1,699,817, for the year ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Translation adjustments net of tax totaled $1,432,623, for the eight months ended August 31, 2011, translation adjustments net of tax totaled $801,583, for the years ended December 31, 2010, respectively.
As of August 31, 2012 and 2011, the exchange rate to the U.S. Dollar was RMB 6.3374 and RMB 6.3755, respectively. The average exchange rate for the year ended August 31, 2012 and 2011 was RMB 6.3345 and RMB 6.5673, respectively.
As of December 31, 2010, the exchange rate to the U.S. Dollar was RMB 6.6227. The average exchange rate for the eight months ended August 31, 2011 was RMB 6.5106.
(g) Comprehensive Income
The Company reports comprehensive income in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 220,
Comprehensive Income
, which established standards for reporting and displaying comprehensive income and its components in a financial statement that is displayed with the same prominence as other financial statements.
Total comprehensive income is defined as all changes in stockholders' equity during a period, other than those resulting from investments by and distributions to stockholders (i.e., issuance of equity securities and dividends). Generally, for the Company, total comprehensive income equals net income plus or minus adjustments for currency translation. Total comprehensive income represents the activity for a period net of related tax and was $9,897,952 and $15,132,571, for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Total comprehensive income was $10,876,683 and $12,767,664, for the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and for the year ended December 31, 2010, respectively.
While total comprehensive income is the activity in a period and is largely driven by net earnings in that period, accumulated other comprehensive income or loss (“AOCI”) represents the cumulative balance of other comprehensive income as of the balance sheet date. For the Company, AOCI is primarily the cumulative balance related to the currency adjustments and increased comprehensive income and equaled $2,690,766 and $2,438,442, as of August 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
(h) Concentrations, Risks, and Uncertainties
All of the Company’s operations are located in the PRC. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to successfully continue to provide the services offered and failure to do so would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results of operations and cash flows. Also, the success of the Company’s operations is subject to numerous contingencies, some of which are beyond management’s control. These contingencies include general economic conditions, teacher salaries, competition, governmental and political conditions, and changes in regulations. Because the Company is dependent on trade in the PRC, the Company is subject to various additional political, economic and other uncertainties. Among other risks, the Company’s operations will be subject to risk of restrictions on transfer of funds, domestic and international customs, changing taxation policies, foreign exchange restrictions, and political and governmental regulations.
(i) Advertising
The Company expenses the cost of advertising as incurred or, as appropriate, the first time the advertising takes place. Advertising costs for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011, and the year ended December 31, 2010 were not significant.
(j) Research and Development
The Company expenses the cost of research and development as incurred. Research and development costs for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011, and the year ended December 31, 2010 were not significant.
(k) Basic and diluted earnings per share
Earnings per share is calculated in accordance with the ASC Topic 260,
Earnings Per Share
. Basic earnings per share is calculated dividing net earnings available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share is based on the assumption that all dilutive convertible shares, stock options, warrants and other equity awards were converted or exercised during the period. Dilution is computed by applying the treasury stock method. Under this method, warrants and options are assumed to be exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issuance, if later), and as if funds obtained thereby were used to purchase common stock at the average market price during the period. In periods where losses are reported, the weighted-average number of common stock outstanding excludes common stock equivalents, because their inclusion would be anti-dilutive.
Basic and diluted earnings per share were $0.32 and $0.32 per share and $0.45 and $0.45 per share, respectively for the year ended August 31, 2012 and 2011.
Basic and diluted earnings per share were $0.31 and $0.31 per share, for the eight months ended August 31, 2011. Basic and diluted earnings per share were $0.43 and $0.43 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2010.
(l) Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with ASC Topic 230,
Statement of Cash Flows
, cash flows from the Company’s operations are calculated based upon the local currencies using the average translation rates. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statements of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets.
(m) Reclassification
Certain reclassifications have been made to the 2011 and 2010 consolidated financial statements to conform to the 2012 consolidated financial statement presentation. These reclassifications had no effect on net income as previously reported.
(n) Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) ASU No. 2010-09 (ASC Topic 855), which amends
Subsequent Events Recognition and Disclosures
, ASU No. 2009-16 (ASC Topic 860), which amends
Accounting for Transfer of Financial Assets
, ASU No. 2009-05 (ASC Topic 820), which amends
Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures - Overall
, ASU No. 2009-08,
Earnings per Share
, ASU No. 2009-12(ASC Topic 820),
Investments in Certain Entities That Calculate Net Asset Value per Share
, and various other ASU’s No. 2009-2 through ASU No. 2012-07 which contain technical corrections to existing guidance or affect guidance to specialized industries or entities were recently issued. These updates have no current applicability to the Company or their effect on the financial statements would not have been significant, except for ASU 2011-05 (ASC Topic 220,
Comprehensive Income
) which will affect the presentation of Comprehensive Income and is effective for periods after December 15, 2011 and early adoption is allowed.
Other accounting standards have been issued or proposed by the FASB or other standard-setting bodies that do not require adoption until a future date and are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
NOTE 4 – INVENTORY
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost, determined on a weighted average basis, or net realizable value. Net realizable value is the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business. The Company’s inventories are typically school supplies used in the normal course of business. When inventories are consumed, their carrying amounts are expensed in the year used. Write-downs for declines in net realizable value or for losses of inventories are recognized as an expense in the year of impairment or loss occurs. Inventories consisted of the following:
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Inventory provision*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* The inventory provision is an inventory allowance for aged or obsolete inventory items.
NOTE 5 - PREPAYMENT AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
Prepayment and other current assets consisted of the following:
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
Cash – individual bank accounts
|
|
$
|
3,216,850
|
|
|
$
|
8,734,422
|
|
|
|
|
|
568,324
|
|
|
|
737,741
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
66,710
|
|
|
|
|
|
292,864
|
|
|
|
67,809
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
4,078,038
|
|
|
$
|
9,606,682
|
|
Cash – individual bank accounts, is for funds advanced to employees for the purchase of school and boarding related materials for the day-to-day operations of the school. Advances to suppliers are primarily advances for travel and other related expenses. The other prepaid and other receivables are primarily for certain operating requirements of the school.
NOTE 6 –
DUE TO RELATED PARTIES
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(i) Ren Zhiqing is the president and a director of the Company, as well as the majority controlling shareholder of the Company. The amounts due to Ren Zhiqing as of August 31, 2012 and 2011, represent loans to the Company, which are unsecured, interest-free and payable to Ren Zhiqing, primarily used for paying the equity holders of the Investment Company as part of the Equity Transfer Agreement dated August 31, 2011.
|
NOTE 7 – LAND USE RIGHTS, NET
Land use rights, net consisted of the following:
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Accumulated amortization
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization expense for years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011 was $1,127,377 and $152,319, respectively. Amortization expense for the eight months ended August 31, 2011 was $102,434 and for year ended December 31, 2010 was $148,637, respectively.
Amortization expense for the next five years and thereafter is as follows
NOTE 8 - PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment
,
net consisted of the following:
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture & education equipment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, depreciation expense was $3,359,844 and $906,701, respectively. For the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and for the year ended December 31, 2010, depreciation expense was $651,674 and $965,795, respectively.
Property and equipment are located at the Company’s three school locations in Shanxi and Sichuan Provinces in the PRC and are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation and amortization are calculated using the straight-line method over the expected useful life of the asset, after the asset is placed in service. Major repairs and betterments that significantly extend original useful lives or improve productivity are capitalized and depreciated over the period benefited. Maintenance and repairs are generally expensed as incurred. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations.
The estimated useful lives for each major category of fixed assets are as follows:
|
Description
|
Useful Lives
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture, Education Equipment, Computers
|
|
NOTE 9 – DEPOSIT PAID FOR LONG-TERM ASSETS
The deposit balance paid for long term assets as of August 31, 2011 was a good-faith, refundable deposit paid to begin preliminary negotiations toward the acquisition of the Investment Company.
NOTE 10 - OTHER PAYABLE
Other payables included traveling and the related expenses incurred by employees on behalf of the Company. These amounts are unsecured, non-interest bearing and generally are short term in nature.
NOTE 11 –
HOME PURCHASE DOWN PAYMENT
According to the Company’s Employee Welfare Policy, the Company may sign a home purchase agreement with teachers which would allow teachers to purchase home property at a discounted market rate. Pursuant to the home purchase agreement between the Company and teachers, teachers were given the right to purchase a home property upon their 8th year of service. There were two payment options:
(1) one-time full payment of the home purchase price based on the signed agreement; or (2) RMB 20,000 down payment with remaining balance to be paid in 8 equal annual installments until their 8th year of service. Those teachers who selected option (2) would be charged an interest of 7% if they do not make payment on time during the 8 year period. If teachers resign or leave the school for any reasons, they will be entitled to a refund based on the terms of the home purchase agreement. There were minimal refunds for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010. For accounting purposes, cash received from teachers through payment options (1) and (2) and late interest payments are recorded as deposits at the time of receipt. The Company recognizes profit when the sale is consummated.
The Company records the home purchase transactions in accordance to the deposit method pursuant to FASB ASC Topic 360-20,
Real Estate Sales
. Under the deposit method, the seller does not recognize any profit, does not record notes receivable, and continues to report in its financial statements the property which has been assumed by the buyer. Cash received from the buyer, including the initial investment and subsequent collections of principal and interest, is reported as a deposit. Interest collected that is subject to refund and is included in the deposit account before a sale is consummated is accounted for as part of buyer’s initial investment at the time the sale is consummated. There were no apartments sold for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010, and as such the Company recognized no income from selling apartments. As of August 31, 2012 and 2011, December 31, 2010, home deposits were $919,458, $878,668 and $823,095, respectively.
NOTE 12 –
ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT LIABILITIES
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of the following:
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Individual tax withholding
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE 13
– STOCK BASED COMPENSATION
The Chief Financial Officer is entitled to receive $6,000 per month in cash compensation for his services, as well as a stock award of $6,000 per month in shares of the Company’s restricted common stock, which vest on a quarterly basis. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2012, the Chief Financial Officer earned and was vested in 88,240 shares of restricted common stock as part of his consideration. As of August 31, 2012, the Company has accrued 74,067 shares of restricted common stock to be issued to its Chief Financial Officer.
Two of the Company’s independent directors are entitled to each receive $9,000 annually in cash compensation for their services, as well as a stock award of $9,000 annually in shares of the Company’s restricted common stock, which vests on a quarterly basis. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2012, the two independent directors collectively earned and were vested in 20,877 shares of restricted common stock as part of their consideration. As of August 31, 2012, the Company has accrued 18,516 shares of restricted common stock to be issued to two of its independent directors.
The financial controller is entitled to receive RMB 20,000 (approximately USD $3,138) per month in cash compensation for her services, as well as a stock award of 5,000 shares of the Company’s restricted common stock, which vest on a quarterly basis. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2012, the financial controller earned and was vested in 20,000 shares of restricted common stock as part of her consideration. As of August 31, 2012, the Company has accrued 18,333 shares of restricted common stock to be issued to its financial controller.
On June 16, 2012, the Company issued 55,101 shares of previously accrued restricted common stock accounted for as stock based compensation to its Chief Financial Officer, independent directors and financial controller.
The above-mentioned securities were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933. The issuance of these shares was exempt from registration, in part pursuant to Regulation S and Regulation D under the Securities Act of 1933 and in part pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933.
NOTE 14 –
REFUNDABLE DEPOSITS
Students were previously required to pay a housing deposit at their initial admissions. The Company has changed this policy and no longer requires a deposit and returns any previous deposit upon graduation. As of August 31, 2012 and 2011, refundable deposits were $134,661 and $795,848, respectively.
NOTE 15 – SHORT-TERM BANK LOAN
The Company’s subsidiary Shanxi Taiji borrowed RMB 100,000,000 (approximately $15,685,044) from a finance company under a one-year term from August 16, 2011 due August 15, 2012 at a 14.0% interest rate, interest-only payable quarterly. The loan was repaid on August 15, 2012.
NOTE 16 – LONG-TERM BANK LOAN
The Company’s subsidiary Shanxi South School borrowed RMB 70,000,000 (approximately $11,045,539) from a bank under a three-year loan from August 16, 2012 due August 15, 2015 at a 7.38% interest rate, interest-only payable quarterly.
NOTE 17 – TAXES
Enterprise Income Tax (“EIT”)
Effective January 1, 2007, the Company adopted ASC 740-10,
Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes
(formerly “FIN 48”, an interpretation of FASB statement No. 109), Accounting for Income Taxes. The interpretation addresses the determination of whether tax benefits claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the financial statements.
Under ASC 740-10, the Company may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. ASC 740-10 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures. As of August 31, 2012 and 2011, and December 31, 2010, the Company does not have a liability for unrecognized tax benefits.
The Company’s estimated income tax savings for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011 are summarized as follows:
|
|
|
For the Years Ended August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Had the Company’s tax exemption not been in the place for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the Company estimates the following pro-forma financial statement impact:
|
|
|
For the Years Ended August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
Net income before tax provision, as reported
|
|
$
|
9,645,628
|
|
|
$
|
13,432,754
|
|
|
Less tax provision exempted
|
|
|
(2,411,407
|
)
|
|
|
(3,358,188
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company’s estimated income tax savings for the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010 are summarized as follows:
|
|
|
For the
Eight Months Ended August 31, 2011
|
|
|
For the
Year Ended December 31, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Had the Company’s tax exemption not been in the place for the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010, the Company estimates the following pro-forma financial statement impact:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the
Eight Months Ended August 31, 2011
|
|
|
For the
Year Ended
December 31, 2010
|
|
Net income before tax provision, as reported
|
|
|
9,444,060
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less tax provision exempted
|
|
|
(2,361,015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company’s operating subsidiaries are tax exempt, since primary and secondary education is not subject to income tax in the PRC. As such, the Company and its subsidiaries have no deferred tax asset or liability. The Company does not anticipate any change in the current PRC regulations regarding the tax exemption for its education sector.
NOTE 18 – EARNING PER SHARE
FASB ASC Topic 260,
Earnings Per Share
, requires a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator of the basic earnings per share (EPS) computations.
Basic earnings per share are computed by dividing income available to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share is computed similar to basic earnings per share except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common shares had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. There were no potentially dilutive securities for the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2010.
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net income per share:
|
|
|
For The Years
Ended August 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic weighted average outstanding shares of common stock
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted weighted average common stock and stock equivalents
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For The
Eight Months Ended August 31, 2011
|
|
|
For The
Year Ended December 31, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic weighted average outstanding shares of common stock
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted weighted average common stock and stock equivalents
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE 19 – EMPLOYEE RETIREMENT BENEFITS AND POST RETIREMENT BENEFITS
According to the Shanxi and Sichuan Provincial regulations on state pension program, both employees and employers have to contribute toward pensions. The pension contributions range from 2% to 8% that was contributed by individuals (employees) and the Company is required to make contributions to the state retirement plan based on 20% of the employees’ monthly basic salaries. Employees in the PRC are entitled to retirement benefits calculated with reference to their basic salaries on retirement and their length of service in accordance with a government managed benefits plan. The PRC government is responsible for the benefit liability to these retired employees.
During the years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011, the Company contributed $257,418 and $248,647 in pension contributions, respectively. During the eight months ended August 31, 2011 and during the year ended December 31, 2010, the Company contributed $176,981 and $214,997 in pension contributions, respectively.
NOTE 20 – BUSINESS COMBINATION - EQUITY TRANSFER AGREEMENT
On August 31, 2011, the Company completed the acqusition of the equity interests in Shanxi Rising Education Investment Company, Limited (the “Investment Company”) from its equity holders (the “Sellers”) for a total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 (approximately $108,226,806) under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement, (the “Acquisition”). The Acquisition has been accounted for as a business combination under Accounting Standards Codification Topic 805,
Business Combinations
(“ASC 805”). The total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 has been discounted to its net present value and allocated to the net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values of August 31, 2011. As of the balance sheet date, August 31, 2011, the exchange rate to the US Dollar was RMB 6.3755.
Description of Acqusition
On August 31, 2011, the Company’s entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement and purchased all of the outstanding equity of Shanxi Rising Education Investment Company Limited (the “Investment Company”) from the equity holders (the “Sellers”) for a total purchase consideration of RMB 690,000,000 (approximately $108,226,806). The net present value of the total fair value consideration transferred equals RMB 650,000,000 (approximately $102,565,721), of which RMB 370,217,933 (approximately $55,444,697) has been paid. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement the balance of the purchase price is to be paid over three years in three scheduled payments as follows:
|
|
1)
|
RMB 119,782,067 (approximately $18,900,822) to be paid by August 31, 2012, but was paid on September 3rd, 2012
|
|
|
2)
|
RMB 100,000,000 (or RMB 87,589,800, approximately $13,821,094, net of discount) by August 31, 2013, and
|
|
|
3)
|
RMB 100,000,000 (or RMB 93,849,000, approximately $14,808,754, net of discount) by August 31, 2014.
|
The net present value of the payments is discounted at the Company’s then current financing interest rate of 6.84%.
The Investment Company is an education company that owns and operates a K-12 private boarding school in the PRC, encompassing kindergarten, primary and secondary education. The Investment Company was established in 2001 and it has share capital of RMB 70,000,000. It is the parent company of Shanxi Rising School (the "Rising School"), founded 2002, which currently serves over 5,400 students from its location in Shanxi Province, PRC. The Rising School is now known by the Company as the “Shanxi South Campus.”
Prior to closing the Equity Transfer Agreement, the Company became involved in the operations of the Shanxi South Campus in the spring of 2011. With the consent of the Investment Company, the Company assisted in the operations, accounting and promotion of the school to attract more and better students for the 2011-2012 school year. Some of these responsibilities included collecting prepaid School Fees in advance of the school year, which combined with better operations, higher tuition rates and an increase in enrollment led to an increase in deferred revenue at August 31, 2011. Company’s involvement was under the direction of Investment Company management until it assumed control of the Shanxi South Campus on August 31, 2011, in accordance with the Equity Transfer Agreement.
NOTE 21 – UNAUDITED PRO FORMA RESULTS
Unaudited pro forma results of operations after giving effect to certain adjustments resulting from the acquisition of the Investment Company, as described herein, were as follows for the twelve months ended August 31, 2011 as if the business combinations had occurred at the beginning of the period presented.
|
|
|
For the Year Ended
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for earnings per share data)
|
|
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings per share, basic and diluted
|
|
|
|
|
The pro forma data is provided for informational purposes only and does not purport to be indicative of the results which would have actually been obtained if the combinations had been effectuated at the beginning of the period presented, or of those results which may be obtained in the future.
NOTE 22 – CORRECTION OF IMMATERIAL ERRORS
The Company also made an immaterial correction of errors in its consolidated financial statements as of and for the balance sheet ended August 31, 2011. The Company used 14% instead of 6.84% for the fair value discount rate, which resulted in improperly recording fixed assets, land use rights, short-term payable acquisition and long-term payable acquisition. The consolidation of balance sheet resulted in an increase to fixed assets of $2,162,226 and to land use rights of $3,167,081, and an increase to short-term payable acquisition of $1,383,107 and an increase to long-term payable acquisition of $3,946,200. The following is a summary presentation of corrections made to the Company’s consolidated balance sheet as of August 31, 2011 previously filed on Form 10-K.
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
As Reported
|
|
|
Correction
|
|
|
As Adjusted
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
$
|
15,090,521
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
15,090,521
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
3,489
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
3,489
|
|
|
Due from related parties
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
9.606,682
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
9,606,682
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
24,700,692
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
24,700,692
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LONG-TERM ASSETS:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
|
|
81,958,342
|
|
|
|
2,162,226
|
|
|
84,120,568
|
|
|
Land use rights, net
|
|
|
45,783,579
|
|
|
|
3,167,081
|
|
|
48,950,660
|
|
|
Deposit paid for long-term assets
|
|
|
18,778
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
18,778
|
|
|
Total Long-Term Assets
|
|
|
127,760,699
|
|
|
|
5,329,307
|
|
|
133,090,006
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
|
$
|
152,461,391
|
|
|
$
|
5,329,307
|
|
|
$
|
157,790,698
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts Payable
|
|
$
|
48,824
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
48,824
|
|
|
Short-term payable-acquisition
|
|
|
21,177,319
|
|
|
|
1,383,107
|
|
|
|
22,560,426
|
|
|
Due to related parties
|
|
|
7,842,522
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
7,842,522
|
|
|
Other Payables
|
|
|
333,202
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
333,202
|
|
|
Refundable deposits
|
|
|
795,848
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
795,848
|
|
|
Prepaid School Fees
|
|
|
39,498,972
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
39,498,972
|
|
|
Home purchase down payment
|
|
|
878,668
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
878,668
|
|
|
Short-term bank loan
|
|
|
15,685,044
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
15,685,044
|
|
|
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities
|
|
|
908,268
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
908,268
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
87,168,667
|
|
|
|
1,383,107
|
|
|
|
88,551,774
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LONG-TERM LIABILITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term bank loan
|
|
$
|
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
Long-term payable-acquisition
|
|
|
22,656,106
|
|
|
|
3,946,200
|
|
|
|
26,602,306
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES
|
|
|
109,824,773
|
|
|
|
3,946,200
|
|
|
|
115,154,080
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock, $0.001par value; 75,000,000 shares authorized; 30,069,624, 30,014,528 issued and outstanding as of August 31, 2012 and 2011
|
|
|
30,015
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
30,015
|
|
|
Additional paid in capital
|
|
|
67,421
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
67,421
|
|
|
Retained earnings
|
|
|
40,100,740
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
40,100,740
|
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
|
|
2,438,442
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
2,438,442
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
42,636,618
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
42,636,618
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
$
|
152,461,391
|
|
|
|
5,329,307
|
|
|
$
|
157,790,698
|
|
NOTE 23–SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Management has evaluated subsequent events from August 31, 2012 and has concluded no events need to be reported during this period, except the following:
On September 3, 2012 the Company paid RMB 119,782,067 (approximately $18,900,822) under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement for the acqusition of the Shanxi South School, which was due on August 31, 2012.
On September 10, 2012, the Company borrowed RMB 50,000,000 (approximately $7,896,275) from a bank under a one-year loan due September 9, 2013 at a 7.2% interest rate, interest only payable quarterly.
Item 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain "disclosure controls and procedures," as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the "Exchange Act"), that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in Securities and Exchange Commission rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that disclosure controls and procedure, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Additionally, in designing disclosure controls and procedures, our management was required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible disclosure controls and procedures. The design of any disclosure controls and procedures also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
As of August 31, 2012, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer, Ren Zhiquing, and Chief Financial Officer, Michael Toups, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in our periodic reports is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified for each report and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) or 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the Company's principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the Company's board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and includes those policies and procedures that:
|
·
|
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company;
|
|
·
|
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and
|
|
·
|
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
|
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Because of the inherent limitations of internal control, there is a risk that material misstatements may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by internal control over financial reporting. However, these inherent limitations are known features of the financial reporting process. Therefore, it is possible to design into the process safeguards to reduce, though not eliminate, this risk.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of August 31, 2012. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control-Integrated Framework. Based on its assessment, management concluded that, as of August 31, 2012, the Company's internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria. For the year ended August 31, 2012, the Company’s management annual report on internal control over financial reporting was not subject to attestation by its independent auditors.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
During the fiscal year ended August 31, 2012, we have taken additional measures to strengthen our financial controls, which have included training for our accounting staff and allocating financial and human resources to support our internal control structure. We have also plan to contract with an outside consulting firm to further assist the Company in our Sarbanes Oxley (“SOX”) compliance and internal controls. The Company continues its process of SOX compliance, including mapping, testing, analysis and assessment. The Company's efforts are designed to address our internal controls for financial reporting and to strengthen our overall control environment. Our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, does not expect that disclosure controls or internal controls over financial reporting will prevent all errors, even as the aforementioned remediation measures are implemented and further improved to address all deficiencies. The design of any system of controls is based in part upon certain assumptions about likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
The implementation of our internal controls is on-going, has required substantial expenditures, and could distract our officers and employees from the operation of our business. However, because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Because of the inherent limitations of internal control, there is a risk that material misstatements may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by internal control over financial reporting. However, these inherent limitations are known features of the financial reporting process. Therefore, it is possible to design into the process safeguards to reduce, though not eliminate, this risk.
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CONTROL PERSONS
The executive officers and directors of the Company are:
|
Name
|
|
Age
|
|
Positions with the Company
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
|
|
|
|
|
|
Executive Vice President and Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vice President and Secretary
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All directors hold office until the next annual meeting of our shareholders and until their successors have been elected and qualify. Officers serve at the pleasure of the Board of Directors.
Ren Zhiqing,
Chairman of the Board, and Chief Executive Officer
. Dr. Ren has been the Chief Executive Officer of Shanxi Taiji Industrial Development Co., Ltd. since its formation in 1997. Previously, he was the president of Shanxi Modern Trade and Economics Institute (1993 to 1997), a privately funded college. He also served as head of the China Yinjing News Agency, Shanxi Branch (1989 to 1993), and was a contributing writer for the China Economic News Agency (1986 to 1989). Dr. Ren earned his medical degree at the Shanxi College of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Pan Mingxiao
,
Executive Vice President and Director
. Mr. Pan has been an officer and director of Shanxi Taiji Industrial Development Co., Ltd since 2004. Previously, he was the Chief Financial Officer of Shanxi Modern Bilingual School and he has over 15 years’ experience in the education field. Mr. Pan earned his Bachelor’s degree from Peking University.
Ren Xudong
,
Vice President and Secretary
. Mr. Ren has been an officer of Shanxi Taiji Industrial Development Co., Ltd since 2010 in operations management and corporate communications. Previously, he was involved in Kia Motors management training and entrepreneurial activities from 2008 to 2010. Mr. Ren earned his Bachelor’s degree in Mathematics in 2006 from Imperial College in London and earned his Master’s degree in Risk Management from Imperial College in 2007.
Michael Toups
,
Chief Financial Officer
. Mr. Toups was appointed Chief Financial Officer in June 2010. Mr. Toups is an accounting and corporate finance executive with over 20 years of experience in senior management with specialties in business strategy, M&A and international trade. He has middle-market corporate finance experience across a variety of industries as both principal and advisor and has served in roles as the CFO, COO, and director of private and publicly traded companies. Mr. Toups expertise includes PCAOB audits, SEC reporting and Sarbanes-Oxley compliance. He is also well-versed in Chinese business practices and has directed strategic business planning for Asia-based companies for over 12 years. Mr. Toups also currently serves as the CFO of Longwei Petroleum Investments Holding Limited, a Taiyuan, Shanxi Province, PRC-based petroleum distributor listed on the NYSE MKT. Since June 2012, Mr. Toups has served as a member of the board of directors and special committee member of First Surgical Partners, Inc., a US-based healthcare company. From December 2010 to December 2011 he served as a member of the board of directors of Lotus Pharmaceuticals, a Beijing China-based manufacturer of pharmaceutical products. Most recently Mr. Toups served as Director of Asia Investment Banking, Midtown Partners & Co. from December 2007 to July 2010 and as the CFO and director of Nork Lighting, a China-based manufacturer and the largest retailer of high-end residential lighting products in China from December 2007 to July 2010. From May 2009 to May 2011, he served as the president and director of Stone Harbor Investments, Inc., a small business consulting company. From January 2001 to December 2007, he served as president and owner of Peak Crown, a consulting company for the import of products from Asia and financial services. Mr. Toups holds an MBA in Finance from the University of Notre Dame and a BBA in Finance from Texas Christian University.
Dora Dong,
Director
. Ms. Dong is an entrepreneur and business leader who works to promote trade and commerce between the US and China. Since July 2000, Ms. Dong has been a member of the board of directors of the Silicon Valley Chinese American Computer and Commerce Association. She served as the association’s CFO from July 2006 to July 2008 and is currently serving as its Vice President since 2008. Since May 2009, Ms. Dong has served as the President of New Continental - USA in Silicon Valley. Since September 2009, Ms. Dong has also served as the Chairman of Suzhou New Continental Education Consulting Company Ltd. in China. Additionally, Ms. Dong has served as a committee member of Suzhou Overseas Chinese Association since May 2010 and was appointed to such position by the government in Suzhou City, China. Since January 2011, Ms. Dong has served as a director of China Bilingual Technology & Education Group, Inc. in Taiyuan City, China. From July 2010 to June 2011, Ms. Dong served on the board of directors of Worldwide Energy & Manufacturing USA, Inc., an international solar manufacturing and engineering firm with multiple factories in China and sales worldwide. Ms. Dong received her Bachelor of Science Degree in Business Administration from John F. Kennedy University in 1990. Ms. Dong’s qualifications to serve as an independent director of the Company are based on her financial management experience in public and private companies in senior level corporate strategic management position combined with her CFO background with the Silicon Valley Chinese American Computer and Commerce Association. Moreover, Ms. Dong and her affiliated organization have been continuing to build the strong relationship with both government and business leaderships in the USA and PRC. As consideration for her service as a member of the board of directors, Ms. Dong is entitled to receive $9,000 per year and a restricted stock grant in the amount of $9,000 per year.
Dr. Jun Zhang
,
Director
. On January 6, 2011, Dr. Jun Zhang was appointed to the board of directors of the Company. Dr. Zhang is a well-recognized academic and research leader. His original research work in the field of pharmaceuticals has been cited as breakthroughs by academic journals and industry news. Dr. Zhang received his PhD from the University of New Mexico in 2001. Dr. Zhang holds two US patents, has published more than 30 peer-reviewed research articles, acts as the editorial board member of two international journals, and reviews research articles for more than 20 international publications. Dr. Zhang is frequently invited to chair and speak at international conferences and is an advisor for the World Academy of Developing Countries. Dr. Zhang’s qualifications to serve as an independent director of the Company are based on his experience as an academic and research leader. As consideration for his service as a member of the board of directors, Dr. Zhang is entitled to receive $9,000 per year and a restricted stock grant in the amount of $9,000 per year.
Ying Fengmei
,
Director
. On January 6, 2011, Ying Fengmei was appointed to the board of directors of the Company. Ms. Fengmei is an economist and finance professional who has worked as an independent consultant to China-based companies since 2003 to assist them with their business planning and financial operations. From 1993 to 2003 Ms. Ying served as the General Manager of the Shanghai Foreign Economic Corporation and from 1987 to 1993 she served as the Vice Plant Manager of the Shanghai Yuzhou Electric Tool Plant. Ms. Ying is a 1986 graduate from the business school of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, one of China’s oldest and most prestigious universities. Ms. Ying is a certified economist.
Ms. Ying qualifications to serve as an independent director of the Company are based on her business dealings as an economist and finance professional who works with China-based companies.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships between or among the above directors, executive officers or persons nominated or charged by us to become directors or executive officers, except for the following: Mr. Ren Zhiqing, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, is the father of Mr. Ren Xudong, our Vice President and Secretary, and the cousin of Mr. Pan Mingxiao, Executive Vice President and Director.
Conflicts of Interest
Certain potential conflicts of interest are inherent in the relationships between our officers and directors and us.
From time to time, one or more of our affiliates may form or hold an ownership interest in and/or manage other businesses both related and unrelated to the type of business that we own and operate. These persons expect to continue to form, hold an ownership interest in and/or manage additional other businesses which may compete with our business with respect to operations, including financing and marketing, management time and services and potential customers. These activities may give rise to conflicts between or among the interests of us and other businesses with which our affiliates are associated. Our affiliates are in no way prohibited from undertaking such activities, and neither us nor our shareholders will have any right to require participation in such other activities.
Further, because we intend to transact business with some of our officers, directors and affiliates, as well as with firms in which some of our officers, directors or affiliates have a material interest, potential conflicts may arise between the respective interests of us and these related persons or entities. We believe that such transactions will be effected on terms at least as favorable to us as those available from unrelated third parties.
With respect to transactions involving real or apparent conflicts of interest, we have adopted policies and procedures which require that: (i) the fact of the relationship or interest giving rise to the potential conflict be disclosed or known to the directors who authorize or approve the transaction prior to such authorization or approval, (ii) the transaction be approved by a majority of our disinterested outside directors, and (iii) the transaction be fair and reasonable to us at the time it is authorized or approved by our directors.
Our policies and procedures regarding transactions involving potential conflicts of interest are not in writing. We understand that it will be difficult to enforce our policies and procedures and will rely and trust our officers and directors to follow our policies and procedures. We will implement our policies and procedures by requiring the officer or director who is not in compliance with our policies and procedures to remove himself/herself and the other officers and directors will decide how to implement the policies and procedures, accordingly.
Involvement in Legal Proceedings
To the best of our knowledge, during the past ten years, none of the following occurred with respect to a present or former director or executive officer of the Company: (1) any bankruptcy petition filed by or against any business of which such person was a general partner or executive officer either at the time of the bankruptcy or within two years prior to that time; (2) any conviction in a criminal proceeding or being subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offenses); (3) being subject to any order, judgment or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of any competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining, barring, suspending or otherwise limiting his involvement in any type of business, securities or banking activities; and (4) being found by a court of competent jurisdiction (in a civil action), the SEC or the Commodities Futures Trading Commission to have violated a federal or state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended or vacated.
Director Independence
Our Board of Directors has determined that currently Ms. Dora Dong, Ms. Ying Fengmei and Dr. Jun Zhang qualify as “independent” as the term is used in Item 407 of Regulation S-K as promulgated by the SEC and in the listing standards of The Nasdaq Stock Market, Inc. – Marketplace Rule 5605(a)(2).
Board Leadership Structure and Role in Risk Oversight
Although we have not adopted a formal policy on whether the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer positions should be separate or combined, we have traditionally determined that it is in the best interests of the Company and its shareholders to combine these roles. Dr. Ren Zhiqing has served as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the Company since the Merger. Due to the small size and early stage of the Company, we believe it is currently most effective to have the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer positions combined.
Our board of directors is primarily responsible for overseeing our risk management processes, and acts as our audit committee. The board of directors receives and reviews periodic reports from management, auditors, legal counsel, and others, as considered appropriate regarding our company’s assessment of risks. The board of directors focuses on the most significant risks facing our Company and our Company’s general risk management strategy, and also ensure that risks undertaken by our Company are consistent with the board’s appetite for risk. While the board oversees our Company’s risk management, management is responsible for day-to-day risk management processes. We believe this division of responsibilities is the most effective approach for addressing the risks facing our Company and that our board leadership structure supports this approach.
Meetings and Committees of the Board of Directors
Our board of directors held no formal meetings during the most recently completed fiscal year ended August 31, 2012. All proceedings of the board of directors were conducted by resolutions consented to in writing by all the directors and filed with the minutes of the proceedings of the directors. Such resolutions consented to in writing by the directors entitled to vote on that resolution at a meeting of the directors are, according to the corporate laws of the State of Nevada and our bylaws, as valid and effective as if they had been passed at a meeting of the directors duly called and held.
Code of Ethics
On January 21, 2011, we adopted a Code of Ethics for our principal executive officers and senior management. The Code of Ethics is designed to deter wrongdoing and promote honest and ethical conduct; full and fair disclosure in reports and documents submitted to the SEC; compliance with applicable governmental laws, rules and regulations; and the prompt internal reporting of violations of the code to appropriate persons by our senior management. Our Code of Ethics is available on our corporate website at http://ir.stockpr.com/chinabilingual/governance-documents.
Committees of the Board of Directors
On January 21, 2011, the Board of Directors appointed an Audit Committee, Compensation Committee, and Nominating Committee and adopted charters relative to its Audit Committee, Compensation Committee and Nominating Committee.
Audit Committee
Ms. Dora Dong, Dr. Jun Zhang and Ms. Ying Fengmei currently serve on the Audit Committee. Ms. Ying serves as the Chairman of the Audit Committee and as the audit committee financial expert. The Audit Committee’s duties are to recommend to our Board of Directors the engagement of independent auditors to audit our financial statements and to review our accounting and auditing principles. The Audit Committee duties also include reviewing the scope, timing and fees for the annual audit and the results of audit examinations performed by independent public accountants, including their recommendations to improve the system of accounting and internal controls. The Audit Committee will oversee the independent auditors, including their independence and objectivity. However, the committee members are not acting as professional accountants or auditors, and their functions are not intended to duplicate or substitute for the activities of management and the independent auditors. The Audit Committee is empowered to retain independent legal counsel and other advisors as it deems necessary or appropriate to assist the Audit Committee in fulfilling its responsibilities, and to approve the fees and other retention terms of the advisors. Our Audit Committee member possesses an understanding of financial statements and generally accepted accounting principles. The charter of the Audit Committee is available at our corporate website at http://ir.stockpr.com/chinabilingual/governance-documents
Compensation Committee
Ms. Dora Dong, Dr. Jun Zhang and Ms. Ying Fengmei currently serve on the Compensation Committee. Ms. Dong serves as the Chairman of the Compensation Committee. The Compensation Committee has certain duties and powers as described in its charter, including but not limited to periodically reviewing and approving our salary and benefits policies, compensation of executive officers, administering our stock option plans and recommending and approving grants of stock options under such plans. The charter of the Compensation Committee is available at our corporate website at http://ir.stockpr.com/chinabilingual/governance-documents.
Nominating Committee
Ms. Dora Dong, Dr. Jun Zhang and Ms. Ying Fengmei currently serve on the Nominating Committee. Dr. Zhang serves as the Chairman of the Nominating Committee. The Nominating Committee considers and makes recommendations on matters related to the practices, policies and procedures of the board and takes a leadership role in shaping our corporate governance. As part of its duties, the Nominating Committee assesses the size, structure and composition of the board and its committees, coordinates evaluation of board performance and reviews board compensation. The Nominating Committee also acts as a screening and nominating committee for candidates considered for election to the board. The Nominating Committee considers, among other things, the diversity of potential board member’s backgrounds, including their professional experience, education, skills and other individual attributes in assessing their potential appointment to the board. The charter of the Nominating Committee is available at our corporate website at http://ir.stockpr.com/chinabilingual/governance-documents.
Compliance with Section 16(a) of the Securities Act of 1934
Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, requires our executive officers and directors and persons who own more than 10% of a registered class of our equity securities to file with the Securities and Exchange Commission initial statements of beneficial ownership, reports of changes in ownership and annual reports concerning their ownership of the our common stock and other equity securities, on Form 3, 4 and 5 respectively. Executive officers, directors and greater than 10% shareholders are required by the Securities and Exchange Commission regulations to furnish our company with copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file.
Based solely on our review of the copies of such reports received by us, and on written representations by our officers and directors regarding their compliance with the applicable reporting requirements under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, we believe that, with respect to the fiscal year ended August 31, 2012, our officers and directors, and all of the persons known to us to own more than 10% of our common stock, filed all required reports on a timely basis, except that each of Michael Toups, Dora Dong and Jun Zhang was late filing a Form 4.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Summary Compensation Table
The table below sets forth, for the last two fiscal years, the compensation earned by (i) each individual who served as our principal executive officer or principal financial officer during the last two fiscal years and (ii) our most highly compensated executive officer, other than those listed in clause (i) above, who were serving as executive officers at the end of the last fiscal year (together, the “Named Executive Officers”). No other executive officer had annual compensation in excess of $100,000 during the last two fiscal years.
|
Name and Principal Position
|
Year
|
|
Salary
($)(1)
|
|
|
Bonus
($)
|
|
Stock Awards
($)*
|
Option
Awards
($)
|
|
Nonequity Incentive Plan Compensation ($)
|
|
|
All Other Compensation ($)
|
|
|
Total
($)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Executive Vice-President and Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vice President and Secretary
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
The Company pays salaries in RMB to all executive officers on a monthly basis, except its USA-based CFO is paid monthly in US dollars. The RMB amount is translated into US dollars when the Company files SEC documents. The exchange rates used were the average rates of for the fiscal years ended August 31, 2012 and 2011 (twelve months), which were 6.3345 and 6.5673, respectively.
|
|
(2)
|
Mr. Toups’ compensation is $6,000 per month cash compensation and $6,000 per month stock compensation in restricted common shares, which vest on a quarterly basis. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2012, Mr. Toups earned and was vested in 88,240 shares of restricted common stock as part of his consideration. As of August 31, 2012, the Company has accrued 74,067 shares of restricted common stock to be issued to Mr. Toups.
|
*Stock awards represent the aggregate grant date fair value computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718.
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table sets forth information with respect to grants of options to purchase our common stock to the named executive officers at August 31, 2012.
|
Outstanding Equity Awards At Fiscal Year-End
|
|
|
OPTION AWARDS
|
|
|
STOCK AWARDS
|
|
|
Name
|
|
Number
of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Options (#)
exercisable
|
|
|
Equity
Incentive
Plan
Awards:
Number of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Earned
Options (#)
unexercisable
|
|
|
Equity
Incentive
Plan
Awards:
Number of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Unearned
Options(#)
|
|
|
Option
Exercise
Price ($)
|
|
|
Option
Expiration
Date
|
|
|
Number of
Shares or
Units of
Stock that
have not Vested (#)
|
|
|
Market
Value of
Shares or
Units of
Stock that
have not Vested ($)
|
|
|
Equity Incentive
Plan Awards:
Number of
Unearned Shares,
Units or
Other
Rights that
have not
Vested (#)
|
|
|
Equity Incentive
Plan Awards:
Market or
Payout Value
of Unearned
Shares, Units
or other
Rights that
have not
Vested ($)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) Mr. Toups’ compensation includes stock compensation of $6,000 per month in restricted common shares, which vest on a quarterly basis.
DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
Two of our outside, independent directors each are entitled to receive as compensation for their services $9,000 per year in cash compensation and a restricted stock grant in the amount of $9,000 per year. The inside directors receive no compensation related to their duties as directors.
Employment Agreements
On July 1, 2008, Ren Zhiqing entered into an employment agreement with Shanxi Taiji, pursuant to which, Mr. Zhiqing agreed to serve as chief executive officer for a term of 5 years. Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Zhiqing is entitled to a salary of RMB 6,000 or approximately $922 per month.
There are no employment agreements between the Company and any employees of the Company, other than stated above.
Consulting Agreements
On September 15, 2010, the Company entered into a Consulting Agreement with Michael Toups (the “Consulting Agreement”), pursuant to which Mr. Toups agreed to serve as Chief Financial Officer of the Company. Mr. Toups’ appointment as Chief Financial Officer was ratified by the Company’s board of directors on November 3, 2010. Pursuant to the Consulting Agreement, Mr. Toups was entitled to receive $6,000 per month in consideration for his services as Chief Financial Officer of the Company. In addition, Mr. Toups was entitled to receive a stock award of $6,000 in restricted shares per month of the Company’s common stock, which vest on a quarterly basis. Mr. Toups was also entitled to reimbursement for all reasonable travel and other business expenses incurred by him. This Consulting Agreement was renewed for a term of six months on September 15, 2011 under the same terms and conditions. The Company currently does not have a written agreement with its Chief Financial Officer, but continues to compensate him under the same terms and conditions as his previous agreement.
On October 1, 2010, the Company entered into a consulting agreement with its financial controller. The agreement was for a twelve-month term. Under the terms of the agreement, the financial controller was to be compensated RMB 20,000 per month and 20,000 shares annually in restricted common shares to be awarded beginning on January 1, 2011 on a quarterly basis. The Company currently does not have a written agreement with its financial controller, but continues to compensate her under the same terms and conditions as her previous agreement.
Risk Management
The Company does not believe risks arising from its compensation policies and practices for its employees are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on the Company.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
The following table sets forth information known to us with respect to the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of November 28, 2012 by the following:
|
·
|
Each shareholder who beneficially owns more than 5% of our common;
|
|
·
|
Each of our named executive officers;
|
|
·
|
Each of our directors; and
|
|
·
|
Executive officers and directors as a group.
|
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC, which deem a person to beneficially own any shares the person has or shares voting or dispositive power over and any additional shares obtainable within 60 days through the exercise of options, warrants or other purchase rights. Shares of our common stock subject to options, warrants or other rights to purchase that are currently exercisable or are exercisable within 60 days of November 28, 2012 (including shares subject to restrictions that lapse within 60 days of November 28, 2012) are deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the percentage ownership of the person holding such shares, options, warrants or other rights, but are not deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the percentage ownership of any other person. Unless otherwise indicated, each person possesses sole voting and investment power with respect to the shares identified as beneficially owned.
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner(1)
|
|
Amount and Nature
of Beneficial
Ownership
|
|
|
Percentage
of Class (1)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All such directors and executive officers as a group (8 persons)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Less than 1% of the issued and outstanding common stock as of November 28, 2012.
|
(1)
|
All shares are owned of record and beneficially. Total shares outstanding were 30,069,629 as of November 28, 2012, (plus accrued shares of 110,916 equal total shares of 30,180,545). Except as otherwise noted, each shareholder’s address is c/o China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc., No. 2 Longbao Street, Xiodian Zone, Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province, China 030031.
|
|
(2)
|
Pursuant to his previous agreement with the Company, Michael Toups shall receive $6,000 per month in consideration for his services as Chief Financial Officer of the Company. In addition, Mr. Toups is entitled to receive a stock award of $72,000 in shares of the Company's common stock, which vest on a quarterly basis. The Company has issued 39,547 shares of common stock to Mr. Toups as compensation for his service tendered and has accrued an additional 74,067 shares of common stock as of August 31, 2012.
|
|
(3)
|
Pursuant to her previous agreement with the Company, Dora Dong shall receive $9,000 annually in consideration of her services as an independent director. In addition, Ms. Dong is entitled to receive a stock award of $9,000 per annum in shares of the Company's common stock, which vest on a quarterly basis. The Company has issued 4,344 shares of common stock to Ms. Dong as compensation for her service tendered and has accrued an additional 9,258 shares of common stock as of August 31, 2012.
|
|
(4)
|
Pursuant to his previous agreement with the Company, Dr. Jun Zhang shall receive $9,000 annually in consideration of his services as an independent director. In addition, Dr. Zhang is entitled to receive a stock award of $9,000 per annum in shares of the Company's common stock, which vest on a quarterly basis. The Company has issued 4,344 shares of common stock to Dr. Zhang as compensation for his service tendered and has accrued an additional 9,258 shares of common stock as of August 31, 2012.
|
|
(5)
|
The Company issued 1,389 shares of common stock to Ying Fengmei as compensation for her services rendered to the Company for the last quarter of 2010 and the first quarter of 2011. Ms. Ying currently does not receive any restricted common stock for her services.
|
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
Ren Zhiqing is the Chief Executive Officer and a director of the Company and ultimate controlling shareholder of the Company. He is the father of Mr. Ren Xudong, our Vice President and Secretary, and the cousin of Mr. Pan Mingxiao, Executive Vice President and Director. Together these three individuals control 77.5% of the outstanding common stock of the Company.
At December 31, 2010, the Company had no amounts due from or due to related parties. At August 31, 2012 and 2011, the Company had the following amounts due from or due to related parties as outlined below:
Due To Related Parties
|
|
|
August 31, 2012
|
|
|
August 31, 2011
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
|
(i)
|
Ren Zhiqing is the president and a director of the Company, as well as the majority controlling shareholder of the Company. The amounts due to Ren Zhiqing as of August 31, 2012 and 2011 represent loans to the Company, which are unsecured, interest-free and payable to Ren Zhiqing. The amount due to Ren Zhiqing as of August 31, 2012 and 2011 represents a loan to the Company primarily used for paying the equity holders of the Investment Company as part of the Equity Transfer Agreement dated August 31, 2011.
|
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Audit Fees
For the years ended August 31, 2011 and 2012, the total fees charged to the Company for audit services, including quarterly reviews were $284,000 and $175,000, respectively.
Audit-Related Fees
For the years ended August 31, 2011 and 2012, the total audited related fees charged to the Company were $13,073 and $0, respectively.
Tax Fees
For the years ended August 31, 2011 and 2012, the total tax fees charged to the Company were $7,500 and $7,500, respectively.
All Other Fees
For the years ended August 31, 2011 and 2012, the total other fees charged to the Company were $0 and $0, respectively.
Audit Committee Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
Our Audit Committee has policies and procedures regarding the pre-approval of the performance of audit and non-audit services by our independent registered public accounting firm. Our independent registered public accounting firm may not perform any service unless the approval of the Audit Committee is obtained prior to the performance of the services, except as may otherwise be provided by law or regulation. All services described above were approved by the Audit Committee.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE
Exhibits
|
Exhibit No.
|
Description
|
|
|
Articles of Incorporation (Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 24, 2009).
|
|
|
By-Laws (Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 24, 2009).
|
|
|
Agreement and Plan of Merger dated June 30, 2010 (filed with 8-K filed on July 2, 2010 and incorporated herein by reference)
|
|
|
Agreement of Conveyance, Transfer and Assignment of Assets and Assumption of Obligations dated June 30, 2010. (filed with 8-K filed on July 2, 2010 and incorporated herein by reference)
|
|
|
Consulting Agreement between China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc. and Michael Toups, dated September 16, 2011 (filed with 8-K filed on October 27, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference)
|
|
|
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated August 31, 2011, by and between the Company and all the equity holders of Shanxi Rising Education Investment Co., Ltd.(filed with Current Report on Form 8-K on September 9, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference)
|
|
|
Loan Agreement, dated August 16, 2011, by and between Shanxi Taiji and Shanxi Trust Co., Ltd.
(filed with Annual Report on Form 10-K on November 29, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document*
|
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase*
|
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase*
|
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase*
|
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase*
|
*Filed herewith.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
China Bilingual Technology & Education Group Inc.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
By:
|
/s/ Ren Zhiqing
|
|
|
|
|
Ren Zhiqing
|
|
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
By:
|
/s/ Michael Toups
|
|
|
|
|
Michael Toups
|
|
|
|
|
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer)
|
|
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature
|
|
Title
|
|
Date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Ren Zhiqing
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and Chairman
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
|
Ren Zhiqing
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Pan Mingxiao
|
|
Executive Vice-President and Director
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
|
Pan Mingxiao
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Michael Toups
|
|
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer)
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
|
Michael Toups
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Dora Dong
|
|
Director
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
|
Dora Dong
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Dr. Jun Zhang
|
|
Director
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
|
Dr. Jun Zhang
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Ying Fengmei
|
|
Director
|
|
November 29, 2012
|
|
Ying Fengmei
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39
Capstone Technologies (PK) (USOTC:CATG)
Historical Stock Chart
From Jan 2025 to Feb 2025
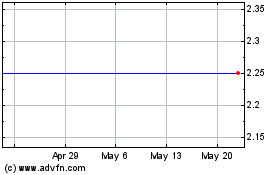
Capstone Technologies (PK) (USOTC:CATG)
Historical Stock Chart
From Feb 2024 to Feb 2025